In land legal relations, the term “land” is used to designate a separate area of the surface, that is, a plot of land.
The main principle of their use is compliance with the intended purpose of such a site.
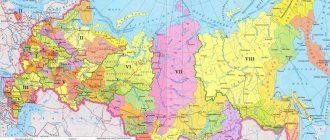
All sites are divided into seven categories, each of which has special parameters unique to it, code, purpose and permitted uses.
What is the main purpose?
The intended purpose is understood as a special function performed by one or another plot of land in public relations.
Areas with similar purposes are grouped into categories. The assignment of lands to one category or another occurs by decision of government authorities and is enshrined in the relevant regulatory documents, the main one of which is the Land Code.
Belonging to a certain category determines:
- legal regime of the site;
- its purpose;
- permitted uses within the category itself: basic and additional.
The owner cannot change them without permission . This limitation in powers is due to the high value of land resources and the state’s attention to preserving their quality.
Private household plots
On plots that are allocated for personal subsidiary farming, the construction of residential buildings is allowed. Rules are established regarding their number of floors - no more than three. In this situation, garages and utility rooms are also not subject to accounting. Particular emphasis is placed on the fact that the house can only be single-family.
On the site having the intended purpose, livestock breeding, gardening and gardening are allowed.
The attention of the land user is drawn to the fact that subsidiary farming in relation to agricultural lands and lands related to settlements are completely different and have different permitted uses.
In the latter case, the construction of houses can be carried out without restrictions, but in another situation, discussed above, approval is required from the commission involved in land use activities. A requirement is also established that the allotment must be used on an ongoing basis in accordance with its intended purpose and must be processed.
Codes
Each land plot that has undergone cadastral registration has a unique code that encrypts its category and intended purpose. There is a special reference book, designed in the form of a table, where each category and subcategory is indicated by the corresponding digital code :
- Thus, agricultural land has the code 003001000000. In order to highlight individual species within this category, the last two zeros are replaced by the subcategory number.
- Arable lands, hayfields, gardens and other farmland have the code 003001000010.
- Lands of settlements are hidden behind the designation 003002000000. And plots allocated for housing construction to citizens (individual housing construction) are encrypted as 003002000050.
- But a code such as 003002000100 denotes other land plots that are not clearly assigned to one of their categories.
- Codes are used, in particular, for tax purposes. For lands of different categories, different amounts of land tax are provided.
- Knowing which category a site belongs to, you can determine its code, as well as vice versa.
To find out which category each specific plot belongs to, you can use the Public Cadastral Map or order a cadastral extract from Rosreestr for the land plot of interest.
Blocked residential building
When we talk about construction of this type, we talk about the possibility of building several houses that will be single-family. It is indicated that the buildings are adjacent to each other.
Requirements are established regarding the number of storeys - as in the situations discussed above, it cannot exceed the value of 3. Premises with utility purposes and garages are not subject to accounting. It is allowed to plant vegetable gardens, orchards, and flower beds on the site.
Composition and characteristics of NP lands
The concept of the structure in question is provided for at the legislative level. An indication is made that the structure must consist of several parts, the maximum is set at 10. It is also stipulated that each of the parts must be provided with a separate exit to the territory, which belongs to the common one.
Land transfer
Lands can be transferred from one category to another.
This can not be done by the owner himself, but only by a competent authority , and only if the law does not directly prohibit such an action. For example, as is the case with protected areas.
An owner of land who wishes to change its intended purpose applies to the local executive authority with a petition.
If there are no obstacles to the transfer, such a request will be granted , and the necessary changes will be made to the land cadastre.
A typical example of such a procedure is the allocation of land for individual housing construction from municipal property.
Citizens can ask to transfer to them both an already existing, that is, allocated plot, and part of the farmland.
If the decision is positive, the selected plot is transferred to a category suitable for individual construction and, as such, is placed on the cadastral register .
a petition is not required to change the purpose of land . This happens, for example, when settlements expand, when part of the farmland or forest plantations falls into the category of settlement land.
But, in any case, a regulatory act of local or federal authorities is needed, by which this transition is fixed and legalized .
Composition and zoning
The urban planning documentation, which is established for each region, prescribes the composition of lands related to settlements. The composition includes the following groups of territories related to zones:
- zones of location of buildings intended for residence;
- territories with industrial purposes;
- lands intended for the location of transport schemes and engineering;
Land composition - agricultural land;
- recreational allotments;
- territories with special purposes;
- lands intended for the construction of objects with military purposes.
Rules regarding land use and development are prescribed in urban planning acts, which are provided for each type of territory individually. In this case, the nuances regarding the development and location of plots must be taken into account, and their capabilities in relation to the combination of different types of use of plots are also important.
If the land is located in a residential area, then only residential buildings can be erected on it; objects with domestic, cultural and other purposes can also be located.
When it comes to the lands of the public and business zone, its purpose is the construction of administrative buildings, objects that have social, educational, social, domestic and other meanings. Industrial zones are subject to development with production and other facilities that can be built in accordance with legislative acts.
Let's sum it up
State measures such as recording all land plots, dividing them into categories, establishing restrictions on use, etc., pursue an important goal - the protection of a valuable natural resource , the quantity of which is limited for objective reasons.
Violation of statutory requirements will have a number of unpleasant consequences . The easiest of them will be a fine. The most severe is deprivation of property, that is, seizure of land in favor of the state .
Such measures also indicate the special attention of the authorities to preserving the land fund.
Land in populated areas for gardening and agricultural use
The components of each category of land plots are lands that have different uses that are permitted for them. When use occurs contrary to established norms, the punishment prescribed by law is applied to violators. The legislator provides rules according to which the allocation of territories for gardening or horticulture is carried out.
The difference between the types of plots under consideration is the permitted use regarding the cultivation of agricultural products on them, as well as the type of buildings that can be erected.
Land for agricultural use as part of the ZNP
A garden plot means an allotment intended for growing vegetables, berries and other fruits. On such territory it is allowed to erect buildings with economic and residential purposes.
It is possible to live in them for 12 months. In this case, a ban on registration actions is established. The plots in question may have private owners as owners, or they may be subject to a lease agreement.
Gardening and vegetable gardening activities cannot be classified as entrepreneurial, which means using the harvest for personal purposes. The laws provide for a maximum size for allotments.
The functions of allocating land for the intended purpose are assigned to municipal authorities. The procedure for extradition is prescribed by law. The order is fixed by the administration. In 2015, adjustments were made to the classifier; to find out what type of buildings are allowed to be erected on the site, you must refer to the specified act.
The types of plots under consideration, including DNT and DNP, can be issued on the basis of perpetual use rights. This provision is carried out by the local administration. If the plot is on this basis, then the citizen can count on receiving ownership of it. This will require a privatization procedure.
When the plots are used by partnerships that have a non-commercial orientation, then they are subject to the ownership rights of the federation or region. Land allocated for gardening can be used for the purpose of erecting buildings of capital importance. If we are talking about gardening, then only temporary buildings are allowed.
According to amendments made to legislative acts in 2021, real estate located on garden plots must have technical documentation.
How to change the type of use: procedure
The first step when changing the territory's VRI is to obtain information from local governments about the current type of use. Changing the VRI of the earth has the following procedure:
- Writing an application to the authorities;
- Establishing the possibility of adjustment based on the analysis of the urban planning plan;
- After this, if the answer is positive, the documents are sent for consideration;
- Conducting a hearing and making possible adjustments;
- Sending the protocol to the administration.
Timeframe for making a decision
Consideration of an application to change the VRI of a land plot is considered no more than sixty days, if hearings are necessary.
When no hearing is held, the procedure may last thirty days. The decision is made by the head of the local administration, with each participant making his own proposals, on the basis of which further decisions are made. The following may refuse to change the VRI:
- If the hearing participants consider the changes not rational;
- If it is not possible to make changes from a legal point of view;
- If all required documents have not been provided.
ATTENTION! After successful consideration of the application, the owner submits a package of documents to Rosreestr to change the data in the cadastral registration.
Documents for Rosreestr:
- Territory survey plan;
- Application written by the owner of the site;
- Title document;
- The administration's decision to change the VRI.
Documents can be submitted in person when visiting Rosreestr or sent by mail, indicating all attachments.
Urban zoning
This procedure is carried out through the adoption of rules relating to land use and territory development. With its help, the basic regulation of activities of an urban planning nature is supplemented and developed. With the help of the rules established regarding the use of plots and their development, a connection is made between the following documentation:
- layout and territorial planning;
- there is a regulatory impact on persons who have rights regarding various real estate objects located on the territory.
Map of the planned functional zoning
Thanks to the zoning of space, the site is divided into different zones, in relation to which boundaries are established. Each of the plots has its own separate legal status. It is also possible to establish some restrictions regarding the use of land.
When preparing rules regarding the use of plots and construction within territorial zones, the following must be taken into account:
- the ability to combine several types of permitted use within one territory;
- the functionality of the zones and the parameters established in relation to the direction that is planned to be applied are taken into account;
An example of an urban planning plan for a land plot - planning and use zones enshrined in legislation;
- changes that will be made to the allotment are also taken into account;
- the possibility of causing damage to objects of capital importance, which are located on adjacent plots, is taken into account.
Regarding the lines of territorial zones, it is established that they pass:
- along the lines highlighted in red;
- lines related to streets, highways, driveways, etc.;
- plot boundaries;
- municipal boundaries;
- other.
When establishing town planning regulations, the following are taken into account:
- actual use of the territory and construction sites;
- combination of different types of use on one plot;
- allotment functionality;
- types of territoriality zones;
- protection of objects related to cultural heritage.
Urban planning documentation applies to land and construction sites located in the same zone.
What categories are there?
In addition to the category of “land of settlements”, there are others, which are designated depending on the permissible activities on the land. Obviously, the site cannot be used in parallel :
- for growing forests,
- railway laying,
- wheat growing,
- construction of a multi-storey residential complex.
There is a legislative division of land categories in order to:
- to delimit the possibilities of land use,
- minimize harmful consequences,
- provide the necessary procedures for the protection and renewal of land.
more about the different categories of land here.
- Agricultural land is the most valuable. These fertile areas are intended for cultivating crops and raising livestock. First of all, they are allocated for farming, and the rest - for other purposes.
- water fund lands - the bottom of reservoirs and lands occupied by technical and other water-related structures.
- reserve lands - empty lands on the territory of the state, the use of which requires a change in category.
All ways to find out the category of a land plot are described here. The simplest of them is by cadastral number.
Areas for individual housing construction
Individual housing construction (IHC) is one of the types of permitted use of settlement lands. The construction of buildings intended for the residence of citizens is permitted on sites within residential zones (clause 5 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). The construction of such facilities is carried out in accordance with accepted designs and is subject to SNiP.
On lands for individual housing construction, it is permitted to build a house whose height above the ground does not exceed three floors for members of the same family to live in. The use of the property as a hotel, hostel or similar public needs is unacceptable. In the area adjacent to the house, cultivation of cultivated plants for personal use is provided. Surplus products can be sold privately, but the controlling government agencies will not allow the organization of greenhouse farming on a personal plot.
At the same time, the cost of plots for individual housing construction is much higher than the price of areas allocated for growing agricultural products or constructing dacha buildings. Therefore, before purchasing, you need to clearly prioritize the use of the land - permanent residence throughout the year or gardening during the warm season with overnight stays in a less-than-comfortable home.
Construction permit
In the context of individual construction, a permit is a document confirming the compliance of the construction project proposed by the owner of the site with the following standards:
- Territory surveying project;
- Sanitary and engineering construction rules;
- Town planning regulations (only for settlement lands).
Permission is required to build a house on a plot for individual housing construction or private plots.
It is important to know that to build housing on a plot for gardening or summer cottage farming, permission is not required (clause 17 of Art.
51 GrK).
To obtain permission to build within the boundaries of a personal plot, the owner must contact the local administration at the location of this plot (clause 4 of article 51 of the Civil Code). The permit is issued by the town planning committee on the basis of an application, a sample of which can be downloaded here.
The application must provide the following information:
- Name of the filing authority;
- Full name, contact details and passport details of the applicant;
- Address landmarks of the building site and its area;
- Type of right to use the site;
- The name of the architectural firm that developed the construction project;
- Information about the project (number of floors, material, area, etc.).
For an architectural firm, you must also indicate the license number and legal address.
According to paragraph 7 of Art. 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the following documents are attached to the application to the town planning committee:
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate on the origin of the right to the plot;
- Urban planning plan of the territory;
- Construction project;
- Situation plan showing communications;
- Plan for connecting the future home to communication networks;
- Work plan of the construction contractor;
- Conclusion of the BTI engineering commission.
After submitting the application, it is reviewed within 30 days, after which a construction permit is issued or refused.
Reasons for refusal may be:
- Inconsistency of the type of permitted land use of the site with the purposes specified in the application (construction);
- Inconsistency of the presented project with territorial zoning;
- Failure to comply with project manufacturing standards.
When preparing a project yourself, you may miss the rules regarding the location of communications. Architectural companies compare the project with the communication plans of the surrounding area and calculate the construction in accordance with accepted standards.
VRI classifier
All types of intended purposes of ZNP are reflected in the classifier. Classifier – document No. 709 dated September 30, 2015, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. But since the composition of these lands is multifunctional, they collectively include a purpose that corresponds to other categories of land plots, in accordance with clause 1 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
| Category of land by intended purpose | code | Type of permitted use |
| Lands of settlements | 2.0 | Residential development |
| 2.1 | Low-rise residential development | |
| 2.2 | Household private plot | |
| 2.3 | Blocked residential development | |
| 2.4 | Mobile housing | |
| 2.5 | Mid-rise residential development | |
| 2.6 | Multi-storey (high-rise) residential development | |
| 2.7 | Maintenance of residential buildings | |
| 3.0 | Public use of capital objects. construction | |
| 3.1 | Utilities | |
| 3.2 | Social service | |
| 3.3 | Household services | |
| 3.4 | Healthcare | |
| 3.5 | Education, enlightenment | |
| 3.6 | Cultural development | |
| 3.7 | Religious development | |
| 3.8 | Public management | |
| 3.9 | Ensuring scientific development, scientific activities | |
| 3.10 | Veterinary service | |
| 4.0 | Entrepreneurship | |
| 4.1 | Business management | |
| 4.2 | Shopping centers | |
| 4.3 | Markets | |
| 4.4 | The shops | |
| 4.5 | Banks and insurance organizations | |
| 4.6 | Public catering | |
| 4.7 | Hotel service | |
| 4.8 | Leisure and entertainment | |
| 4.9 | Transport service | |
| 5.0 | Rest and recreation | |
| 5.1 | Sport | |
| 5.2 | Natural and educational tourism | |
| 5.3 | Hunting Fishing | |
| 5.4 | Berths intended for small vessels | |
| 5.5 | Golf and horse riding courses |
DNP
A dacha non-profit partnership is a variant of organizing a dacha farm, created by the owners themselves (more than three founders are required) to resolve various economic and social issues.
DNP lands are a territory allocated by the district administration or the body responsible for land distribution at the disposal of dacha partnerships for the management of dacha, gardening, and vegetable farming and the construction of dacha houses. These are dacha cooperatives!
To organize a partnership, two types of land can be allocated:
- related to the territory of a populated area;
- being agricultural land.
In any case, DNP lands must be:
- mastered no later than three years after the formation of the partnership;
- built up with summer dachas or permanent houses (this type of dacha farming requires mandatory construction on the site).
The territory of the DNP, which belongs to a populated area, is practically equal to plots for individual housing construction, because:
- located near roads;
- is located near power lines, water supply, sewerage, gas pipelines, etc.;
- Permanent registration in a built house is allowed;
- next to the dacha partnership there is the entire infrastructure of the settlement: hospitals, kindergartens and schools, shops, etc.;
DNP plots, as a rule, have a lower value than individual housing construction or SNT lands because they are less fertile.
However, if the partnership is located in a city or town, the value of the land increases.
Status of dacha partnership lands
At the time of registration, the lands of a dacha partnership receive the status of a legal entity, which can be a plaintiff or defendant in court and is obliged to assist partnership members in solving social and economic problems.
Each DNP has property:
- private (individual) - plots for which partnership members made entrance fees and then privatized or bought out;
- general, created through contributions from participants: roads, common fences and gates, playgrounds and recreation areas, waste collection areas, fire-fighting structures, etc.
All property in common ownership belongs to the DNP as a legal entity.
The main body of the DPP is the board. This body is authorized, without the consent of the other members of the non-profit organization, to carry out various actions on behalf of the entire dacha partnership. Decisions made by the partnership board are very difficult to challenge.
You can get a plot in the DNP only by becoming its member. To do this, you need to write an application to the DNP administration. A new participant must pay an entrance fee, which is the fee for obtaining a plot. After some time, the site can be privatized.