Labor legislation establishes the standard working time - 40 hours per week. In my opinion, limiting working time and establishing its norm is a key achievement of civilization. Just remember how many upheavals, riots, and revolutions occurred precisely because of excess working hours!
What is the essence of working time? According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties. ILO conventions describe this time to workers more categorically: this is the time during which the worker is at the disposal of the employer.
But doesn’t the current situation with working hours remind you of the plot of science fiction novels? When deviations from the norm were at first rare occurrences, then more frequent, and then it was difficult to meet the norm, because deviation from it sooner became the norm. So it is here. Non-standard working hours, non-standard ways of providing rest, unusual forms of employment, etc. are increasingly being used. Let's answer some common questions regarding non-standard working hours.
Article 91. Concept of working time. Normal working hours
Working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to working hours.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
Normal working hours cannot exceed 40 hours per week.
The procedure for calculating the norm of working time for certain calendar periods (month, quarter, year), depending on the established duration of working time per week, is determined by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing state policy and legal regulation in the field of labor.
(Part three introduced by Federal Law dated July 22, 2008 N 157-FZ)
The employer is required to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee.
Article 92. Shortened working hours
Shortened working hours are established:
for workers under the age of sixteen - no more than 24 hours a week;
for workers aged sixteen to eighteen years - no more than 35 hours per week;
for employees who are disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 hours per week;
for workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions - no more than 36 hours a week in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations.
(Part one as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ dated June 30, 2006)
The length of working time for students of educational institutions under the age of eighteen, who work during the academic year in their free time from school, cannot exceed half of the norms established by part one of this article for persons of the corresponding age.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
This Code and other federal laws may establish reduced working hours for other categories of workers (teaching, medical and other workers).
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
What are the possible options for providing a lunch break?
As you know, lunch is provided lasting from 30 minutes to 2 hours, every 4 hours of work (Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, there are not many employers who set specific lunch hours (for example, from 13 to 14 hours), more and more often employers set the duration of rest and the period in which it can be used (for example, 1 hour during the period from 12 to 15 hours) . Lunch time is not paid. In addition, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of taking food at the workplace if the work does not allow the employee to take a break. In this case, lunch time is included in working hours and is paid.
There is also a division of the working day into parts (in cases where the break is more than 2 hours), which is used, for example, for drivers (Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 93. Part-time work
By agreement between the employee and the employer, a part-time working day (shift) or a part-time working week can be established both upon hiring and subsequently. The employer is obliged to establish a part-time working day (shift) or part-time working week at the request of a pregnant woman, one of the parents (guardian, trustee) with a child under the age of fourteen years (a disabled child under the age of eighteen years), as well as a person carrying out caring for a sick family member in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
When working part-time, the employee is paid in proportion to the time he worked or depending on the amount of work he performed.
Part-time work does not entail for employees any restrictions on the duration of annual basic paid leave, calculation of length of service and other labor rights.
Article 94. Duration of daily work (shift)
The duration of daily work (shift) cannot exceed:
for workers aged from fifteen to sixteen years - 5 hours, for workers aged from sixteen to eighteen years - 7 hours;
for students of general education institutions, educational institutions of primary and secondary vocational education, combining study with work during the school year, from fourteen to sixteen years old - 2.5 hours, from sixteen to eighteen years old - 4 hours;
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
for disabled people - in accordance with a medical report issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
For workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, where reduced working hours are established, the maximum permissible duration of daily work (shift) cannot exceed:
with a 36-hour work week - 8 hours;
with a 30-hour work week or less - 6 hours.
A collective agreement may provide for an increase in the duration of daily work (shift) compared to the duration of daily work (shift) established by part two of this article for employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, subject to the maximum weekly working hours time (part one of Article 92 of this Code) and hygienic standards for working conditions established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
(Part three as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
Duration of daily work (shift) of creative workers of the media, cinematography organizations, television and video crews, theaters, theatrical and concert organizations, circuses and other persons involved in the creation and (or) performance (exhibition) of works, in accordance with the lists jobs, professions, positions of these workers, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations, can be established by a collective agreement, a local regulatory act, or an employment contract.
(Part four was introduced by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006, as amended by Federal Law No. 13-FZ of February 28, 2008)
Article 95. Duration of work on the eve of non-working holidays and weekends
The length of the working day or shift immediately preceding a non-working holiday is reduced by one hour.
In continuously operating organizations and in certain types of work, where it is impossible to reduce the duration of work (shift) on a pre-holiday day, overtime is compensated by providing the employee with additional rest time or, with the employee’s consent, payment according to the standards established for overtime work.
On the eve of the weekend, the duration of work in a six-day work week cannot exceed five hours.
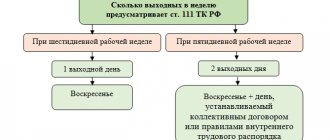
What is rest time according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
By rest time, labor legislation understands periods when an employee is released from work duties and has the right to use them at his own discretion. These are the following breaks:
- during the work shift (lunch, special: provided within the framework of the law to nursing women, workers in cold working conditions for heating, air traffic controllers);
- between shifts;
- weekend;
- holidays recognized as non-working days by labor legislation;
- vacations: annual paid and additional.
Article 96. Night work
Night time is the time from 22:00 to 6:00.
The duration of work (shift) at night is reduced by one hour without further work.
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
The duration of work (shift) at night is not reduced for employees who have a reduced working time, as well as for employees hired specifically to work at night, unless otherwise provided by the collective agreement.
The duration of work at night is equal to the duration of work during the day in cases where this is necessary due to working conditions, as well as for shift work with a six-day work week with one day off. The list of specified works may be determined by a collective agreement or local regulations.
The following are not allowed to work at night: pregnant women; workers under the age of eighteen, with the exception of persons involved in the creation and (or) performance of artistic works, and other categories of workers in accordance with this Code and other federal laws. Women with children under three years of age, disabled people, workers with disabled children, as well as workers caring for sick members of their families in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation , mothers and fathers raising children under the age of five without a spouse, as well as guardians of children of the specified age, may be involved in night work only with their written consent and provided that such work is not prohibited to them for health reasons in accordance with the medical report. At the same time, these employees must be informed in writing of their right to refuse to work at night.
(as amended by Federal Laws dated July 24, 2002 N 97-FZ, dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ)
Procedure for night work of creative workers of the media, cinematography organizations, television and video film crews, theaters, theatrical and concert organizations, circuses and other persons involved in the creation and (or) performance (exhibition) of works, in accordance with the lists of works , professions, positions of these workers, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations, can be established by a collective agreement, a local regulatory act, or an employment contract.
(as amended by Federal Laws dated June 30, 2006 N 90-FZ, dated February 28, 2008 N 13-FZ)
Employee rest during a 24-hour shift
An important point in this case is that a shift schedule is established for employees. This means that general weekends such as Sunday and Saturday, provided that a shift falls on them, will not count as days off. At the same time, the peculiarity is that the daily schedule can be used not only in relation to shift work. This can also be done using a flexible schedule. This is stated in the provisions of Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The legislation allows for shifts lasting 24 hours. Such a schedule indicates that the citizen performs the duties of his position during the day, without leaving work. This period includes both daytime and nighttime. This schedule has significant differences from the schedule of those workers who work in a 5-day work week.
When such a schedule is established, the employee will rest during the days following the shift. In addition, rest periods are also set during the shift. When establishing rest, the provisions of labor legislation must be taken into account. It says that the duration of rest between shifts should be 2 times longer than the shift itself.
Article 97. Work outside the established working hours
(as amended by Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006)
The employer has the right, in the manner established by this Code, to involve an employee in work beyond the working hours established for this employee in accordance with this Code, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, collective agreements, agreements, local regulations, employment contract (hereinafter referred to as the working hours established for the employee):
for overtime work (Article 99 of this Code);
if the employee works on irregular working hours (Article 101 of this Code).
Payment for processing
Work beyond the established working hours and on weekends must be paid in accordance with Article 153 of the Labor Code at a double rate. This rule applies to any remuneration system.
It is acceptable to provide a day of rest (time off). In this case, the employee may be given a choice: time off or double tariff. In the first case, the day off worked is paid in the usual manner (single payment).
Double payment is calculated without taking into account bonuses, compensation and other incentive payments.