An abandoned plot does not mean that it has no owner. Perhaps there is an owner, but for some reason he does not use the land. If an outsider begins to use a plot that has an owner, namely: erect buildings, carry out agricultural work, this will be considered unauthorized seizure. Administrative liability is imposed for such actions. Read the article about how to legalize unauthorized occupied land.
Land in our country is immovable property and for this reason it is possible to become the legal owner of a land plot only after registration of ownership rights. This is set out in the Land Code of the Russian Federation. In this regard, until the ownership of the land is properly registered, and the boundaries of the site are not determined, all manipulations with the land are illegal.
In other words: squatting is the use of someone else's land plot for one's own purposes, without having the legal right to do so. Such actions include: erection of buildings, cultivation of land for agricultural purposes. In this case, the use of the site occurs exclusively for personal purposes, and the seizure of the territory is on one’s own initiative.
Don’t think that only ordinary citizens engage in squatting by placing a vegetable garden in an abandoned neighboring dacha. In most cases, the law is violated by officials who have information about land plots. Having information about plots that are not in demand by the owners, land is seized.
If you encounter something like this, when an unknown person uses your land for personal purposes without having the right to do so, contact law enforcement agencies and the offender will be held accountable.
You can use land for personal needs in our country if one of several factors is present:
- property rights;
- lease agreement;
- easement;
- inheritance rights.
If the person using the land plot does not have any of the above documents, it can be assumed that he has appropriated the plot and is a violator of the law. These persons do not have the right to perform any actions with the land plot, namely: sell; rent out to third parties; make a will; alienate rights in other ways. If the person who has committed the seizure of someone else's territory is engaged in commercial activities on this land, the funds derived from this activity will be considered illegal income.
Land Use Basics
The principles and basic norms for the use of land plots are defined. Their main postulates are listed in Art. 1:
- the importance of land as the main component of life;
- the priority of its protection as an essential element of the environment and a means of production;
- the primacy of protecting human life and health;
- uniformity of fate of sites and related objects;
- payment for use;
- the right to participation of public and religious organizations, as well as individual citizens in resolving issues related to the implementation of their rights to land;
- the primacy of the conservation of especially valuable lands and protected areas;
- division into categories according to intended purpose;
- equal respect for the legitimate interests of citizens and society.
Read more about the principles on which land use in the Russian Federation is based.
Legal ways to restore the right to real estate
The law gives all owners of land plots the authority to restore and protect rights violated during squatting (Articles 59, 60 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). At its discretion, the legal owner may take actions to expel the “invader” from its territory independently or with the involvement of regulatory and judicial authorities:
- Self-defense (Article 14 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This term refers to the independent active actions of the property owner, including the use of physical force. For example, dismantling or moving a fence installed in violation of the boundaries of neighboring plots (read more about how to determine the boundaries of a land plot). It is important that the actions of the injured property owner do not go beyond the law.
- Complaint to supervisory authorities. You will need to contact the Rosreestr department, which is obliged to monitor the legality of registration and use of land plots under its jurisdiction. At the request of the Rosreestr inspector, they will conduct an inspection and draw up a protocol, on the basis of which administrative proceedings will be initiated. In addition, control can be carried out by the bodies of Rosselkhoznadzor and Rosprirodnadzor.
- Sending a demand to the offender. The transmission of an official letter with demands to stop committing illegal actions on the use of land must be recorded and confirmed. For example, the request may be sent by registered mail. At the same time, the land owner can supplement the letter with a claim for compensation for damage received as a result of unauthorized occupation of the site.
- Appeal to court (Articles 301, 304 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The next step after refusing or ignoring the land owner’s demand against the offender is filing a statement of claim in court. Along with the restoration of the violated right to a plot of land, the claim may include claims for compensation for damage and benefits lost due to the inability to use the plot.
An important condition for considering a civil claim is that the owner of the plot must submit documents confirming his rights to the property.
The owner's package of documents must include:
- title documentation - the basis for obtaining rights to real estate (a certificate of inheritance, a municipal decision on the transfer of a plot of land or an agreement confirming the acquisition of property);
- legal documents: Rosreestr certificate of state registration of land rights, extract, cadastral passport.
If, in the process of preparing for the trial, it turns out that one of these documents is missing, it is necessary to complete all the missing documentation before the claim is considered.
What is the essence of self-capture
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, ownership and use of land becomes legal only after state registration of rights to it. Until the boundaries are determined, registration is made and ownership is obtained, any actions regarding the exploitation and transactions with plots are considered illegal.
Unauthorized seizure of land is its appropriation and use by a person who does not have legal rights to the land, on his own initiative and to achieve personal goals.
Not only ordinary citizens, but also officials can become offenders. Exploitation and possession of a plot of land without permission and documentation is classified as illegal seizure of land and is a violation for which administrative liability is provided.
Sanctions against offenders are provided for (Article 7.1) and the Land Code (Article 76).
In addition to the measures provided for by these laws, other sanctions are applied to persons who occupy land without the owner’s permission. First of all, they are obliged to return the plot to the owner and compensate him for the damage caused.
Before deciding to appropriate someone else's territory, it is worth understanding what squatting of a land plot is and what legal consequences it may have.
Grounds for refusal of state registration in 2021
Reasons that registration authorities may cite:
- lack of a complete package of documents necessary for registration of property rights;
- presence of a conflict with previously registered rights;
- detected errors and inconsistencies in the submitted documents;
- the presence of proceedings regarding land surveying.
They may also refuse due to the lack of information about the coordinates of the boundaries of the site or the intersection of the boundaries of already demarcated territories and those registered in the cadastral register.
Legislation regarding squatter territories and unauthorized buildings is constantly changing. Unauthorized occupation of large plots of land is an illegal action and entails liability for the persons who carried it out. They face administrative liability, and in some cases even criminal liability.
How is land illegally acquired?
Citizens can appropriate other people's land plots in different ways. The objects of their encroachments are both private territories and public agricultural lands. For example, one of the neighbors carries out an unauthorized construction and seizes public land. By building structures on it for personal purposes, the violator is narrowing the passage to the plots of other landowners and trampling on their right to unhindered access of vehicles to the house.
Landowners whose rights have been violated report the invaders' actions to local authorities, who respond accordingly.
Unauthorized appropriation of lands owned by other citizens occurs much less frequently than squatting of public land, since such cases are established very quickly and can be challenged in court.
Unauthorized seizure: definition in law
The Code of Administrative Offenses (Administrative Offenses Code of the Russian Federation) defines unauthorized occupation of a land plot as the unlawful seizure and use of this real estate by persons who do not have legal rights to it (Article 7.1 of the Administrative Offenses Code of the Russian Federation). Self-capture includes the following actions:
- violation of the boundaries of one’s own plot of land established by the boundary plan: removal of a constructed building or fence onto the territory of an adjacent neighbor;
- construction of any buildings on the site or installation of structures, as well as the use of land for storage (warehousing) of property without prior registration of title documentation;
- use of land for agricultural purposes (gardening, vegetable garden, summer cottage farming) or for commercial activities without obtaining permits, as well as after the expiration of its validity;
- other illegal actions due to which the owner of the site cannot fully use his property.
It happens that a person using land that does not belong to him does not even suspect that he is committing an administrative crime. This is especially true for “spontaneous” vegetable gardens and dacha plots that arose on unexploited agricultural territory or tenants who did not renew the contract with the land owner in a timely manner. Let's consider what consequences can await an “invader” who voluntarily or unwittingly violates someone else’s property rights.
Return of illegally occupied land plots
If a person arbitrarily took part of someone else’s territory into his own allotment, he must be confronted with legal methods. A citizen who has become a victim of this illegal act must know where to turn and what to do in such a situation.
This is what the approximate procedure for a landowner looks like, part of whose territory has been seized. He must:
- Notify the citizen who took possession of the land that its implementation is illegal.
- Find out whether there is fraud, illegal registration of land ownership, sale or lease of someone else's land.
- If the invader acts deliberately and maliciously, warn the offender about the illegal nature of his act and present papers confirming ownership of the land, for example, a title document that has undergone cadastral registration and registered in Rosreestr (Article 131).
- If you were unable to vacate the unauthorized land plot on your own, submit an application to the local administration, which is authorized to resolve such issues.
- In case of refusal of a local government body, request an extract or a copy of the protocol of the administrative commission.
- Apply this document to the court at the location of the land.
Four scenarios
- If the plot belongs to local government or SNT, you must provide an application for the allocation of this land plot for personal use to the applicant.
- In the case where the plot belongs to the state, you will need to take part in the auction and, accordingly, emerge as the winner. The auction provides the potential to increase land area and formalize the squatting of public areas quickly and inexpensively. The cost per square meter in this case will be 15% of the cadastral valuation.
- Perhaps the land already has an owner and in this situation there is only one way out - to enter into negotiations and insist on the alienation of property rights. In simple words - persuade them to sell and do it as cheaply as possible.
- Another option is that the land is ownerless, which means it has no owner. Then you need to contact local authorities with an application for registering the land with cadastral registration. But this procedure is quite long, since after registration in the cadastre the plot will become the property of the municipality in a year. And only after a year can you become a contender for the right to use the land.
Sanctions for illegal seizure
The types of punishment for illegal seizure of land are established by Art. 7.1 Code of Administrative Offences. The incident may also fall under article if the plaintiff manages to prove that the appropriation and exploitation of the site is associated with other offenses, for example, fraud.
What fine a violator will pay for squatting a land plot in 2021 depends on two criteria:
- whether the plot is registered in the cadastral register;
- what is its estimated value.
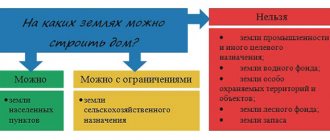
The concept of unauthorized occupation of land
The law grants the right to use land not only to the owner, but also to the tenant, the borrower under a gratuitous use agreement, and other persons on other grounds.
This means that each specific case is determined by the current legislation. Legal norms also establish the illegality of such an act as unauthorized occupation of land - and it has legal consequences.
Even the concept itself provides for the fact of using land in the absence of the corresponding right. The main signs of this type of offense include:
- lack of relevant documentation, including permission. For example, a lease agreement gives the right to temporary use, a purchase and sale agreement provides rights for permanent use based on ownership, and so on. But the absence of any document raises doubts about the legality of using the object;
- expiration of documents. For example, the rental period has ended;
- using the plot for other purposes, for example, building a multi-storey building on a plot that is intended for agriculture;
- illegal expansion of land allotment, in which case part of the land is considered seized;
- conducting activities that are contrary to the law.
Illegal use of land will have consequences, but a specific measure will be taken by the court on the basis of the law.
Responsibility for unauthorized occupation
The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, in article 7.1, defines the punishment for the illegal use of land. Thus, the article indicates that unauthorized occupation, as well as the use of an allotment in the absence of rights, may entail:
- a fine in the amount of 1 to 1.5 percent of the cadastral value, but not less than five thousand rubles - if the violators are individuals, from 1.5 to 2 percent, but not less than twenty thousand, if the norm is violated by officials, from 2 to 3, but not less one hundred thousand if organizations violate the law;
- a fine of from five to ten thousand for citizens, from twenty to fifty for officials and from one hundred to two hundred for organizations, if the cadastral value is not determined.
If a person conducts business activities, but does not register the appropriate status, then the tax will be paid as a legal entity.
Responsibility is not limited only to the application of administrative rules. If the occupation of someone else's land led to financial losses, then the losses can be compensated through the court. Thus, Article 76 of the Land Code states that damage caused by land violations is compensated in full.
Administrative punishment
When applying administrative measures, sanctions provided for by the Code of Administrative Offenses are imposed. In this case, it matters what category the person who illegally took possession of the land belongs to.
The amount of fines directly depends on the value of the plot and amounts to:
- legal entities – 2 – 3% (not less than 100,000 rubles);
- officials – 1.5 – 2% (not less than 20,000 rubles);
- individuals – 1 – 1.5% (not less than 5,000 rubles).
If the land plot has not been assessed, the fine is fixed and amounts to:
- legal entity – 200 – 300 thousand rubles;
- officials - 40 - 50 thousand rubles;
- individual – up to 10 thousand rubles.
Possibility of the court to overturn the decision
The court has the right to declare illegal and cancel the decision to bring a person to justice. This is possible in each of the cases:
1) the court has established the absence of an offense;
2) administrative body:
• has not proven a violation of the law or guilt;
• incorrectly classified the offense.
Moreover, even if there was an offense, in some cases the decision can be challenged on procedural grounds. In particular, if the statute of limitations for prosecution has expired or the administrative body violated the rules when it compiled:
• protocol on the offense or
• inspection report.
In addition, the court has the right to recognize the violation as minor.
As a result of the appeal:
1) the decision of the administrative body may be canceled.
2) the fine for the offense may be reduced. Moreover, the court has the right to reduce the fine to an amount of less than 100 thousand rubles, although the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not provide for going beyond this limit.
Examples from judicial practice
Hearings on claims for land squatting are quite common in civil courts. Having failed to find a compromise in disputes about acres and the boundaries of their own plots, citizens go to court to resolve the problem. However, even there the dispute over land is not always decided in favor of the plaintiff.
When preparing to file a claim in court, you need to carefully consider the arguments of your claims and prepare documentary evidence of your claims. Otherwise, as judicial practice shows, the claim may be denied.
What to do when seizing land
In a situation where the site is illegally occupied by other persons, the owner is recommended to take a number of consistent actions aimed at returning his rights and compensation for damage:
- try to resolve the situation peacefully. In some cases, the violator of land boundaries may simply not be aware that someone’s rights are being violated. For example, when areas have no visible landmarks. In such cases, there is a high chance of solving the problem without going to court or turning to other authorities;
- prepare an official claim demanding the release of the occupied plot, indicating the actual boundaries of the land;
- record the fact of violation. Depending on the situation, this may be Rosprirodnadzor or Rosreestr;
- prepare an application to the court;
- submit an application and take part in the trial.
After the judicial act is issued, all that remains is to wait for it to come into force. Then you need to obtain a writ of execution and contact the bailiff service, who will assist in the enforcement of the decision.
If the boundaries of the site were not previously determined or points were not removed from the area, it is recommended to do this before going to court. Otherwise, it will be more difficult to prove your position.
If stopping the violation (unauthorized occupation of the plot) is impossible, the court may decide to buy it out. The price is calculated in this case according to market indicators prevailing in the region.
Compensation for harm for unauthorized occupation
Compensation for damage for unauthorized occupation of land is made only in civil law.
The owner can file a claim for damages immediately with the claim to vacate the territory or separately. In each case, you need to correctly calculate the amount of the claim.
Damage may include not only direct losses, but also lost profits. However, it is more difficult to calculate and prove. It is necessary to collect documentary evidence that the profit was not received precisely because the plot was illegally seized, as well as the fact that under other circumstances there were all the factors for obtaining it, for example, there is a grain supply agreement, but due to the impossibility his cultivation agreement was not fulfilled.
Collection of funds is carried out through the court. If after this the debtor does not give up the land and does not compensate for the damage voluntarily, it is necessary to contact the bailiff service to begin the forced collection procedure.
Forced seizure
A plot that was illegally seized will still be confiscated from the person who seized it. At the same time, his voluntary release will avoid not only the participation of bailiffs in the case, but also additional costs.
To exercise their powers, FSSP employees can involve third-party specialists, for example, Rosreestr employees to determine local boundaries. The violator will first be asked to voluntarily vacate the territory, and then forced action will follow.
How to legitimize squatting
If the territory was occupied without the consent of the authorities, the question arises of how to legalize the squatting of the land. This is possible, but there are some limitations to consider.
The rules for the redemption of an allotment are established by Art. 39.18 Land Code of the Russian Federation. However, certain categories of land in respect of which illegal appropriation has been committed cannot be legalized. These include:
- territories that open into the forest zone;
- areas beyond the “red lines”, which fence off power lines, gas pipelines, and communication elements.
In addition, it will be possible to legitimize only areas that are not claimed by legal entities, private individuals or partnerships. In this case, you can either register the land as your property or rent it from the owner.
Self-occupying plots. Causes and background of the problem
Like any piece of real estate, a plot of land has its own history. Once upon a time, once separated from a larger one, it received its own area and boundaries, and these data did not always coincide with what was indicated on paper.
Considering the tools and qualifications of land surveyors at that time, whose experience for a long time left much to be desired, errors in calculating the boundaries of land plots arose everywhere. At the same time, neighbors most often resolved issues on their own, either by reaching an agreement or playing dirty tricks on each other until one of them gave up.
Land plots were received from the state in different ways:
- into lifelong inheritable possession;
- for unlimited use;
- for rent.
Then they were gradually privatized. One way or another, disputes in people's courts about determining the boundaries of land plots were extremely rare; usually everything was resolved amicably, between neighbors, at most, at the level of local Soviets. And at that time land was allocated with a reserve, so as not to lead to a scandal.
The procedure for legalizing an occupied plot
Having settled all controversial issues with the owner, you can try to legitimize the squatter. First you need to submit an application to the local administration for the redistribution of land. By this time, documents confirming ownership of the plot must be ready, and a land survey plan must be drawn up.
If a positive decision is received, a cadastral passport must be issued for the land. To do this, the following documents should be attached to the above documents:
- statement;
- receipt of payment of state duty;
- geodetic plan of the territory;
- document on ownership of the plot;
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation.
That's all you need to know about how to legitimize a plot of land by squatting.
After receiving the documents, Rosreestr employees are required to produce a cadastral passport for the land plot within 5 working days, in accordance with the provisions.
A separate procedure is registration of rights to a plot. It is necessary to write another application and pay the prescribed fee. In addition, you must provide documents confirming:
- alienation of land,
- purchase,
- ownership of an allotment.
If the applicant follows the instructions on how to register land ownership, his actions will almost certainly be crowned with success. The main thing is that he does not try to circumvent the law and tries to avoid disagreements with third parties.
How to prove land squatting?
You can prove a violation of land legislation using documents for a land plot or several land plots. In this case, the actions will most likely be proven by the owner of the neighboring plot, from whom parts of the land were seized.
You can refer to the public cadastral map and view the location of objects and the boundaries of the site from a satellite. The map will show objects and boundaries of the site, and the actual use of the site, which will allow you to determine whether there is squatting or not. You can also go to the site and, taking into account information from the public map, determine the presence or absence of a violation.
You can use the help of a cadastral engineer who, if the plot is registered in the cadastral register, will be able to determine whether a person has occupied the plot without permission.
Who to complain about land squatting
If the illegal occupation of a territory is beyond doubt, and the fact of its exploitation is established, the owner has a question about where to complain about the illegal actions of the invader.
The first instance is the local administration, which is competent to resolve such issues. If the expected result is not achieved, you will have to file a claim in court at the location of the land.
The statement of claim must include:
- the circumstances of the seizure of the memory;
- grounds for the emergence of ownership of the plot;
- a list of measures taken to return the site.
When drawing up a claim, it is advisable to focus on a sample request for the release of a land plot. It contains an urgent request to return the illegally seized plot.
A package of required documents must be attached to the statement of claim.
So, the legal rights of the owner can be restored on the basis of an administrative resolution or a court decision.
Registration of ownership - step-by-step instructions
It should be noted that amendments to land legislation with the introduction of Chapter IV make it possible to redistribute lands of a municipal or state fund to their plots, subject to a number of conditions and on the basis of an agreement between the parties. Thus, it is quite possible to legitimize squatted land. But we are not talking about huge territories, but only about small areas, so that the result is an allotment up to the established maximum sizes.
The step-by-step procedure for legalizing land acquisition can be outlined by the following algorithm:
1. Determine the owner - legal holder of the seized land.
There are several ways:
- Free - does not require financial investment, is to obtain information on a public cadastral map.
- Paid - order an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
- Request to municipal authorities.
Further, depending on the form of ownership, the situation is resolved in the following order:
- if the site is in municipal or state ownership, it is necessary to send an application to the administration to grant it ownership. Then the authority is obliged to follow the entire procedure, including the announcement of the auction, its conduct, the conclusion of the contract and the purchase of property.
- if the plot is privately owned. Then it is possible to make attempts to find the owner and buy back the ownerless land.
- Things are more complicated when this territory has not yet passed state registration, i.e. owner is not determined. In this case, you should contact the administration at the location of the land to initiate the land surveying procedure and register it with the cadastral register. Then it is possible to conclude a lease agreement with the administration and subsequently buy the plot.
2. Demarcation of the boundaries of the plot enlarged by the occupied territory and obtaining a cadastral extract.
You will first need to agree on the boundaries with your neighbors and make sure that they will not interfere with the land surveying procedure.
We will tell you how to demarcate a plot of land in this article.
3. Registration of ownership of a newly formed plot.
All data on formed rights to real estate are in the Unified Register maintained by Rosreestr.
The extract is issued on the basis of the following documents:
- citizen identity card;
- documents for the right to dispose, own and use the site;
- boundary and geodetic plan;
- document confirming payment of state duty.
The registrar accepts documents for processing, gives the applicant a receipt of acceptance and sets a date for receiving the extract. The result of state registration is an extract from the Unified State Register with the name of the owner in the appropriate column.
Land protection
The definition of legal protection of land resources includes a system of measures enshrined in legislation that are aimed at ensuring the rational exploitation of lands, preserving and increasing their fertility, and protecting them from destruction and depletion.
These measures are applied comprehensively and are carried out with the aim of:
- preventing land degradation/destruction and other negative consequences of management by stimulating environmentally friendly production technologies;
- ensuring the restoration and improvement of agricultural areas that have been disturbed or degraded;
- creating rules for checking and accounting for the environmental status of resources.
The legislation provides for preventive and restoration measures and legal liability for violation of land legal standards.
Find out in more detail what legal land protection is and how it is carried out.
Unregistered buildings
Agree, not everyone would think of registering a gazebo or enclosure for a dog.
But, often, these and many other structures on the site, from the point of view of the law, are real estate objects that must be registered with Rosreestr, and for which taxes must be paid. Many people have buildings on their plots that were erected many years ago, from what was there, and have not been used for their intended purpose for a long time. So, standing in the far corner of the site, on an improvised foundation, a pile of nails and sticks must also be registered with Rosreestr and taxed. Otherwise you will have to pay fines.