There are situations in life when parents cannot bear such a burden as raising children, and therefore decide to abandon them. Some do this immediately at the birth of the child, while others, for a number of reasons, do this until the child reaches adulthood.
It is not legally possible to simply abandon a child. There is not a single article in the legislation of the Russian Federation that would regulate the process of unauthorized refusal to support and raise a child. Therefore, further in the article the legal basis for abandoning children, the reasons and consequences of such a decision will be considered.
What does the law say?
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 938-81-90 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 467-32-77 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 301-79-36 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
The legislator does not provide for the existence of such a thing as voluntary relinquishment of parental rights. However, despite its absence in legislative acts and regulations, the procedure is implemented quite often.
Having written a waiver, you should not consider yourself an absolutely free person, since the obligations to support the child will be maintained in any situation.
Regarding the renunciation of parental rights, the rules that are inherent in the deprivation of parental rights will apply, namely Article 69, Article 70, Article 71 of the RF IC.
Thus, the legislator equates the two procedures.
At the same time, you need to remember that the application for deprivation of parental rights must have a certain format and meet all the requirements:
- How to register it is stated in Article 131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- But the trial accompanying the deprivation of parental rights will be held with an eye to the requirements of clause 4, clause 1, Article 23 - Article 24 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
These legislative acts will help resolve the issue of how a father can refuse voluntarily.
Article 106 of the Criminal Code: up to 5 years in prison
The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation has Article 106, which deals with the killing of a newborn by a mother during childbirth or after childbirth. Lawyers do not really define the exact meaning of the word “after”, but a child is considered “newborn” up to 4 weeks; experienced lawyers interpret the legal term “after birth” as “one day”.
Every year, courts in the country consider several hundred such cases, but it must be taken into account that there are cases when the crime remains unsolved. It must be remembered that in the article murder is understood not only as direct actions leading to the death of an infant. For a defenseless baby to die, it is not at all necessary to use violence or run to the nearest trash container: it is enough to simply stop feeding. From a legal point of view, there is no difference.
When investigating cases under Art. 106 a psychiatric examination of the mother is mandatory. If the murder was committed during childbirth, if the woman was in a state of passion and did not realize the danger of her actions, if the mother was sick with schizophrenia or had previously been diagnosed with other mental illnesses, you can count on the leniency of the court.
By the way, if the birth went well, but the mother still committed a heinous crime some time later, the murder can be reclassified under Article 105 “murder,” which entails a much more severe punishment. The investigation is always interested in motives and the presence of malicious intent: rest assured, this will still come up during the investigation.
The punishment is terrible. The child cannot be returned. From the point of view of any religion, the grave sin of infanticide has been committed; all human laws, not only legal ones, have been violated. Don’t commit a crime: you can abandon your child officially and legally: you won’t get anything for it, at least here on Earth, but in heaven – who knows?
Concepts
In general, there is no such thing as a voluntary renunciation of parental rights in any legislative act.
However, this does not mean at all that it does not exist. It’s just that the state equates this procedure with the usual deprivation of parental rights.
The parent has many rights and responsibilities towards the child, approved and enshrined at the state level.
Among them are:
- priority in the educational process;
- representing the interests of the child in any instance;
- the right to live together with a minor;
- the right to receive all information regarding the child from educational and medical institutions.
Please note that the automatic termination of these obligations will occur when the child reaches the age of 18.
An exception will be situations when a parent voluntarily renounces his rights and transfers them to another person. In this case, there must be a notarized refusal.
Abandoned does not mean abandoned. The problem of runaways.
Childbirth without documents (passports) still occurs, and the mother can at least call herself the Queen of England so that no one finds out about the birth of the baby. In the maternity hospital they cannot refuse to attend a birth. Even if there is no insurance policy, the woman in labor will be placed in the infectious diseases department just in case and will receive medical care.
Such mothers usually choose a very irrational strategy: they simply run away from the maternity hospital “in a robe and slippers”, without signing any statements, because they cannot: the mother’s identity is not verified, there are no documents. The child seems to exist (he’s lying there and is capricious), but according to the law, it’s as if he doesn’t exist.
Thus, the fugitives “suspend between heaven and earth” the newborn legally, preventing his adoption from the point of view of the law. What's the baby's fault? So that no one finds out? Everything will open up anyway, sooner or later.
Causes
Sometimes you may encounter a situation where the head of the family oppresses his loved ones so morally and physically that they are ready to ask him to renounce paternity.
This is one of the key reasons for relinquishing parental rights.
Another popular reason is the situation when a mother and child remarry, and her new husband expresses a desire to take on all the care of the baby by adopting him.
However, this requires that the father whose name is written on the birth certificate renounce his paternity.
Documentation required for registration of refusal
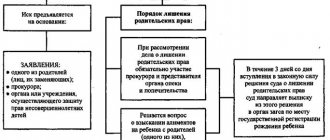
Having decided to renounce parental rights and responsibility for caring for the child, the mother must send a corresponding application to the local state guardianship and trusteeship service. In this appeal, she should indicate her desire, give consent to the adoption of her children by other parents, and provide convincing arguments explaining such an intention. To confirm the circumstances that led to the abandonment of the baby, one or more official documents are required:
- to justify a difficult financial situation - a certificate from the place of work about the amount of wages or a document from the employment center confirming that the woman is registered as unemployed;
- as evidence of unfavorable living conditions for living together with children - a corresponding conclusion on the results of a housing inspection by local authorities;
You need to provide certain documents: a certificate from your place of work, a doctor’s report, etc.
- in case of dysfunctional family relationships - confirmation from social services or local internal affairs bodies;
- if the mother or her child has serious illnesses, a medical report from the relevant medical institutions;
- if the mother has an alcohol or drug addiction that interferes with the further upbringing and care of the child, it is necessary to present a certificate stating that the woman is registered with a drug treatment center.
Based on the reasons specified in the application and supporting certificates, the guardianship authorities will decide whether to grant or deny the mother’s request to leave the child. If necessary, the guardianship service may request additional information and documents about the circumstances that prompted the woman to commit such an act.
Important! However, the final decision depriving the mother of parental rights is made by the judiciary.
The guardianship authorities and the court directly participate in the decision-making process
Legal consequences
The main consequence of relinquishing parental rights will be the complete termination (cancellation) of all legal and legal aspects that originally arose on the basis of the relationship of two people.
The consequences may be the following:
- Lack of educational function regarding the child of the abandoned parent.
- The impossibility of providing for any interests of the child in a variety of organizations.
- Cancellation of all benefits that were paid to the parent for the maintenance of the child.
- Impossibility of inheritance.
However, financial responsibility to the baby will be fully preserved.
This means that the parent who has waived his or her rights will still be required to take an active role in child support matters. Consequently, the refusing parent is not exempt from child support, unless, of course, there are any additional agreements between the parents on this issue.
How to arrange child support for parents? Read our material. What to do with the birth certificate? Find out here.
Trial
After the guardianship services consider the mother’s consent to the adoption of her child by other parents, the case with the recommendations of the guardianship authorities is transferred to the local court. If the application with documentation confirming the reasons for the woman’s desire to renounce parental rights meets the requirements established by law, the court will open appropriate proceedings.
During the proceedings, the judge may require additional documents related to the essence of the case. This could be the woman’s characteristics from her place of work, various petitions, certificates from social services, local internal affairs bodies, executive authorities, and medical institutions.
Important! The judge may invite witnesses - relatives, neighbors, work colleagues - to question.
The judge may invite witnesses
Based on the results of consideration of all presented arguments and testimony, a final hearing is held to make a final judicial decision. In addition to the mother, representatives of the prosecutor's office, the state guardianship service, as well as the child's future adoptive parents are required to participate in it. In cases where the case concerns children over the age of 14, they must also take part in the court hearing.
Important! When making decisions, judges must be primarily guided by the protection of the rights and interests of the child.
Voluntary relinquishment of parental rights by father and mother in 2020
The legislator provides for the possibility of voluntary abandonment of a child, which is indicated in the relevant articles of the Family Code.
At the same time, it must be taken into account that in no legislative act there is such a thing as voluntary refusal, therefore, according to all documents, the procedure will be carried out as deprivation of parental rights.
In 2021, there were no fundamental changes in the procedure for renouncing parental rights, however, some new restrictions and requirements appeared, which we will discuss below.
How to do this and where to start?
Since the process of deprivation of parental rights is considered to be a rather complex and problematic procedure, it should begin with a consultation with experienced lawyers and notaries who will tell you how to do everything correctly in the shortest possible time and with an eye to the actual rules of law.
Also, at the initial stage of preparation, you will need to visit the guardianship authorities, who will provide complete and accurate information regarding the further procedure and give recommendations on certain issues that will be raised during further judicial consideration of the case.
Where to contact?
The procedure for voluntary refusal is quite complex from a legal point of view, and therefore it will be necessary to involve not only the courts, but also other bodies and departments, the main goal of which will be to protect the interests of the child and monitor the proper fulfillment by parents of their obligations to the child.
A parent's renunciation of his responsibilities regarding a child can be carried out solely at the request of the father or mother himself.
To relieve yourself of all rights and obligations, you will need to file a claim with the appropriate authorities. The law establishes that the courts, notarial authorities and guardianship and trusteeship authorities will be required to resolve this issue.
Court
All cases, the result of which may be the fact that the child risks being left without the care of one of the parents, are considered in district or regional courts.
The application must be sent to one of the authorities with an eye to the permanent place of residence of the child and the second parent.
If for certain reasons it is impossible to establish the place of residence, then the claim may be transferred to the authority that serves the place of residence of the applicant.
Guardianship and trusteeship authorities
Guardianship and trusteeship authorities in cases of deprivation of parental rights will play more of a consultant role.
The fact is that parents will be required to inform the guardianship authorities about the upcoming judicial procedure for renouncing parental rights. In turn, guardianship staff will conduct a thorough analysis of the situation and prevent situations in which the interests of the child are not taken into account or grossly violated.
In addition, if necessary, you can get detailed advice from the guardianship authorities on how the procedure will be carried out, how to abandon the child without violating his interests in accordance with all legal requirements.
Guardianship authorities will be important during the subsequent adoption procedure. They will not only help speed up the procedure, but will also explain how to receive special benefits provided in our country for guardians and adoptive parents.
It should also be noted that at all court hearings on this issue, specialists from the guardianship and trusteeship authorities will be present without fail as representatives of the state.
Notary
Interaction with notary offices on issues of renunciation of parental rights will be only superficial.
The notary will not make any legal decisions, and his main task will be to provide support regarding the preparation of an application to the court and its compliance with all legal requirements.
Registration procedure
The specific procedure for formalizing a refusal to exercise parental responsibilities will directly depend on the situation that takes place and the individual parameters of the case.
Given that there are some differences between different processes, it is recommended to first consult with a qualified lawyer and notary, who will help determine the exact procedure and give valuable advice on how to avoid additional difficulties and conflicts.
In favor of the second parent
The transfer of all parental functions in favor of the second parent is quite common.
Most often, this procedure is carried out to provide the child and his mother with additional government support. These actions provide an opportunity to receive certain benefits.
The initiation of the procedure for voluntary abandonment of a child will be carried out provided that the interests and rights of the minor are taken into account and are not violated in any way.
Also, the second parent must confirm that despite the refusal, he will continue to financially support his child.
The principle of filing a claim here will be standard. It will be necessary to indicate a request to the court to deprive parental rights and indicate the reasons why such a decision was made.
In favor of the adoptive parent
One of the most common reasons for renouncing parental rights is the expressed desire of another person to adopt a child and assume all parental responsibilities.
A similar situation occurs when the child’s parents are divorced and the mother is planning to remarry.
In order to renounce parental rights in favor of another person, the parent will have to write a statement renouncing parental responsibilities and give official consent to the subsequent adoption of the child.
This way he will avoid any responsibility to his child, including a financial one.
For a disabled person
Alienation of parental rights can only be done through the court. According to the law, a disabled child must be placed in a specialized medical institution.
At birth
Sometimes the abandonment of a child can be recorded at birth.
Then the mother will need to write a written consent to waive her rights to him and the subsequent transfer of the baby to a specialized institution.
Six months from the date of writing such a paper, the question of deprivation of parental rights will be raised, and from that moment the child can be adopted by other persons.
Step-by-step instructions for establishing paternity in court are in our article. Is it possible to apply for alimony without marriage? See here.
How long does it take to restore a marriage certificate? Find out here.
Is the child's consent required?
Article 57 of the RF IC states that the court is obligated to take into account the wishes of the child and his opinion if by the time the issue of deprivation of parental rights is raised he is 10 years old.
Package of documents
The submitted statement of claim must be accompanied by relevant documentation, which may include:
- information about the conclusion and subsequent dissolution of marriage relations;
- documentation certifying the birth of the child;
- information on alimony obligations, in particular, a court decision to withhold alimony or a copy of a peace agreement on the payment of alimony between parents;
- court decision regarding deliberate evasion of alimony obligations;
- a description from the child’s place of study, which fully reflects the emotional state of the child and the impact on his psyche of the decision of one of the parents to renounce parental rights;
- information about the child’s place of residence;
- act of living conditions of the child;
- characteristics of parents from neighbors, guardianship authorities and work.
In addition, the court may require additional documentary information, which will notify the plaintiff when considering his application.
Sample consent (application)
A sample consent can be viewed at the notary's office with the help of the court where the statement of claim is sent.
In general, all general requirements approved at the highest legislative level are met here.
Thus, the consent must be complete and take into account all the nuances, the text must not contain any grammatical or punctuation errors, and in addition, the document must bear a notary’s visa, which makes it legally significant.
Example of drawing up a consent:
Application for refusal in favor of the other parent
Trial in court
The court will be the main authority entrusted with the duty to consider an application to remove from a parent his rights and obligations in relation to a minor child.
The trial of the case will take place according to general principles and rules approved at the highest state level.
It is worth noting that the basis for starting a judicial procedure for deprivation of parental rights will be a statement of claim.
It will need to indicate your request to the court to waive parental rights, as well as an indication of the reasons why the user decided to initiate such a procedure.
Jurisdiction
The legislator approved that a claim should be filed based on the place of residence of the second parent. This principle is approved in Article 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
If for some reason it is impossible to establish the actual location of the parent and his place of residence, then filing a claim should be carried out with an eye to the provisions of Article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
Statement of claim
One of the main points when renouncing parental rights will be the preparation and subsequent filing of a statement of claim. It is approved at the legislative level and fully complies with all legal requirements. Special attention is paid to the text of the statement.
Thus, the law requires that the document contain the following information:
- full name of the court that will consider the application;
- personal data of the plaintiff , including his full name, information about registration and place of actual residence: you will need to provide the original passport and its notarized copy;
- consent to renounce parental responsibilities regarding a minor child;
- argumentation of the reasons that prompted the plaintiff to apply for relinquishment of parental rights: in addition to the circumstances, here you will also need to indicate information about the child, namely his full name, date of birth and other data;
- consent to the adoption of a child by another citizen in the foreseeable future;
- name of the locality , date of writing the paper and personal signature of the applicant.
Decision making procedure
The algorithm of actions for a user who wants to terminate his responsibilities regarding a child will be as follows:
- Drawing up a document certifying the parent’s consent to the adoption of a child by another person.
- Drawing up an application and collecting all the necessary documentation, consulting with a specialist on this issue.
- A visit to a notary’s office and certification of the application, after which it will need to be submitted to the courts.
- Attending all court hearings on this issue and waiting for the final verdict of the court.
- After receiving the final court decision, you will need to go to the registry office and make adjustments to the child’s personal documentation.
Consequences
Deprivation of parental rights will entail a number of irreversible consequences, including:
- prohibition on participation in the child’s educational process;
- prohibition on entering into inheritance and the right to receive inheritance, except in situations where the user’s name is indicated in the will;
- loss of the parent's right to demand financial support from his child for the foreseeable future;
- inability to give consent to any transactions with real estate that belongs to the child;
- a ban on reclaiming a child from citizens who do not have the right and grounds to retain him;
- impossibility of receiving state benefits or benefits provided for the child by the state.
Measures to combat the phenomenon of mothers abandoning their children
In order to reduce the number of cases when a mother decides to leave her newborn baby in the maternity hospital, a special preventive program has been developed, the implementation of which is entrusted to doctors of maternity hospitals and representatives of social care services. Such prevention is based on methods of psychological persuasion and the provision of material assistance. Doctors and social workers should try to convince the woman of the recklessness of her action, to help her understand all the negative consequences both for the future life of an abandoned child and for the state of her own psyche.
Psychologists, doctors, and social workers try to convince the woman that her action is reckless
The program consists of three main stages. At the first stage, doctors must respond in a timely manner to the mother’s decision not to take her baby from the hospital. The guardianship service must be notified of this desire immediately. Before social workers arrive, doctors should try to dissuade the woman from wanting to give up the child. This must be done taking into account the individual characteristics of her character, the possible influence of postpartum stress on the psyche of the woman in labor.
Important! If doctors’ attempts to convince the woman do not lead to the desired result, the next stage of preventive action begins.
At the second stage, social service workers with an experienced psychologist come into action. They must assess the psychological state of a woman who has just given birth, and find out in detail the reasons and circumstances that prompted her to abandon her newborn baby. At the third, decisive stage of the program, representatives of the guardianship authorities must take all available means of assistance that will allow the mother to believe in the possibility of a full life with her child.
A conversation between a woman and a psychologist is required: perhaps she suffers from depression and cannot make sober decisions at the moment
Such support includes such measures.
- Providing financial assistance in the form of basic necessities for the baby - hygiene products, baby food, clothing.
- Help in solving everyday problems.
- Providing legal support in obtaining child benefits, various benefits, petitions, appeals to local executive authorities in order to improve housing conditions.
- Psychological assistance in overcoming postpartum stress or depression, uncertainty in one’s ability to raise and raise a child.
The state provides support to women who wish to take such a step
If all attempts to convince the mother to leave her baby are unsuccessful, social service employees must take measures to protect the rights and interests of the child. It is necessary to find out whether the mother has relatives who can be entrusted with the maintenance and care of the baby. The most acceptable option would be to register the baby in the name of the father or grandparents. Growing up with close relatives will give your child a chance to grow and develop in a real family.
Important! If there are no such close people or they categorically refuse to accept the newborn, social workers register the abandoned baby in an orphanage.
Nuances
A claim for voluntary relinquishment of parental responsibilities can only be filed by a certain group of persons, namely:
- by the child himself, upon reaching the age of 18;
- parents whose names are indicated on the child’s birth certificate;
- the guardian of the parent if he is a disabled person or has limited legal capacity, as well as the guardian of the child himself.
The court is obliged to take note of the application and schedule a trial.
However, in 2 situations the claim will be guaranteed to be rejected:
- If a child was born through the IVF procedure, and the woman has written consent from the man to use his biological material.
- If the child’s father was aware that he was not his biological parent, but despite this he agreed to have his name entered on the birth certificate in the “father” column.
If the renunciation of parental rights occurs on the basis that the man is not the biological father of the baby, which he found out completely by accident and has evidence in the form of a DNA test, then the court will decide to cancel his paternity, and he will not be assigned financial responsibilities providing for the child.
Further responsibilities of a parent
If the court upholds the claim for relinquishment of parental rights, then the parent will retain only one obligation related to the financial support of the child.
But even here there are some peculiarities. So, if the child’s mother remarried and her new husband is ready to adopt the child, then after completing the procedure, the obligation to provide financial support for the child will be canceled, and all parental responsibilities will be transferred in full to the adoptive parent.
Subsequent adoption
You can adopt a child only after the temporary restrictions are lifted.
The legislator has established that the adoption procedure can be started after 6 months from the announcement of the court decision on deprivation of parental rights.
If at the time of adoption the child is 10 years old, then in accordance with Article 132 of the RF IC it will be necessary to obtain his consent to the procedure.
In general, subsequent adoption will be marked by several fundamental points:
- The procedure itself will take into account the state requirements outlined in Article 125 of the RF IC.
- You can find out the list of all interested parties who can influence the final decision from the text of Article 127 of the RF IC.
- Adoption is possible only with the voluntary consent of the parents and this requirement is enshrined in Article 129 of the RF IC.
However, the state provides for a number of situations when parental consent for adoption is not required.
All cases falling under the exception are listed in Article 130 of the RF IC and Article 71 of the RF IC.
You will find the grounds for deprivation of parental rights in our article. What is the state fee for changing your last name after marriage? Find out here.
Is it possible to restore rights?
It is likely that a parent who voluntarily abandoned his child decides to restore his rights and wants a decision in favor of the guardian.
The state provides such an opportunity, but with an eye to the fact that restoration does not contradict the interests of the child and in no way violates his rights.
If the court determines that restoration will entail certain negative consequences for the child, the procedure will not be implemented.
In general, the procedure for restoring parental rights will take place in accordance with the provisions of Article 72 of the RF IC.
Should I pay child support?
Child support obligations will be maintained in any case, even despite the renunciation of parental rights.
The legislator initially assumes that in relation to his child, a parent deprived of paternity must fulfill material maintenance obligations.
And the withholding of alimony for children who have not reached the age of 18 will be carried out according to the principles specified in Article 80 of the RF IC.
A decision to refuse to pay alimony can only be made in a situation where a written agreement is concluded between the parents indicating the fact that there are no material claims for alimony against the second parent.
Regarding adult children, the payment of alimony payments will be maintained if the child is disabled due to his or her inability to work. Or is in dire need of financial support.
If the child is subsequently subject to the adoption procedure, then, according to Article 120 of the RF IC, the responsibilities for his maintenance will be transferred to the adoptive parent, and the parent deprived of his rights will not be required to pay alimony, except for the situations specified in Article 137 of the RF IC.
Legal consequences for mothers who abandon their child
Regardless of the voluntary or forced registration procedure, the legal consequences will be the same for all women who abandon their children - they lose parental rights to the child they abandoned. The law deprives mothers of the following opportunities:
- educate or in any way influence the further upbringing of your child;
- a woman will not be able to receive various benefits and allowances related to the birth and care of children;
- the mother does not have the right to demand maintenance or financial assistance from her grown children in cases of illness, loss of ability to work, or reaching old age.
If a child is abandoned, the mother is completely deprived of parental rights.
According to legislative norms in the family sphere, the presence of parental rights in citizens is determined by the factor of kinship. Legally formalized renunciation of family ties entails the deprivation of a woman of the full scope of rights to a child provided for by law. At the same time, she must perform maternal functions and childcare responsibilities until the court makes an appropriate decision to terminate such responsibilities.
Important! Until the child reaches adulthood, the mother who abandoned him is obliged to pay alimony in the amount established by the judicial authorities.
Alimony obligations will cease to apply only if the child is officially adopted by another family, to which the responsibilities for his provision and maintenance will be transferred. Refusal to pay child support will result in its collection by force.
Before the child is adopted by another family, the mother is required to pay child support.
It should be noted that Russian legislation does not provide for direct criminal liability for abandoning one’s children. However, this does not mean that women can arbitrarily abandon their children with impunity. For example, leaving it on the street, throwing it to other people, which, unfortunately, is practiced by mothers with low moral qualities.
Important! Such actions can be classified by law enforcement agencies as facts of child abuse and even deliberate attempted murder. All of this may result in severe criminal penalties.
Judicial and foreign practice
When considering cases of this category, the court will need to take into account many parameters, in particular:
- What does the child himself think about the deprivation of parental rights and the impossibility of further participation of the second parent in his upbringing.
- Was the issue of alimony obligations previously considered, and whether serious conflicts arose in this area.
- Is there a user who is ready at any time to adopt a child left without the care of a father or mother?
- Under what circumstances did the refusal of parental responsibilities occur?
In general, analyzing judicial practice in Russia and other countries, we can conclude that it is almost identical.
Any state sets the interests of the child as its priority and is interested in the child growing up in a full-fledged family.
That is why the process of deprivation of parental rights will take into account many factors.
Moral and legal aspects
In general, society has a negative perception of mothers abandoning their children. However, in an era of constant economic crises and the leveling of family and moral values, public censure has ceased to serve as an obstacle to a woman’s decision to abandon her child. Nevertheless, the state is making every effort to combat this phenomenon and protect the rights of children.
When legally registering a refusal, it is necessary to be guided by the norms of Article 129 of the RF IC. It defines a woman's decision to give up her child as consent to his adoption by other people. The Code provides for the conditions and a certain procedure for the implementation of such an intention. Situations where the consent of his parents is not required for adoption by other people are regulated by Article 130 of the Family Code.
Important! In any case, until a court decision, the mother bears full responsibility for the life and health of her children.
Until a court decision, the mother cannot abandon the child and must bear responsibility for his life and health.
In addition to the Family Code, when considering a case related to a mother’s desire to refuse further maintenance, education and care of her children, judges must take into account the recommendations of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 44 dated November 14, 2017. This document provides explanations to the judicial authorities on the procedure for applying legislative norms when resolving disputes about restrictions or deprivations of parental rights, protecting the interests and rights of children in cases of immediate threat to their life or health.
Amount and procedure for calculating alimony payments
Many women are interested in how much money will be withheld from the mother? In a situation where a woman left her child in a maternity hospital, the general rule applies: for one child you will have to pay a quarter of the income, for two children - 33%, and for three - half of the salary.
It should be noted that many women who leave their children in maternity hospitals do not work at all.
In this case, the court has the right to establish a fixed amount of money or oblige the payment of alimony based on the average salary in the country. In this case, we can conclude that even if there is no money, you will still have to pay.
It will not be possible to evade the alimony obligations imposed by law. The latter protects the rights and interests of children.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!