According to FSSP statistics for the first half of 2021, about 1.2 million judicial acts on the collection of alimony were being executed by the FSSP. In approximately half of all these cases, alimony providers are in arrears. Of course, not all of them are malicious non-payers of alimony, but there are also plenty of them, and many of them are far from poor people. Therefore, the state provides for enforcement measures that are used in extreme cases. Let's figure out what alimony debt can lead to imprisonment and when you should be wary.
How to go to jail for alimony: conditions for establishing such a punishment
The impending prison sentence acts as a catalyst for the negligent parent.
Not every debtor can be imprisoned for failure to pay alimony, since life is unpredictable, and a person can lose his job at any moment. Therefore, judges consider each case in connection with the individual circumstances under which they may be imprisoned for unpaid alimony. According to Article 157 The Criminal Code of Russia allows a persistent offender to be imprisoned for alimony if his behavior confirms the signs of a crime. The question arises: can they be imprisoned for failure to pay child support? A malicious evader who should be given a prison sentence for failure to pay alimony is considered to be a person who commits the following actions:
- non-payment of money for more than 4 months;
- change of place of registration;
- concealment of income;
- being wanted due to non-payment;
- reluctance to look for work;
- formation of significant alimony debt.
How long can you avoid paying child support?
The answer is simple. Not at all. If there is a court order to assign alimony, then it must be paid on time. Otherwise, the state, that is, bailiffs, will monitor compliance with these obligations.
Alimony is paid at least once a month, so delay for a longer period will be considered a violation of the law. If alimony payments are late, the debt will constantly grow, and when it comes to the bailiffs, you will have to pay additional fines.
Concealment of income, change of registration - can they be sent to prison for alimony in these cases?
The case of concealing income is not the only one in our country. Can they be jailed for failure to pay child support? More than half of the male population in Russia receives wages “in envelopes,” which is an offense.
Those debtors who want to hide from bailiffs sin by changing their place of registration. Will there be a prison sentence for failure to pay child support in this case? Finding a person wanted for non-payment of alimony is one of the signs of a malicious offense. The reluctance to look for work becomes the fact that a person deregisters himself from the Social Employment Center. The reasons for this action can be different: working conditions are unsuitable, low wages, lack of prospects for further growth.
Questions for a lawyer
Alina S. Tell me, do they go to prison for low alimony payments if the father has been on the employment exchange for more than a year and only pays a thousand rubles from benefits?
Lawyer's answer: No, in such cases the payer cannot be held liable. He conscientiously pays alimony from his available income, and the low amount of alimony is not a reason for prosecution.
Marina K. How long can I be imprisoned if my ex-husband has not helped our child for three years? They collected alimony, but I have the sheet and the bailiffs have nothing. Can he be imprisoned in this case?
Answer: No, they cannot. Enforcement proceedings are closed if you have the sheet, so you can only insist on collecting alimony for the previous period. The father of the child cannot be held accountable in this situation.
Counteractions to repay alimony debt
In case of prolonged evasion of the alimony payer from fulfilling his duties, a significant debt arises. Can a court impose a prison sentence for failure to pay child support? This depends on the length of the non-payment period. According to Art. 157 of the Criminal Code of Russia, the period allowing a similar preventive measure to be applied to a debtor, under which it is possible to be imprisoned for alimony, becomes 3 months.
Many malicious debtors, in order not to be imprisoned for alimony, buy toys, food and wardrobe items for their child. Judicial workers cannot imprison fathers who have taken the path of reform. Judges can imprison you for non-payment of alimony if the moment of non-payment of alimony is notarized and appears several times in the court case. The plaintiffs have a question: can they be sent to prison for failure to pay alimony for the maintenance of an heir on time? This issue, which concerns the period of non-payment, is regulated by the administrative-legal method in the form of charging a penalty.
Valid reasons for non-payment of alimony
Failure to pay alimony violates the rights of the recipient, regardless of the reasons. In some cases, this can lead to significant consequences, but the payer’s intent is not always present. To correctly analyze the legal situation, it is necessary to find out why alimony is not paid.
There are two options:
- willful non-payment
- non-payment for valid reasons.
The first situation is obvious - the payer knows that he has an obligation and simply ignores it or completely evades fulfillment (hides, provides false documents, hides his real earnings, and so on).
The second case is less simple, since the degree of validity of the reason cannot always be determined without a thorough analysis of the situation.
The legislator has identified some reasons under which a person cannot be held liable for non-payment of alimony, or the liability can be significantly mitigated.
These include:
- loss of a job and lack of other regular income with obvious attempts to correct this situation (see more about alimony from an unemployed person);
- lack of wages for reasons beyond the control of the person (actual delay by the employer);
- illness or disability that deprives a person of the opportunity to earn money;
- other reasons in which a person is deprived of regular income for reasons beyond his control.
In such situations, if the person is not released from criminal or administrative liability, then late fees may not be assessed.
Cases of punishment of a defaulter under Article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
Cases of punishment of alimony defaulters in the form of imprisonment have occurred in judicial practice. Art. 157 of the Criminal Code of Russia provides for such types of punishment as:
- performing corrective labor for a period of up to 1 year;
- imprisonment for up to 3 months;
- imprisonment for up to 1 year.
In 2021, a person who evades payment of alimony benefits for a long time, up to 12 months, may be sent to prison if the legislation does not change. A judge can put a debtor in prison for a period of up to 3 months for alimony, based on an analysis of the individual circumstances of the defendant’s life. Having a criminal record for non-payment of alimony carries with it a number of unpleasant consequences, such as:
- signing a decree not to leave the country;
- limited ability to travel within one country;
- prohibition from holding leadership positions.
You can be jailed for child support not only for a person who has children, but also for refusing to support elderly parents.
What is considered malicious evasion of alimony payments?
Evasion of payment of maintenance funds should be understood as:
- direct refusal to pay alimony
- failure to inform the bailiff or the person receiving alimony about dismissal
- failure to inform about a new job
- concealing your earnings, including additional earnings or other income
The concept of malicious evasion of alimony payment is not defined in the law and is evaluative. In judicial practice, this characteristic is usually understood as:
- repetition of a similar crime
- evasion of payment despite appropriate warning
- search for a person obligated to pay alimony, etc.
Alimony payers very often hide their income, for some reason they immediately become officially unemployed and have absolutely no property in their property. And the bailiff simply throws up his hands, since he cannot do anything, but in the end - there is a debt, but there seems to be nothing to pay it with, and the question arises: “How to force the draft dodger to fulfill his obligations?” There are ways and let’s look at them individually with the help of our lawyer at the Law Office “Katsailidi and Partners”:
The procedure for bringing a debtor to criminal liability
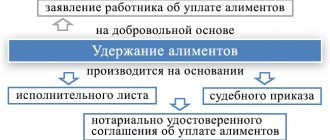
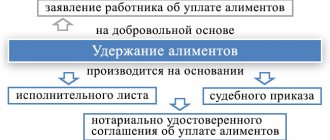
The procedure for bringing a debtor to criminal liability begins from the moment the defendant is brought to pay alimony. A document regulating the payment of alimony, drawn up on a voluntary basis and certified by a notary, acquires the force of a writ of execution submitted to the bailiff service for the purpose of collecting alimony. A lawsuit for child support that is granted by the court ultimately results in the issuance of a writ of execution to the plaintiff.
The plaintiff shows the writ of execution to the employer, who withholds the required amount from wages in favor of supporting the children. The document is also submitted to the bailiff service, which initiates enforcement proceedings. In certain cases, the debtor's account is seized and he may be given a prison sentence for failure to pay alimony.
If the debtor continues to evade the payment of alimony, according to the articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, a fine of several thousand rubles is assessed. A court ruling deciding the case in favor of paying a fine can become significant evidence in bringing the debtor to criminal liability, who may be imprisoned. It became possible to initiate a case to bring the defaulter to criminal liability through bailiffs and by contacting the Ministry of Internal Affairs. The case materials are submitted to the court, and during the consideration of the case, a verdict is made on the guilt or innocence of the person who may be imprisoned.
What happens if you fail to pay child support for a long time?
In practice, administrative and criminal measures are not applied immediately.
In this case, a certain period of time is qualified by its measures of influence.
More than 4-6 months
Thus, if alimony is not paid for up to six months, the bailiff has the right to:
- announce a search for the debtor (if his whereabouts are unknown) and his property;
- fulfill a number of requests to various authorities;
- calculate the penalty that the recipient of alimony may collect.
At the same time, administrative liability may be initiated.
Failure to pay child support for more than a year
Further, when the delay is more than a year, in practice, administrative measures most often begin to be applied, and if they have already been applied, then criminal liability.
Theoretically, they can be used earlier, but the workload of FSSP employees and the lack of knowledge of claimants about their rights slow down the process.
In addition, what bailiffs can do with a defaulter:
- the debtor may be subject to a driver's license restriction;
- travel outside the Russian Federation is limited;
- foreclosure on property to pay off debt.
When can they be charged under 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation?
The basis for prosecution under Art.
5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is non-payment of alimony for more than 2 months from the date of initiation of enforcement proceedings, if the debtor does not pay them for unjustified reasons, violating the requirements of a court decision or alimony agreement. Previously, the bailiff may apply other measures of influence on the debtor:
- Restriction on the use of a special right (driver's license).
- Seizure of bank accounts.
- Wanted notice.
- Ban on leaving the territory of the Russian Federation.
The most important factor for attracting under Art. 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is the intentional nature of non-payment. If the debtor proves that he had valid reasons for the delay, he may be released from liability.
How to avoid paying alimony legally?
Exemption from alimony payments and preparation of a statement of claim
Grounds for exemption from liability
The debtor may be released from liability if the debt arose not through his fault or there are good reasons:
- Serious illness during the period of non-payment, stay for treatment in a medical institution.
- Dismissal due to downsizing or liquidation of an enterprise.
- Difficult family circumstances that require large financial investments.
- Receiving disability.
The list of reasons is not exhaustive. Situations are considered by bailiffs and courts individually. Based on the results, the debtor may be required to repay the debt within the established time frame or pay in installments.
As evidence of valid reasons, you will have to provide a certificate of disability, an ITU conclusion, a certificate from the Employment Center or another document confirming the existence of grounds for exemption from liability under the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Administrative penalties
In July 2021, changes were made to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and a new article was introduced - 5.35.1. It provides for administrative liability of parents who evade paying alimony for minors or disabled children, unless the offense contains elements of a criminal offense.
Stipulated penalties:
- up to 150 hours of compulsory work;
- up to 15 days of administrative arrest.
If the violator cannot be subject to administrative arrest by law, he will have to pay a fine of up to 20,000 rubles.
These persons include:
- minors;
- pregnant women;
- persons raising children under 14 years of age;
- disabled people of groups 1 and 2;
- military personnel, employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and other government agencies.
According to the Russian Federation GD dated December 12, 2014 No. 1358, citizens suffering from severe acute chronic diseases or diseases contagious to others are not subject to arrest.
Even with a one-time failure to pay, the alimony obligee may be held accountable. The reason is non-compliance with the requirements of executive documents (IL). Sanctions are provided for in Art. 17.14 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The debtor faces a fine of 2,500 rubles.
Additional measures
In addition to prosecution under the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, other sanctions may be applied to debtors:
| Measure | Conditions of use | Additionally |
| Restrictions on the use of a driver's license | Applies to debt amounts greater than RUB 10,000. at the initiative of the claimant or bailiff. The resolution is sent to the traffic police, loses relevance after the debt is disputed or repaid | The measure is not prescribed if using a car is the only way to earn alimony |
| Ban on leaving the Russian Federation | Imposed on debts of RUB 10,000 or more. The FSSP resolution is sent to the border service authorities | Cancelled upon full repayment of debt. Without this, the person obligated for alimony will not be able to pass border control. |
| Wanted ad | Debt is more than 10,000 rubles. Copies of resolutions are sent to all government agencies. Further proceedings are carried out at the FSSP at the place where the debtor was found, the documents are transferred there | Cancellation is allowed upon complete liquidation of debts or discovery of the debtor |
Arbitrage practice
If there are clear signs of an administrative offense and there are no valid reasons, as a result of legal proceedings, debtors are most often prosecuted under Art. 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, and the statements of the claimants or the petitions of the bailiffs are satisfied. Confirmation – extensive judicial practice:
- The bailiff drew up a report and submitted it to the court. The man did not pay child support because he did not know what details to use to transfer it. By a resolution of July 13, 2021, in case No. 5-471/2017, he was found guilty and sentenced to 20 hours of mandatory work.
- The man did not pay child support, believing that unemployment was the basis for non-payment. By resolution of July 13, 2021, in case No. 5-602/2017, compulsory work was imposed for 80 hours.
- The man periodically did not pay child support in full, and a debt arose. Based on the Resolution of July 6, 2017, in case No. 5-571/2017, he was arrested for 15 days.