As the population grows, so does the need to build housing and create infrastructure for people. The state must foresee such developments in advance and carry out the transformation of empty territories into cities and settlements gradually, as necessary.
To this end, in laws and regulations, the authorities establish the exact parameters of areas that may be subject to development for settlements, as well as the procedure for carrying out development. Such categories of land are defined in legislation by the term “settlement lands”.
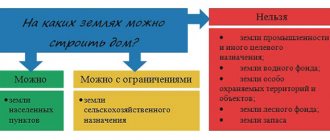
What it is?
Land legislation provides for seven categories into which plots of land can be divided. This document gives the concept of lands belonging to settlements. It is indicated that such plots are those that do not extend beyond the boundaries of the populated area.
The purpose of such lands is to develop infrastructure and carry out construction work. The types of permitted land use are specified in a specially developed classifier. The boundaries of territories are indicated in legislative acts. Some subjects have the authority to change them.
The concept of NP lands
These include:
- bodies carrying out government activities at the federal level;
- local authority;
- judicial authorities.
Individual housing construction on settlement lands
The construction of residential premises is the main purpose of cities and settlements. The purpose of providing the site is indicated in the document that serves as the basis for the transfer of ownership of the property.
To begin work on housing construction, it is necessary to collect all the necessary permits. These include:
- a document confirming ownership of the plot;
- an extract from the cadastral service stating that the territory is intended for individual housing construction;
- technical documents of the newly constructed structure;
- building permit issued by local authorities.
In certain cases, other documents may be required, depending on the individual characteristics of the land plot.
Composition and zoning
The urban planning documentation, which is established for each region, prescribes the composition of lands related to settlements. The composition includes the following groups of territories related to zones:
- zones of location of buildings intended for residence;
- territories with industrial purposes;
- lands intended for the location of transport schemes and engineering;
Land composition - agricultural land;
- recreational allotments;
- territories with special purposes;
- lands intended for the construction of objects with military purposes.
Rules regarding land use and development are prescribed in urban planning acts, which are provided for each type of territory individually. In this case, the nuances regarding the development and location of plots must be taken into account, and their capabilities in relation to the combination of different types of use of plots are also important.
If the land is located in a residential area, then only residential buildings can be erected on it; objects with domestic, cultural and other purposes can also be located.
When it comes to the lands of the public and business zone, its purpose is the construction of administrative buildings, objects that have social, educational, social, domestic and other meanings. Industrial zones are subject to development with production and other facilities that can be built in accordance with legislative acts.
Conditions for provision of land
All issues regarding obtaining a plot on such lands for the construction of a residential building, its size, and conditions of use are specified in the lease agreement or in a special permit for its provision. As soon as such a document is in your hands. You can safely start building the site. The main condition is its compliance with urban planning regulations and requirements. There are lands. Where it is unrealistically difficult to obtain a plot within the boundaries of settlements, and the principle of increased demand and cost of such plots works here.
This includes such regions as Moscow, Leningrad, Crimea. And there are also places and regions where such a plot can be obtained almost free of charge. Often these are areas in northern lands or small populated areas.
The size of the land plot will depend on its actual use and urban planning regulations that are in force at the time of applying for land. You will have to actually prove that the specified plot sizes are exactly what you need. The procedure is simple and usually limited to a written application.
Kinds
The permitted use for the category of land in question is established in a special classifier. All plots related to settlements can be conditionally divided into zones by territory.
Indicate areas such as:
- location of residential buildings;
- buildings of a public and business nature;
- for conducting business activities;
- use for public purposes;
- organization of recreation.
Legal regime of lands
The above zones include several types of use. Including:
- Residential areas include those uses that involve the construction of residential buildings. According to the classifier, they include:
- houses built like townhouses (blocked type);
- high number of storeys includes the construction of buildings above 8 floors;
- average number of storeys – up to 8.
tent cities – this means a mobile variety;
Individual residential buildings, for example, cottages, private houses, etc., can also be built. In addition, the construction of buildings for domestic purposes, such as a garage and utility room, is allowed. The possibility of running a personal subsidiary plot with the construction of a private house for this purpose is provided. In this case, a person must have a main goal - growing a vegetable garden, orchard or livestock.
Signs of NNP
conclusions
Lands of populated areas are the central category of lands, since they form the basis of human life .
Today, when almost the entire population of the state is concentrated in the ZNP, the question of the rational use of the available limited areas is of particular importance.
First of all, this concerns compliance with legislative regulations - urban planning regulations, VRI, as well as the inevitability of applying sanctions for violations.
Since land is a non-renewable resource, the following are also important:
- compliance with the principles of land protection,
- implementation of safe land use,
- causing minimal damage to the natural environment,
- compensation for damage caused.
Private household plots
On plots that are allocated for personal subsidiary farming, the construction of residential buildings is allowed. Rules are established regarding their number of floors - no more than three. In this situation, garages and utility rooms are also not subject to accounting. Particular emphasis is placed on the fact that the house can only be single-family.
On the site having the intended purpose, livestock breeding, gardening and gardening are allowed.
The attention of the land user is drawn to the fact that subsidiary farming in relation to agricultural lands and lands related to settlements are completely different and have different permitted uses.
In the latter case, the construction of houses can be carried out without restrictions, but in another situation, discussed above, approval is required from the commission involved in land use activities. A requirement is also established that the allotment must be used on an ongoing basis in accordance with its intended purpose and must be processed.
Blocked residential building
When we talk about construction of this type, we talk about the possibility of building several houses that will be single-family. It is indicated that the buildings are adjacent to each other.
Requirements are established regarding the number of storeys - as in the situations discussed above, it cannot exceed the value of 3. Premises with utility purposes and garages are not subject to accounting. It is allowed to plant vegetable gardens, orchards, and flower beds on the site.
Composition and characteristics of NP lands
The concept of the structure in question is provided for at the legislative level. An indication is made that the structure must consist of several parts, the maximum is set at 10. It is also stipulated that each of the parts must be provided with a separate exit to the territory, which belongs to the common one.
Transfer of lands into settlement lands
Plots of a certain type are open to conversion to the form of land for settlements and cities. Basically, these are zones of agricultural importance and reserve lands. In rare cases, both water and forest lands may be transferred (drying of the river bed, clearing of forests).
However, the main determining parameter is the value of the land. In other words, depending on the value of the land, the question of the possibility of transfer is decided. Thus, if land costs 50 percent or more more than the average cost of land plots in the territory of a particular municipality, then it is not subject to transfer.
The transfer is carried out at the request of citizens and organizations. In some cases, the transfer can be carried out by decision of local government authorities if it is necessary to implement a plan to expand the settlement.
Land in populated areas for gardening and agricultural use
The components of each category of land plots are lands that have different uses that are permitted for them. When use occurs contrary to established norms, the punishment prescribed by law is applied to violators. The legislator provides rules according to which the allocation of territories for gardening or horticulture is carried out.
The difference between the types of plots under consideration is the permitted use regarding the cultivation of agricultural products on them, as well as the type of buildings that can be erected.
Land for agricultural use as part of the ZNP
A garden plot means an allotment intended for growing vegetables, berries and other fruits. On such territory it is allowed to erect buildings with economic and residential purposes.
It is possible to live in them for 12 months. In this case, a ban on registration actions is established. The plots in question may have private owners as owners, or they may be subject to a lease agreement.
Gardening and vegetable gardening activities cannot be classified as entrepreneurial, which means using the harvest for personal purposes. The laws provide for a maximum size for allotments.
The functions of allocating land for the intended purpose are assigned to municipal authorities. The procedure for extradition is prescribed by law. The order is fixed by the administration. In 2015, adjustments were made to the classifier; to find out what type of buildings are allowed to be erected on the site, you must refer to the specified act.
The types of plots under consideration, including DNT and DNP, can be issued on the basis of perpetual use rights. This provision is carried out by the local administration. If the plot is on this basis, then the citizen can count on receiving ownership of it. This will require a privatization procedure.
When the plots are used by partnerships that have a non-commercial orientation, then they are subject to the ownership rights of the federation or region. Land allocated for gardening can be used for the purpose of erecting buildings of capital importance. If we are talking about gardening, then only temporary buildings are allowed.
According to amendments made to legislative acts in 2021, real estate located on garden plots must have technical documentation.
Procedure
In general, changing the permitted use of land is carried out in the following order:
- The land user collects the necessary documents and submits an application to the head of the executive branch;
- If the application is drawn up correctly, the town planning and land committees form a commission;
- The Commission sends notices of upcoming hearings to land users whose plots are located in the same zoning area as the applicant's plot;
- Public hearings are held;
- Based on the results of the hearings, the commission makes a decision;
- If the decision is positive, an act on changing the VRI of the declared site is drawn up;
- Based on the act, changes are made to the Unified State Register.
A sample application text can be downloaded from this link. The application must include the following information:
- Full name and contact information of the land user;
- Category of land and address landmarks of the site;
- Current and requested VRI;
- Reason for changing land use;
- List of attached documents.
The maximum period between the distribution of notices of hearings through the media or mail and the commission’s adoption of a decision is established by local legislation, but cannot exceed 30 days (Clause 7, Article 39 of the Urban Planning Code).
During public hearings, the applicant speaks, arguing for the need to change the VRI, and interested parties express their opinions on the consequences of changing land use to members of the commission.
Dissenting opinions and objections must be submitted to the commission members in writing.
When making a decision, the commission is guided by the following factors:
- The feasibility of changing the VRI;
- Consequences of changes in VRI for the environment;
- Legal and economic consequences for neighboring land users.
For example, if the owner of a gardening plot wants to change the VRI to build a house, the commission may reject the application due to the threat of shading of the neighboring cultivated plot.
If the commission decides to change the type of land use of the site, a copy of the decision is sent to all participants in the hearing. 10 days after the decision is made, an act on changing the VRI is drawn up, a copy of which is issued to the applicant. The applicant must contact Rosreestr to register changes in the cadastral register, attaching the following papers to a copy of the act:
- A copy of your passport;
- Receipt for payment of state duty;
- Application for amendments;
- Cadastral passport for the plot.
The new type of permitted land use will be displayed on the cadastral map of the area within 7-10 days from the date of application to Rosreestr.
If the applicant does not agree with the decision of the commission, he can challenge this decision in court (clause 12 of article 39 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Urban zoning
This procedure is carried out through the adoption of rules relating to land use and territory development. With its help, the basic regulation of activities of an urban planning nature is supplemented and developed. With the help of the rules established regarding the use of plots and their development, a connection is made between the following documentation:
- layout and territorial planning;
- there is a regulatory impact on persons who have rights regarding various real estate objects located on the territory.
Map of the planned functional zoning
Thanks to the zoning of space, the site is divided into different zones, in relation to which boundaries are established. Each of the plots has its own separate legal status. It is also possible to establish some restrictions regarding the use of land.
When preparing rules regarding the use of plots and construction within territorial zones, the following must be taken into account:
- the ability to combine several types of permitted use within one territory;
- the functionality of the zones and the parameters established in relation to the direction that is planned to be applied are taken into account;
An example of an urban planning plan for a land plot - planning and use zones enshrined in legislation;
- changes that will be made to the allotment are also taken into account;
- the possibility of causing damage to objects of capital importance, which are located on adjacent plots, is taken into account.
Regarding the lines of territorial zones, it is established that they pass:
- along the lines highlighted in red;
- lines related to streets, highways, driveways, etc.;
- plot boundaries;
- municipal boundaries;
- other.
When establishing town planning regulations, the following are taken into account:
- actual use of the territory and construction sites;
- combination of different types of use on one plot;
- allotment functionality;
- types of territoriality zones;
- protection of objects related to cultural heritage.
Urban planning documentation applies to land and construction sites located in the same zone.
Legal advice
The land issue requires careful consideration, meticulousness, and patience. In most cases, issues of providing land plots take a very long time to resolve. But you can buy land from private individuals very quickly. Within 15 days after the conclusion of the purchase and sale agreement, the cadastral authority, at the request of citizens, enters the property rights in the records of changes in the owner of the property in a special register.
But even in this case you need to be careful. Since the land may be included in the urban planning plan of government bodies, may be burdened with obligations, etc. All information about real estate can be obtained from the cadastral authority. And in the case of state and municipal lands, all information can be obtained from the authority of the relevant locality.
In any case, knowing all the ins and outs of a land plot, meaning legal characteristics, you can protect yourself and facilitate the process of acquiring and operating land in your ownership.