Any rights to a land plot must be legalized.
Such rights are subject to state registration by Rosreestr authorities. Registration of the right to use a land plot, the ownership of which belongs to another person, is carried out in any region of Russia, regardless of the location of the land plot.
The complex of registration actions consists of several stages and includes the registrar checking many aspects, starting from the content of documents and ending with the intended purpose and type of permitted use of the land.
What types of land use are there?
Rights to a land plot can take the following forms:
- Rent. The most common form of legalization, which can be used by both citizens and companies for a fee under the conditions specified in the contract;
- Easement. This is a restriction of the right to use land by a person who is not its owner, but has legal grounds for this (for example, the right to place a gas pipeline, water supply; right of passage);
- Free use on an urgent basis. This is the rarest type of legal relationship that arises when an agreement is concluded and the land is the property of its parties;
- Permanent (indefinite) use and the right of lifelong inheritable ownership of land. These types of rights are available only to persons who received such a privilege before 2001, that is, before the adoption of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. Now the land is not formalized in this way, and these forms are gradually losing their relevance.
Procedure for terminating permanent (unlimited) use
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 45 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, the right of permanent (indefinite) use can be terminated voluntarily by submitting an application for waiver of the right by the landowner with the attachment of documents provided for in Art. 53 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation to the executive body of state power or local government body authorized to provide land plots (for citizens - copies of an identity document; for legal entities and state and municipal enterprises - a document confirming the consent of the body that created the corresponding legal entity, or other acting on behalf of the founder of the body to renounce the right of permanent (indefinite) use of a land plot), other grounds for termination of the right may be established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In paragraph 2 of Art. 45 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation establishes a closed list of grounds for the forced termination of the right of permanent (perpetual) use, namely in connection with the use of a land plot in violation of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation (use of a plot not for its intended purpose or if its use leads to a significant decrease in the fertility of agricultural land or damage to harm to the environment; damage to land; failure to fulfill obligations for land reclamation, mandatory measures to improve land and protect soils, obligations to bring land into a state suitable for its intended purpose; failure to use a land plot intended for agricultural production or housing or other construction, within the established time limits) and when withdrawing a land plot for state or municipal needs; creation or erection of an unauthorized structure on a land plot or failure to fulfill obligations to demolish such a structure (Part 11 of Article 55.32 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Forced termination of the right to permanent (indefinite) use of a land plot on the grounds specified in paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 45 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (when using a land plot in violation of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation), is carried out exclusively on the basis of a judicial act on the seizure of the land plot that has entered into legal force (subject to the failure to eliminate the improper use of the land plot after the imposition of an administrative penalty in the form of a fine) (clause 3 of Art. 45, Article 54 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
When registration is not required
Legalization by entering data into the register is always necessary if this is expressly stated in the law. In particular, the obligation applies to lease agreements and land easement agreements. However, there are exceptions. Registration is not required if the term of the lease agreement does not exceed one year or is concluded for an indefinite period.
The copyright holder who received land for use before January 1998 is also not required to go through the registration procedure, but can do this at his own discretion. Such a right is called pre-existing. However, the lack of state registration of a previously arisen right creates certain risks for the copyright holder. Avoidance of mandatory state registration of a previously acquired right to land does not give rise to legally significant consequences for third parties. That is, the actual owner will not be able to prove his status and protect his interest. In addition, counterparties may be required to take legalization actions in court.
List of documents
Free use of the site for a specified period is carried out in the form of a standard agreement, for the conclusion of which the following documents are required:
- passport of the owner of the land plot or his legal representative;
- power of attorney to represent the interests of the owner of the site (if necessary);
- title documents for this territory;
- cadastral passport of the land plot;
- constituent documents of a company that owns land or intends to register it for temporary use.
For further registration of the contract in Rosreestr, confirmation of payment of the state duty is additionally required. This procedure is mandatory for contracts concluded for a period of more than one year.
Example of free use of land
Managing director . In order to receive a free plot of land on which the building was to be erected, the man contacted the administration of his city and submitted a corresponding application.
A few days later he was refused without explanation. The man re-applied and asked to justify the refusal.
Administration officials explained that they cannot provide land for commercial development, regardless of which tender the organization wins.
The director hired a lawyer, and a claim was filed in arbitration. The judge, guided by the Land Code of the Russian Federation, explained to the defendants that when constructing an object at the expense of the state budget, the contractor has every right to receive the necessary territory for temporary use.
Conclusion
Thus, several conclusions can be drawn:
- Free exploitation of land plots is another opportunity to acquire someone else’s space. Such a transaction can apply to lands owned by state and city authorities, as well as plots owned by legal entities and individuals. Land users can also be legal entities and individuals, including government agencies and city enterprises. These areas are used for the construction of sacred sites, complexes raised at the cost of budgetary resources, for the construction of parks and other legal resources. The legal relationship is carried out in the form of a concluded agreement. The duration of the contract is set by the parties. If it is more than a year old, the document must be registered in the Federal Register of Entrepreneurs. Before concluding a contract, it is necessary to obtain a positive decision from local authorities or employers.
What are the stages of the procedure for legalizing the right to use land?
Registration of the right to use a land plot begins with the preparation of documents, including drawing up an application and paying the state fee. A legal examination is carried out to determine the reliability and completeness of the information and the compliance of the transaction with the law. After submitting documents for registration, the registrar checks whether there are any contradictions related to the right to use a specific object. After this, the updated data is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate, and the applicant receives confirmation of registration in the form of an extract. From this moment on, land rights are considered legal. Refusal to register or suspension entails additional stages, including defending interests in the appeal commission of Rosreestr and the court.
Illegal use
The Land Code strictly prohibits the use of reserve lands for illegal purposes. The basis for termination of the right to gratuitous temporary use of an allotment will be a number of violations that may be illegal, these are:
- unauthorized occupation of land by citizens, whose roles are legal or physical persons;
- destruction of signs installed on plots of land included in the reserve;
- the use of subsoil located on this land, namely the illegal extraction of various types of natural resources. An exception in such a situation can only be a special permit for such activities;
- unauthorized development of a reserve plot of land with real estate objects or other buildings;
- damage to facilities that provide water supply and are located on reserve lands;
- causing damage to bodies of water located on such land, namely ponds, lakes or rivers;
- illegal mining of amber on land classified as a reserve reserve.
As a rule, according to the law, these grounds for terminating the right to gratuitous temporary use of plots are quite sufficient. We talk in more detail about the grounds on which the right to perpetual use of memory can be terminated here.
Important. For committing the violations listed above, a fine is provided, which can range from 5,000 to 200,000 rubles. depending on the seriousness of the offense and other circumstances.
Completed projects
Recognition of ownership of land
In the court of first instance, it was possible to defend the interests of the Principal in the claim of the DGI of Moscow to recognize the ownership of the land plot as absent. According to the DGI of Moscow, the Principal’s plot is located within the city of Moscow (Zelenograd Autonomous Okrug), was not alienated by Moscow to third parties and crosses the boundaries of other land plots owned ... Read more
all projects
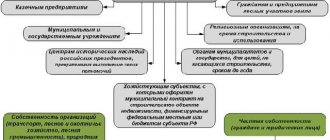
Grounds for transferring a land plot for free use
To transfer land for temporary use, a legal basis is required. Such reasons may be:
- Transfer of land to religious associations for development with special types of objects;
- allocation of land to citizens or businesses for the construction of parks and recreation areas;
- use of land plots for the construction of residential buildings and other complexes at the expense of regional or federal budget funds
- Organization of operation of historical places that are in state or municipal ownership;
- allocation of land plots to employees for organizing recreation on personal plots or on roofs.
The right of a citizen or company to use land arises only after the conclusion of a formal contract, the issuance of a decision by the district council and a decision made by the organization in which the citizen works and which provides the employee with the site.
For what purposes are the plots provided?
Land plots are provided indefinitely for the following purposes:
- construction (residential buildings, as well as educational, industrial, warehouse, trade, sports or other purposes);
- agricultural works;
- gardening, horticulture;
- entrepreneurship;
- use of reservoirs, underground resources, etc.
Land transferred for permanent use must belong to categories that fully meet the goals. This means that if a plot is requested for a specific type of activity, then the land can only be allocated to a category that meets the requirements specifically for the chosen type of use. For example, the allocation of fertile agricultural land for construction is unacceptable.
Features of the use of lands of various categories
Lands of various categories are subject to intended use, that is, the rights granted to users will be strictly limited. But the Land Code enshrines the basic principles by which the rights of subjects (that is, those who act as users) are determined:
- when the site is transferred to use, all existing plants and their derivative elements (seeds, seedlings) become property (but only if this does not contradict legal norms, for example, some trees are strictly prohibited from being cut down);
- carrying out business activities (all manufactured products also fall under the right of ownership, the user can use them at his own discretion within limited legal frameworks);
- natural resources located on the site may be used (for purposes limited by law);
- carrying out construction work if its intended purpose does not contradict the law;
- formation of water bodies (reclamation measures);
- receiving financial and other compensation for the care or cultivation of the plot (more often applied to agricultural land after the cultivation of the site).
We recommend: The process of allocating a share in kind in a private house.
How to buy back a share? Again, the user has the right to demand other compensation established by the legal act under which the land plot is used. But all such conditions must be stipulated either in the lease agreement or in another act (if provided by the local administration).
When is refusal possible?
Local authorities may refuse an applicant if:
- the documents of the authorized person are drawn up incorrectly;
- the information provided is not true;
- the selected plot does not belong to the local administration;
- the cadastral number is identified with a completely different plot;
- the chosen hectares are located on a piece on which restrictions are imposed or withdrawn from circulation.
It is also impossible to obtain the plot in relation to which the trial is being carried out.
When purchasing land for individual housing construction, it is necessary to take into account many nuances. Donating a plot of land to relatives follows a simplified procedure. Read more about this here. When you take out a mortgage to purchase an apartment, you can get a tax deduction. You will learn how to do this from our article.
Preparation of a documentation package
Before contacting government agencies to re-register ownership, you will need to prepare a package of documentation.
It should include:
- application to the local administration;
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- checks confirming payment for registration and transfer of the site;
- perpetual lease agreement;
- application to Rosreestr;
- resolution issued by the administration;
- copies of all papers.
Attention! The list of documents may change. Experts advise clarifying the list.
This can be done by visiting the government agency to which you plan to apply.
Security rules
Any piece of land that is located within the borders of Russia is protected by the state. All points prescribed in the legislation consider land as a prerequisite for the normal life of citizens.
When using land in reserve, certain conditions must be met:
- ensure the safety of the land in environmental terms;
- ensure that the land retains its ability to serve the benefit of the homeland as a means of production;
- it is necessary to use the land only in production or other economic activities.
Land conservation is done for a reason. It pursues certain goals, such as:
- Preventing degradation of reserve areas, as well as their clogging.
- Preventing any kind of influence that could have a negative effect of various kinds.
- Improving the general condition of the land in reserve.
- Restoration of areas that have received certain damage.
To organize land protection, the following actions are performed:
- ensuring soil protection from various invasions;
- organizing the protection of land from erosion associated with wind or water;
- organization of protecting a plot of land from overgrowing with trees and various weeds;
- if the need arises, carrying out the elimination of various types of pollution;
- preservation of land reclamation;
- from time to time carrying out work related to soil reclamation.
How long will the wait take?
When submitting an application, a person should be prepared to wait. The duration of its consideration is 30 days. During this period, government officials make a decision on providing the site or refusing the application received. If the verdict is positive, a purchase and sale agreement for the property is drawn up and sent to the applicant for signature. The manipulation is carried out in accordance with Article 36 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
Government authorities do not always make a positive decision on an application. They may reject the request or offer the citizen to rent the plot. In this situation, the applicant has the right to try to appeal the decision by going to court. To begin the proceedings, you need to file a statement of claim. It must indicate the requirement to appeal the decision. The right to such actions is enshrined by the Constitutional Court in Determination No. 187-0.
In what cases can you get a refusal? Let’s look into the reasons?
When wishing to transfer land into ownership, a citizen must understand that in a number of cases a request for land ownership may be refused.
The list of grounds for rejecting an application is enshrined in paragraph 1 of Article 20 of the Law on State Registration of Rights.
According to the provisions of the regulatory legal act, a request for ownership of a plot of land will be refused if:
- the person who applied to the state body does not have the rights to claim the land;
- one or more documents do not comply with the requirements of current legislation;
- the title document does not confirm that the applicant has the right to the objects located on the site;
- the person has prepared an incomplete package of documentation;
- information about the site is not available in the cadastre.
If Rosreestr denies the applicant registration of property rights, he is sent a corresponding notification. The document must be sent to the applicant within 5 days from the date of the decision. The law allows a citizen to appeal the decision. To do this you will need to go to court.
Proceedings concerning the possibility of obtaining ownership of immovable plots are handled by the arbitration court. The verdict of the government body depends on the specifics of the current situation.
The video story will tell you about the intricacies of the legislative framework when registering land leased from the state with the right to purchase