Maintaining your own (or so-called personal) subsidiary plot allows you to grow vegetables and fruits on your land to meet the food needs of the family.
The allocation of land for this type of farming is carried out in accordance with clearly defined requirements. These requirements are prescribed in legislation and ensure the regulation of relations between the land owner and the state. Therefore, before taking a plot for private household plots, it is important to understand the nuances of its use.
Private household plot lands: definitions and concepts
You can find the legally established definition of personal subsidiary farming in Federal Law No. 112-FZ. It outlines the scope of responsibility and the conditions for allocating plots for this type of management.
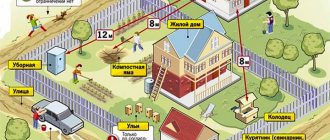
According to the law, no more than 0.5 hectares of land are allocated to a person for running a personal subsidiary plot. Products grown on it should be used only for household needs. If, as a result of the full production cycle, there remains a surplus of products, then the law allows it to be sold, and there is no need to pay taxes for this volume.
The activities of farmers on personal plots are not considered entrepreneurship. And products produced on the sites are not subject to income tax after sale. This is the main feature of private household plots.
True, there is a nuance in this context - the owner and members of his family can directly cultivate the land; hired workers cannot be involved.
Permitted use of land owned by citizens
Among land plots owned by citizens and located within settlements and territories of SkhN, one of the most common VRIs are “for personal subsidiary plots” (hereinafter referred to as private household plots) and “for individual housing construction” (hereinafter referred to as individual housing construction).
Private plots
Targeted exploitation of land plots with permitted use “for running private household plots” involves conducting economic activities, primarily aimed at the production of agricultural products that satisfy the personal needs of the owner (or user) of the land and his family members for food.
The targeted exploitation of private plots is determined by the following criteria:
- Lack of hired workers - all activities are carried out by the owner of the farm and his family.
- Products are manufactured exclusively for the personal use of the owner and his family.
- The activities carried out are not aimed at making profit.
Despite the above criterion, the law does not prohibit the sale of any volumes of surplus manufactured products.
According to the law, plots of private household plots can be located on lands classified as agricultural land or settlement lands. Depending on the land category, plots of private household plots, in turn, are divided into:
- Household plots are plots located within the boundaries of settlements. In addition to conducting permitted agricultural activities on personal plots, the construction and operation of permanent buildings intended for residence of members of the same family, as well as the construction of real estate for auxiliary purposes, are permitted.
- Field plots are plots located on agricultural lands outside settlements; the intended use of these plots involves exclusively agricultural activities. The construction and operation of any permanent buildings is strictly prohibited, however, the construction of non-permanent buildings and auxiliary structures is permitted: sheds, barns, cellars, etc.
Individual housing construction plots
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, individual housing construction sites can only be located within populated areas, within the boundaries of functional zones for the corresponding purpose. VRI of individual housing construction plots involves the construction and operation of residential buildings designed to accommodate members of one family.
Financing of construction is carried out at the expense of the owner of the site.
The main criterion for the intended use of an individual housing construction site (subject to the absence of a built and put into operation real estate property) is the ongoing construction of a residential building. According to the law, construction work must begin within three years from the date of registration of ownership of the site. The construction work that has begun is determined by the presence of a laid foundation for the future building on the site.
On individual housing construction plots, it is prohibited to conduct subsidiary farming, as well as similar types of economic activities.
Advantages of running private household plots
To organize a personal subsidiary plot, the owner does not need to go through a number of bureaucratic procedures and registrations. All records are maintained through local authorities through the voluntary provision of information. Consequently, the owner is exempt from tax reporting.
Among the advantages of private household plots it is also worth noting:
- availability of benefits when allocating land to certain categories of citizens;
- no personal income tax, even if you sell the rest of the products;
- there are no obligations for mandatory contributions to the pension fund, the decision is made by the owner individually;
- tax benefits for equipment used for cultivating land, etc.
Personal subsidiary farming can also be compared with a peasant farm (peasant farm), with the exception of restrictions on the volume of allocated land.
Disadvantages of maintaining private household plots
- The main disadvantage of this type of farming is the limitation on the size of the allocated land. It is impossible to obtain more than the legally established 0.5 hectares;
- When owning a plot of private household plots, it is quite difficult to obtain loans and subsidies - due to the fact that activities on such plots are not considered entrepreneurial, and there is no taxation;
- Products grown on the site cannot be certified and do not receive declarations of conformity.
In addition, there are restrictions on conducting activities. If you need a small area for growing agricultural products for sale, it is better to consider the option of running a peasant farm (peasant farm). In pursuit of tax benefits, you may encounter a number of nuances that will hinder farming activities on a legal basis.
What benefits can be obtained on the lands of private household plots?
There is a state program in Russia that provides for the allocation of funds for the development of personal subsidiary farming. Persons who own an allocated plot of land can receive it. Money can be spent on purchasing:
- seed material;
- animals;
- stern;
- bees;
- tools for working on the ground.
One of the conditions for receiving social assistance is that the family has income at the subsistence level. In addition, the area must be allocated legally.
A big advantage in terms of allocating benefits will be the absence of arrears in payments for land. The amount of allocated assistance is determined individually. Only municipal authorities can influence the process.
Simply submitting an application is not enough to receive funds. The interested party must provide the commission with a clear plan for the use of financial assistance, indicating the intended use of the funds.
After receiving the money, you can spend it exclusively for its intended purpose, in accordance with a pre-approved plan. And, on the fact of spending funds, you need to constantly report. If property or equipment is purchased with social assistance money, they must be insured.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main disadvantage of field sites is the ban on the construction of permanent buildings and structures . Facilities for agricultural production have limited options for use.
Thus, a barn built on a field plot can be used for storing agricultural equipment, but not for storing grown crops.
The question of supplying electricity and gas to the field site also remains open.
It is possible to install communications directly to ensure agricultural production, but not for electrification and heating of a change house and garage.
Advantages
Despite all the restrictions in terms of construction, field plots also have advantages over household plots:
- low land tax rate;
- impressive size;
- no personal income tax on the amount of profit from sold agricultural products produced on private plots.
The fact of production on private plots of land must be confirmed by a certificate from the municipal authority responsible for registering private plots.
Taxes when running private household plots
In fact, products produced from personal subsidiary plots are exempt from taxes. However, in this case, it is worth monitoring compliance with a number of conditions established by law:
- to conduct business, the owner does not hire hired help and thus does not put production on stream;
- the allocated land does not exceed 0.5 hectares.
The last factor is regulated, since the local administration may decide to allocate a larger plot for farming.