Home / Divorces / Divorce with three children
Divorces with children are one of the most complex categories of cases in family law. Such cases are complex not so much from a procedural point of view as from a legal one, since they require solving several problems at once: divorce, respect for the rights of children and the rights of parents, and sometimes the division of property. Often the divorce process is complicated by resolving all sorts of disputes between spouses. Therefore, such marriages are dissolved only in court - the court takes into account all the circumstances and characteristics of family relationships.
How divorce occurs in a large family, what its procedure and legal consequences are - the article is devoted to these issues.
How does divorce happen with three children?
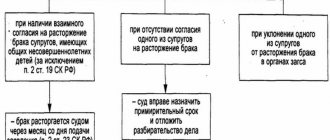
If there are children, divorce is possible only in court - such a restriction is justified by the need to protect children's and parental rights.
Exceptions (divorce administratively through the registry office) are allowed only in the following cases:
- children - not joint (born in previous marriages of the husband and/or wife) or already adults (clause 1 of article 19 of the RF IC). If there is a mutual desire to dissolve the marriage, a married couple may divorce in the same manner as a childless couple;
- the husband or wife, by a court decision, was declared dead, incompetent, and sentenced to imprisonment for a term of 3 years (clause 2 of article 19 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). These circumstances must be documented (court decision, sentence, certificate from the Federal Penitentiary Service or the police) - then you can divorce unilaterally, regardless of the presence of children and the consent of the spouse.
As for the standard divorce procedure through the court, procedurally, a divorce with three children is almost no different from a divorce with two children or one small child. Read more about the procedure below.
Features of divorce with children
If you have children, you can only get a divorce through the court (Article 21 of the RF IC). Both spouses—husband and wife—have the right to file for divorce.
The number of children does not matter, only the age of the children is of fundamental importance. If at least one child is under 1 year of age, or if the wife is pregnant, the husband cannot file for divorce without first obtaining the wife's written consent. Divorce will not take place without the wife's consent. Thus, the law takes care of protecting the rights of the most vulnerable and unprotected social groups - pregnant women, women with small children . It is noteworthy that the wife’s rights to divorce her husband are not limited - she can initiate divorce proceedings both during pregnancy and during the first year of the baby’s life.
Simultaneously with the divorce, the court must consider related issues, such as...
- Child support;
- Place of residence of children;
- Division of property acquired over the years of married life.
At the same time, the law allows spouses to resolve these issues independently: by signing an agreement - by virtue of paragraph 1 of Art. 24 IC RF. An oral agreement or a written document that contains the agreements of the husband and wife on all controversial issues is submitted to the court for consideration. If the court does not find any violation of the interests of the husband, wife, or children in the document, it will approve it, and the document will acquire the legal force of a court decision. Spouses can agree on everything they deem necessary, for example, with whom the children will live, how often the children will meet with the one who will live separately, what amount of money is needed to support the children, how the children should be raised, etc.
If no disputes arise between husband and wife, the court will dissolve the marriage quickly, without additional proceedings.
If all these issues cause conflicts between the spouses, and it is not possible to reach an agreement, they will have to be referred to the court . During the trial there will be...
- decided where and with whom the children should live,
- alimony was collected for children and for the mother (if the children are under 3 years old),
- The joint property of the spouses is divided.
Expert opinion
Semyon Frolov
Lawyer. 7 years of experience. Specialization: family, inheritance, housing law.
Dividing joint property in divorce proceedings is not necessary unless it is urgent. It can be done …
- peacefully (without trial)
- in separate proceedings - before or after a divorce, thereby reducing the duration of the divorce process.
Likewise, no one prohibits the spouse with whom the children will live from filing a lawsuit to collect alimony after the divorce. The second spouse can challenge the place of residence of the children, the amount of alimony payments, the order of raising children, even their own paternity. All of these issues can be addressed after the divorce.
Property disputes, along with disputes about children, are one of the main reasons for the long and grueling process. If the spouses have the goal of a quick divorce, it is advisable to agree on all controversial issues before the start of the trial. Or postpone it - for quality preparation and consideration in a new trial. An experienced family law attorney can help them with this.
Divorce procedure with children
The divorce procedure in court is provided for by the provisions of the Family and Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation.
To begin the divorce process, spouses need to follow the following sequence of actions:
- Preparation of a parental agreement on the place of residence of children, on the procedure for paying alimony, on raising children (if the divorcing spouses can resolve these issues peacefully);
- Preparation of a statement of claim;
- Collection of documents;
- Notification of the second party (defendant) - innovation from October 1, 2021;
- Filing a claim in court (choosing a judicial body - according to the rules of jurisdiction);
- Waiting for a summons with the date and time of the first court hearing;
- Attending court hearings;
- Waiting for the court decision to come into force;
- Registering a divorce with the Civil Registry Office and obtaining a divorce certificate;
- Execution of a court decision (in terms of payment of child support, change of place of residence of children).
Where to file a claim?
The choice of the judicial authority in which to file a claim for divorce depends on several factors:
Presence (absence) of disputes between husband and wife:
- To a city or district court - if, simultaneously with a divorce, it is necessary to resolve controversial issues (about the division of jointly acquired property worth more than 50 thousand rubles, about choosing a place of residence for children, about paying maintenance for children);
- To the magistrate's court - if you only need to dissolve the marriage, and all controversial issues are resolved by the spouses in a contractual form;
Place of residence of the spouses:
- The plaintiff spouse must file a claim at the defendant’s place of residence (Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- The plaintiff spouse can file a claim at his place of residence if, simultaneously with the demand for divorce, he makes a demand for payment of alimony, and also if he lives with minor children or is sick (you need to present a supporting document to the court), and for this reason cannot visit the court at the place of residence of the defendant spouse (clauses 3-4 of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- Spouses can agree on the choice of a judicial body (Article 32 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
State duty
To file a claim in court you need to pay a state fee:
- 600 rubles – for divorce (paid by the plaintiff);
- from 400 to 60,000 rubles (calculation of the exact amount is based on the price of the claim) - for the division of joint property;
- 150 rubles - for collecting alimony for children, or 300 rubles - for collecting alimony for children and a mother on maternity leave (paid by the defendant if the court satisfies the request).
- 300 rubles – for determining the place of residence of children.
For state registration of divorce in the registry office:
- 1300 rubles (both parties pay 650 rubles).
Additional expenses: notary services (certification of power of attorney, divorce consent, other documents) or legal consulting services.
Payment is made strictly according to the details provided by the judicial authority or the registry office. You can make a payment at the cash desk of any bank or post office. The receipt must be kept and attached to other documents - without it, administrative and judicial services will not be provided.
Divorce proceedings in the presence of children under age
The process of divorce with minor children in 2021 is not surprising, if not commonplace.
The country's Prime Minister even made a proposal to increase the state fee for divorce from 650 to 30,000 rubles. Such a measure may perhaps stop some families on the verge of separation, but it is unlikely to affect the reason for the increase in the number of divorces in the presence of minor children. The modern rhythm of life has significantly changed the vector of development of relations between a man and a woman. Now spouses are more like partners for a certain period of life, rather than two parts of a single whole, where the man is the breadwinner and protector, and the woman is the keeper of the hearth. Wives and husbands have the opportunity to earn the same amount of money, choose their goals and lifestyle, and are often unable to sacrifice their own interests for the sake of their son or daughter, even if they are minors. There are situations when separation is really necessary and it will only be better for the children if the parents are happy separately, but often the spouses simply do not want to make an effort and try to save the family.
The process of divorce in the presence of minor children is a psychologically difficult story not only for parents. It is no less difficult for their children to understand and accept the fact that mom and dad no longer love each other and will never live together. The separation of spouses is often a trigger in the development of teenage depression and inappropriate actions of a son or daughter. Yes, and raising a child for one parent is not so easy - no matter how much the second one strives to participate in the upbringing process, he will not be able to do it in a way that he would not be able to do before, if only because he lives separately.
Statement of claim
The statement of claim cannot be drawn up in any order. If the claim contradicts the rules established by Art. 131 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the court may refuse to accept the document to the plaintiff and return it to correct the deficiencies.
A properly prepared claim must be legally competent, accurate, written in an official business style, with a concise statement of all essential circumstances. The structure of the claim should be as follows:
- Name, address of the judicial authority;
- Plaintiff's details: full name, address, contacts;
- Defendant's details: full name, address, contacts, INN, SNILS, etc.;
- The price of the claim (indicated if the claim contains property claims that are subject to monetary valuation, for example, for the division of property acquired during marital life or debt obligations);
- Title: “Statement of claim for divorce, for the choice of place of residence for joint minor children, for the collection of alimony for the maintenance of joint minor children, for the division of joint property and debts”;
- Descriptive part: date of marriage, circumstances of married life, reasons for divorce (reasons for divorce can be specified at length, without intimate details, for example, the impossibility of living together due to disagreements, loss of trust, alcohol abuse);
- Information about children: full name, date and place of birth, place of residence;
- The justified position of the plaintiff (or the agreed position of the parties) regarding the children: the place of residence of the children after the divorce, the procedure for maintaining the children;
- List of disputed property (indicating the estimated value) that is subject to division, the position of the plaintiff (or the agreed position of the parties) regarding the division of joint property;
- Petition part: claims for divorce, choice of place of residence for joint children, collection of child support, division of joint property;
- List of attachments (documents confirming each of the above circumstances);
- Date of;
- Plaintiff's signature.
The sample presented for review is suitable for a simple, fairly typical divorce situation. But in practice, divorce is often complicated by abuse, disputes over children, savings, debts, real estate documents, etc. Spouses who do not have a legal education and experience in litigation will find it difficult to prepare a competent claim and collect a strong evidence base to defend their interests in court. That's why we offer you help. Consultation with our lawyer is free. Write or call the hotline to get advice on your divorce case.
Is it possible to get a divorce if the child is under 1 year old in Russia?
There is no direct ban on divorce if the child is under 1 year old in the Russian Federation. The Family Code establishes only certain restrictions on divorce initiated by the husband.
Article 17 of the RF IC clearly establishes the consent of the wife as a mandatory condition for such a divorce.
This provision implies a forced restriction of the husband’s right to unilateral divorce, since many married couples are experiencing a severe crisis after the birth of a baby and cannot adequately assess the situation. Men lack female attention, women are overloaded with caring for the baby - the result of this combination of circumstances is divorce.
If the marriage is dissolved on the initiative of the mother, then no restrictions are provided.
Divorce cases are not that complicated from a lawyer’s point of view, but they can deprive you of a lot of time and nerves due to the flurry of emotions and passions that reign in the court hearing. Consult our lawyers completely free right now.
Documents for divorce
Art. 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation contains a rule for the formation of a package of documentation. According to this rule, every circumstance that is indicated in the claim as an argument or evidence must be documented. Based on this, an approximate list of attachments to the divorce claim will look like this:
- Copies of the statement of claim (according to the number of participants in the process);
- Copies of passports;
- Copies of children's birth certificates or passports;
- A copy of the marriage certificate (if the certificate is lost or hidden, you can obtain a certificate or a duplicate from the registry office);
- A copy of the marriage contract (if concluded);
- Parental agreements on place of residence, maintenance of joint children, division of property (if they were concluded in writing);
- List of joint property that must be divided, title and valuation documents for each property;
- Written consent for divorce (may be required if the wife is pregnant or gave birth to a child less than 1 year ago);
- Other documents: police reports, court decisions, medical certificates, characteristics, income certificates, bank statements of expenses, promissory notes, loan or deposit agreements, etc.
- A document confirming payment of the state duty.
Divorce in court: what difficulties may arise
Sometimes difficulties may arise during the trial. For example, the defendant ignores the meeting. But if he was notified about it and did not appear, this will not be an obstacle to the divorce. Also in such a situation, you can send a representative of the spouse or request that the meeting be temporarily postponed. But for the petition to be granted, it is necessary to find significant evidence justifying the absence of one of the parties.
If the spouse has disappeared and cannot be notified of the proceedings. But if you send a notice to his known address, the person will be considered to have been notified. If it is not clear where a person is in principle, you can use the judicial practice of declaring him missing. In this case, divorce in court will not be required - you can complete the proceedings in the registry office.
Sometimes a spouse may be pregnant by someone else. But you cannot divorce her without her consent until the child is one year old. You need to get permission, and only then begin the procedure. If you have lost your marriage certificate, before going to court, you need to restore it by requesting another document from the registry office.
The court may not accept the application. This usually happens if you haven’t paid the state fee, indicated impossible requirements, or filed a claim in the wrong court. If the case is not reviewed and returned, its deficiencies will be indicated. They need to be eliminated, and then the case must be returned for consideration.
Who will the children stay with?
In most cases, after a divorce, children live with their mother. But this does not mean that fathers cannot claim to live together with their own children - such cases are also known in judicial practice.
Expert opinion
Dmitry Nosikov
Lawyer. Specialization: family and housing law.
If the parents themselves have agreed with whom the children will remain, there will be no proceedings on this issue. It is enough to indicate this in the statement of claim or attach to the claim a separate written agreement on the place of residence of the children. The court will review the parental agreement in a court hearing, and if no violations of the rights of children or parents are found in it, it will be approved by a court decision.
If parents cannot voluntarily decide who their children will stay with, they will have to sort it out in court. The court takes into account the following factors:
- Children's attachment to mother and father;
- Financial situation of mother and father;
- Housing and living conditions of parents;
- Lifestyle, moral qualities of parents;
- The opportunity to provide children with all the conditions for development, upbringing, and education;
All of the above factors are considered by the court as a whole; none of them is decisive for the court. For example, if the father’s income is higher than the mother’s income, this does not guarantee him an advantage, but if the mother is characterized negatively (does not care about the children, leads an immoral lifestyle, suffers from alcohol addiction), the father has a greater chance of receiving a positive court decision (see . “In what case can a child be left with his father during a divorce”).
When making a decision, the court is guided not only by the documents submitted by the spouses (certificates, characteristics), but also by the conclusion of the guardianship and trusteeship authority - it is drawn up based on the results of a study of the living conditions of the mother and father.
The court also asks the children which parent they want to live with? The children are interviewed in the presence of a teacher. Children can express their point of view, and if they are already 10 years , it will definitely be taken into account by the court in conjunction with other factors.
Since there are three children, the court can divide them between the parents, but only taking into account the children’s attachment to their parents and to each other.
Example After a divorce, the court left her 5-year-old twin sons with their mother. An adult 16-year-old daughter expressed a desire to stay with her father, since his apartment was located next to a college and a sports club, and her mother changed her place of residence and moved to the suburbs.
If the court finds it difficult to accurately determine the degree of attachment and closeness of children with their mother or father, it may order a psychological examination . Its result is announced at the court hearing and serves as one of the factors, and in some cases, the decisive factor for making a decision.
Young children (under 3 years old) will most likely stay with their mother; children over 14 years old can decide for themselves which parent they want to live with.
Through the registry office
In case of mutual consent, a divorce from a husband without children goes through the registry office, the documents are submitted to this body. You will need to write an application according to the specified template and attach to it the documents required for the procedure. The first meeting after filing the application must take place with the participation of both parties. If the other party does not have the opportunity to personally attend the meeting, then he must contact a notary who will help draw up and certify the letter. The contents of the letter serve as confirmation of the spouse’s consent to the divorce. At repeated meetings, if citizens so desire, one citizen may be present.
Alimony in divorce with three children
The parent with whom the children remain has the right to demand child support for three children. You can also collect alimony for yourself, for example, if the mother (less often the father) is caring for a child under 3 years old or a disabled child under 18 years old).
For the maintenance of three children, 50% of the official income is required to be paid (Article 81 of the RF IC).
If the parent’s income is unofficial or unstable, the court assigns a fixed amount of alimony. Its size must be a multiple of the subsistence level in the region in which the children live, and must ensure the same level of financial status of the children. A fixed amount is also assigned to the disabled parent.
Amounts of money must be transferred monthly , in the form of cash (with the obligatory execution of a receipt) or by wire transfer to the bank or postal account of the parent with whom the children live.
The amount of alimony ordered by the court may subsequently be increased or decreased in the event of changes in the marital or financial situation of the parents. As practice shows, such a claim can be brought to court...
- mother - if the father got a job with a higher salary, but continues to pay a meager amount of child support;
- father - if a child was born in a new family, if he lost his job or his financial situation worsened.
Division of property if there are three children
The division of marital property is a process that is not necessarily related to divorce, since it can occur both before the start of the divorce process and after its completion. There is time for this: the statute of limitations for the division of disputed marital property is 3 years , and this period is counted not from the moment of divorce, but from the moment of violation of property rights (Clause 1 of Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Expert opinion
Semyon Frolov
Lawyer. 7 years of experience. Specialization: family, inheritance, housing law.
The number of children also does not in any way affect the order of division of property between spouses, since children do not have the right to claim the property of their parents, just as parents do not have the right to claim the children's property. Everything that was purchased for the children during the marriage remains the property of the children and is transferred for use to the parent with whom the children will live. This can be not only children's clothing and toys, but also furniture, sports equipment, musical instruments, as well as funds in accounts opened in the child's name.
What is subject to division? Everything that was acquired during married life (except for gratuitous transactions - donation, privatization, inheritance), regardless of whose money this or that property was purchased with, in whose name it was registered. This could be real estate, cars, cash savings, land, household items, jewelry, and debts. The shares of the spouses are equal, regardless of his contribution. Even if one of the spouses did not work at all, but raised and raised children, ran a household, and made other contributions, he has the right to claim half of the joint achievements and bears half of the joint debt obligations - by virtue of Art. 38 RF IC.
Example After marriage, the wife quit her job and devoted all her time to housekeeping and then caring for a newborn child. A few years later, two more children were born into the family. Only my father worked. The family purchased furniture, household appliances, and a car on credit. After the divorce, the wife filed a lawsuit for the division of household furniture and household appliances. The court divided the joint property into equal shares, and the car loan debt was also divided equally.
A fair exception may be made to the rule of equal marital shares. The spouse with whom the children will live may demand an increase in the share in the interests of the three children - in kind or in the form of monetary compensation. In contrast, the share of one of the spouses can be reduced if misbehavior in the family, dependency without good reason, or unreasonable expenses contrary to the interests of the family are established (Clause 2 of Article 39 of the RF IC).
Lawyers often advise dividing property in separate court proceedings in order to dissolve a long-term marriage, or even better, without a trial, on your own, by preparing and signing (in the presence of a notary) a voluntary agreement on the division of property.