All people are probably familiar with the most basic rules of inheritance - property is transferred either according to a will, and in the absence of a will, it is divided between family members in equal shares.
But this is just a theory; in practice, everything may turn out differently.
It is important to take into account the persons to whom it is necessary to transfer part of the inherited property, regardless of the opinion of the heir. These persons will be able to receive part of the inheritance starting next 2021. They were determined by court decision.
From 2021, pre-retirees have a mandatory share in the inheritance
In December 2021, the Federal Law on a mandatory share of inheritance for citizens of pre-retirement age was adopted. He introduced an additional rule into the 3rd part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in order to eliminate possible negative situations of pre-retirement age and inheritance.
The essence of the new guarantee for pre-retirees
Here's what else you need to understand about pre-retirees and inheritance. The generally established retirement age has been increased since 2021. Accordingly, the age at which these heirs acquire the right to an obligatory share will also increase. In particular, this may include:
Important! The inheritance agreement may contain a clause regarding the executor. After the death of the testator, the executor has a number of obligations of both a property and non-property nature, which the testator will secure in this inheritance agreement.
On June 1, 2021, the federal law of July 19, 2020 No. 217-FZ “On Amendments to Article 256 of Part One and Part Three of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation” comes into force; in essence, these are amendments to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in sections about inheritance.
About innovations
Each of the spouses at any time and even after the death of the other spouse has the right to cancel the joint will and dispose of the property at its own discretion. When performing these actions and in the event that the spouses are alive, the notary is obliged to notify the second spouse in writing.
- an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate as the main document of title indicating ownership of the apartment;
- certificate from the housing cooperative confirming payment of shares for housing;
- information on the market, inventory or cadastral price (at the choice of the successor under the will) of the object of inheritance;
- certificate of payment of property tax (if the apartment was inherited or gifted to the deceased).
The procedure for registering inheritance according to law
To enter into inheritance, a citizen will need:
- Collect a complete package of documents.
- Send the application to a notary.
- Pay the state fee.
After receiving the certificate, property registration is carried out.
Preparation of documents
The first step is collecting documents.
The heir needs to prepare papers in accordance with the list:
- Original death certificate of the testator. It is issued by the civil registry office at the place of residence of the deceased. A death certificate is submitted to the institution to receive it.
- Documents confirming the right to receive an inheritance. This could be a birth or marriage certificate.
- To verify the identity of the applicant, you will need a passport.
- Documents confirming the citizen’s residence at the time of death. These include a certificate of registration.
Submitting an application
Tangible and intangible property is accepted on the basis of an application for inheritance. The form is issued by a notary.
The document must be drawn up in accordance with legal requirements:
- In the upper right corner the address of the notary's office and the notary's details are written down. The last name, first name, patronymic, and registered address of the heir are also reflected.
- The main part reflects information about the deceased and the degree of relationship with him. As well as the wording on accepting the inheritance.
- At the end of the application, the attached documents are listed. The date of preparation and signature of the heir is indicated.
Attention! The application must be sent within six months after the death of the citizen. If the deadline is missed, you must go to court. Otherwise, the property will be transferred to state ownership.
If a citizen cannot send an application personally to a notary, he can submit it by mail, via courier or by e-mail. The signature is certified by a notary or other authorized person who can perform such actions.
Cost of registration of inheritance
The price of the procedure is based on the cost of the state duty, as well as payment for notary services. Costs depend on the valuation of the property and the number of applicants.
The amount of the state duty is specified in Article 333.24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If deposit money is accepted, you will need to pay 0.5% of the full amount. But the payment cannot exceed 20 thousand rubles.
The type of relationship also affects the amount. If the heirs are parents, spouses, children, siblings, then 0.3% of the value of the property is withheld. But the amount cannot exceed 100 thousand rubles. Other relatives will have to pay 0.6% of the amount, but not more than 1 million rubles.
Notary services are paid in accordance with the tariffs. They are approved by Article 22.1 of Fundamentals No. 4462-1, as well as in accordance with the rates of the regional chamber.
Some categories of citizens are exempt from paying state duty or pay a smaller amount.
These include:
- government agencies;
- disabled people (pay 50% of the cost);
- individuals receiving privatized real estate when living before and after the death of the testator;
- incompetent citizens (minor children under guardianship with mental disorders).
The benefit applies only to state fees. Notary services are paid in accordance with the tariffs.
The value of real estate is determined by the cadastral value, and of other property - by organizations that have a license for valuation.
Obtaining a certificate of inheritance rights
After the property is distributed among the heirs, each is issued a certificate. The form of the document was approved by Order of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation No. 313 dated December 27, 2016. If property is distributed in shares, a joint certificate may be issued.
When the document is received, the citizen can use and dispose of the property. When transferring real estate, you will need to reflect the data in a unified federal database. The securities must be transferred to the name of the new owner. The vehicle is registered with the traffic police.
Registration of property rights through the MFC
After receiving a certificate of inheritance in relation to real estate, it is required to register it with Rosreestr. The procedure is carried out directly at the registration authority or through the MFC. The applicant must have a passport and a certificate of inheritance.
When an entry is made in the register, the registrar records ownership. The applicant is given an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, confirming the right to dispose of the property by the heir.
Inheritance by will
As stated in Article 1131 of the Civil Code, a will after the death of the author is annulled by a court decision. The claim can be initiated by relatives of the deceased who do not agree with his will regarding inheritance, or by other persons claiming the inheritance.
Inheritance of land
After the death of the testator, the heirs, in order to accept the inheritance, provide a certain list of papers indicating their rights. It is of an individual nature; the composition of the documents must first be clarified with a notary, because their number and specificity depend on the subject of inheritance.
The definition of gardening and vegetable gardening for the form of partnership is of great importance. Owners of garden plots have the right not only to grow crops on their plots, but also to build permanent buildings suitable for housing.
And the founders of vegetable garden partnerships have the right to build only economic buildings on their plot. Law No. 217 finally gave a clear definition to such buildings.
Outbuildings include greenhouses, bathhouses, gazebos, and temporary huts. According to the law, a house suitable for habitation is considered to be a house that has a foundation and complies with all construction rules and regulations.
This division will greatly simplify the payment of taxes for each type of partnership.
Deadlines for registration of inheritance
Many of our clients are interested in the question: “What is the deadline for registering an inheritance? How long will you have to wait before the successor takes over?”
According to the provisions of the Civil Code, the timing of registration of inheritance after the death of the testator may vary. The time frame is approved by Article No. 1154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Depending on the grounds for registering an inheritance, the entry dates will be as follows
- 6 months after opening of inheritance
- 6 months after the refusal of another heir, or his recognition as unworthy by the court
- 3 months after representatives of the previous queue did not claim their rights
Missed deadlines can be restored if there are valid reasons for missing the deadline.
The new law on summer cottages will come into force on January 1, 2021
Expert opinion
Romanov Igor Severinovich
Lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in developing legal documentation.
According to the new law on dacha farming, which will come into force in 2021, at least 7 founders can create a garden or vegetable partnership. But there are citizens who want to run their own households.
If these citizens use the services together with the founders of the partnership, this means public services - garbage removal, lighting of the territory, security of the site, then they must pay all fees equally with everyone else. For refusal to pay contributions, the meeting of the partnership has the legal right to resolve this issue in court.
According to the new law of 2021, it will become much easier to obtain registration
Deputies of the Federal Assembly, when adopting Law No. 217, significantly simplified this procedure. From January 1, 2021, the founders of garden partnerships that have a building on their site that is suitable for citizens to live in and that complies with the norms and rules of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation can easily register their residence.
To do this, you only need to have a state register of land.
The law provides for two types of inheritance: by will and by law.
In a will, property is transferred in accordance with the will of the deceased. If the deceased did not leave a will, then inheritance occurs according to law.
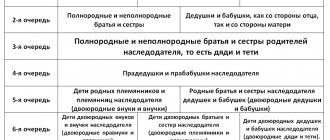
There is a sequence according to which the relatives of the testator can claim the inheritance. There are eight inheritance queues in total.
Who is the first priority heir?
The heirs of the first stage according to the law are Art. 1142 Civil Code of the Russian Federation:
- Children of the deceased.
- Surviving spouse.
- Parents of the deceased.
- Grandchildren and their descendants, entering by right of representation.
Also, along with the primary heirs, the dependents of the deceased enter into inheritance rights. Next, I will talk in detail about each of these categories of assignees. You will learn about all the nuances that they may encounter when confirming their belonging to the first line of heirs.
Which child has the right to inheritance?
All children of a deceased citizen, by law, have equal rights to property.
Children have the right to inherit after the death of their father/mother:
- Those born in marriage for whom paternity has not been disputed.
- Born within 300 days from the date of dissolution/invalidity of the marriage, unless paternity is contested.
- Illegitimate children for whom paternity/maternity has been established voluntarily, with the consent of the guardianship and trusteeship authority or through the court. If the child has not been officially recognized, then his descent from the testator can be tried to be established in court even after death.
- Adopted persons, even if at the time of opening the inheritance the adoption was canceled by a court decision, but has not yet entered into legal force. If a stepson or stepdaughter was officially adopted, they are considered equal to natural children.
- For those born within 300 days of the death of the testator, paternity is certified by a record of marriage with the mother of such heir. If the parents were not married - on the basis of an application submitted to the registry office during pregnancy (during the life of the testator) or in court (posthumously).
- In respect of which the testator was deprived of parental rights or voluntarily renounced them. If the child was subsequently adopted, the court decision on adoption indicates the preservation of rights and obligations in relation to his relatives by origin.
- Wards not included in the circle of relatives, if they lived with the testator for more than 1 year and were supported by him. This applies to disabled children, minors and full-time students (up to 23 years old).
Important! The testator's dependents have the right to enter into inheritance rights along with the first priority.
Cannot inherit:
- Adult children of the testator who maliciously evaded the fulfillment of their responsibilities for his maintenance - such a circumstance must be confirmed in court.
- Children of the deceased who have committed deliberate unlawful acts against the testator or his heirs - the circumstances must be confirmed in court.
- Those given for adoption to other persons - they do not inherit after their biological parents, unless the rights and obligations were reserved for them in the court decision on adoption.
What are the features of allocating a share for minor heirs?
Minors inherit the property of a deceased parent according to the general rules, i.e. in equal shares with other first-line legal successors. The law does not establish any privileges for this category of heirs.
But the registration of the inheritance and the collection of all necessary documents should be handled by their legal representative (the surviving parent, trustee, guardian). With the consent of their legal representatives, minors over the age of 14 have the right to independently accept an inheritance.
In what cases do parents inherit?
The first-degree successors include the parents of the testator:
- Blood - provided that the relationship was formalized during life or established through court after death.
- Adoptive parents - they are equal to relatives by origin.
- Those who have used artificial insemination or embryo implantation are considered biological parents.
- Those who agree to implant an embryo into another woman for the purpose of carrying it are recognized as the parents of the child if the surrogate mother has given her consent to this.
Parents cannot inherit from their children:
- Those who were deprived of parental rights and did not restore them at the time of opening of the inheritance.
- Biological, after their child was adopted by others.
- In respect of which the adoption was canceled in court and at the time of opening of the inheritance such a decision had already entered into force.
- Those who maliciously evaded fulfillment of alimony obligations - removal of such heirs is possible only by court decision.
- There is no information about maternity/paternity in the birth certificate and in the birth register.
On a note. If, by a court decision, the adopted child has maintained a relationship with one of the parents by origin, then after his death this parent will inherit.
What are the features of inheritance by a surviving spouse?
After the death of a husband or wife, according to the law (without a will), the surviving spouse inherits along with other first-degree heirs. But this rule only applies if the marriage is officially concluded, i.e. executed in the manner established for state registration of acts of civil status.
On a note. Marriages concluded outside of Russia between citizens of the Russian Federation are recognized as valid provided that they are concluded in compliance with the laws of the state in which they were registered. The rule also applies to marriages between citizens of the Russian Federation and foreign citizens or stateless persons.
If the spouses lived separately, but their marriage was not dissolved, the right to inheritance is retained. In the event of a divorce through the court, the former spouse of the testator has the right to inherit in the specified capacity, if on the day of opening the inheritance the court decision has not entered into legal force.
In cases where the marriage was “civil”, inheritance relations do not arise by law. In this situation, it will be possible to obtain a share in the property of the deceased only by proving the fact:
- Being dependent on the testator due to incapacity for work.
- Living together with him for the last year.
Please pay attention to the following nuances:
- Same-sex marriages legalized by the laws of other countries do not comply with the family legislation of the Russian Federation and are not recognized as official. Therefore, a union of men or women living together has no legal status—the other has no right to inherit after the death of one spouse.
- In the event of a divorce in court, the former spouse is excluded from the list of first-priority heirs by law. An exception is that the divorce decision did not enter into legal force until the day the inheritance was opened.
- Spouses who die on the same day do not inherit after each other - the inheritance opens after each of them.
- If the marriage was declared invalid, the spouse is deprived of the right to inherit, even if the court decision entered into legal force after the opening of the inheritance.
What is the spousal share and why is it allocated?
All property acquired by spouses during legal marriage and in the absence of a marriage contract is considered their joint property. Each of them is the owner of ½ part, regardless of who paid for the purchases and to whom the ownership was registered. If a marriage contract has been concluded, the share is determined according to its terms.
The right of inheritance belonging to the surviving spouse does not detract from his right to part of the property acquired during the marriage with the testator - Art. 1150 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The composition of the inheritance includes only half (part) of this property, which passes in equal shares to his heirs by law.
If the marriage was not dissolved at the time of the husband/wife’s death, the surviving spouse should:
- First, contact a notary to allocate the marital share.
- Then apply for acceptance of the inheritance.
If the spouses divorced and did not divide the property, the allocation of the marital share is possible only in court.
Important! After the death of a spouse, the marital share must first be allocated, and only then the remaining property must be divided among the heirs. If you ignore the process of allocating the marital share, all property will be included in the inheritance mass and will be divided among the heirs.
When grandchildren inherit first
As independent legal successors, grandchildren cannot claim the inheritance. However, the law provides for such a concept as the right of representation. It applies when the son or daughter of the testator died before or at the same time as him - the right of inheritance passes to his grandchildren and their descendants.
Important! Grandchildren, great-grandchildren and more distant descendants, when inheriting by right of representation, take the place of “retired” heirs, i.e. inherit only the share due to their deceased parent. If there is only one grandson, he inherits the entire share due to his father/mother, and if there are several grandchildren, the parent’s share is divided equally between them.
Which of the dependents of the deceased inherits along with the 1st line
Dependents will receive property on an equal basis with the heirs of the first stage, even if they are not included in it.
The testator's dependents are classified as a special category of successors by law and are entitled to the same share in the inheritance as the heirs of the first stage. This method of entry is most often used:
- Former spouses.
- Cohabitants, so-called "civilian" husbands and wives.
- Children of cohabitants.
- Children who were under guardianship (trusteeship).
- Guardians (trustees) of the deceased.
- Grandchildren with living parents, etc.
In order to claim the inheritance together with the 1st stage legal successors, they will have to prove:
- Your disability.
- Staying dependent on the testator for a period of at least 12 months before his death.
- Living together with the testator for a year before his death - this rule applies only to citizens who do not belong to the circle of heirs by law (stages 2-7).
On a note. Recipients of annuities under a lifelong maintenance agreement with dependents concluded with the testator are not entitled to inherit as dependents.
The following citizens are recognized as disabled:
- Those who have not reached the age of 18 and have not married before reaching adulthood - provided that the day of majority (marriage) came later or coincided with the day of opening of the inheritance.
- Men and women who have reached the age of establishing an old-age labor pension - regardless of their actual ability to work. But provided that the birthday occurred before the opening of the inheritance.
- Officially recognized as disabled children, disabled people of groups I, II or III. Only if disability is established before the opening of the inheritance or on that day. And if it is given indefinitely, until the date coinciding with the day of death or until a later date.
Please note that the fact of dependency can be established both out of court and in court. The notary or the court makes a decision by determining the relationship between the amount of assistance received and the dependent’s own income.
Important! The permanent nature of the assistance suggests that it was not random or one-time, but was provided systematically - it was a constant and main source of livelihood.
Persons who received from the testator:
- Full content.
- Systematic assistance, which was the main, but not the only source of livelihood for this person.
On a note. The legislation does not exclude dependents from having any income of their own - earnings, pensions, scholarships and other payments. When assessing the evidence presented, it will be taken into account whether the amount of the disabled person’s own income was sufficient to meet the necessary needs of life.
Joint will of spouses
- There is no need to divide the property of one of the spouses among other heirs in the event of his death.
- The size of shares in the right of common property can be determined immediately when drawing up the document, and therefore the rule on equal rights to property of spouses can be changed.
- After the death of one of the spouses, it will not be possible to revoke the will at the request of the other party.
- The ability to display in the document the will of both spouses at once, and each one separately.
New law from June 1, 2021
Another change in the legislation is the emergence of the opportunity for a citizen to dispose of property by agreement with the heirs by drawing up an inheritance agreement . This document differs from a will in that it is a bilateral transaction and it may contain conditions, only upon fulfillment of which the inheritance can pass to the legal successor.
Issues and problems related to inheritance of property always cause a lot of controversy and litigation. In practice, there are many examples when the testator’s acquired property goes not to the person with whom he lived for many years, but to a completely different person who happened to be nearby in the last minutes.
And, on the contrary, if the will of the testator was to leave the property to a specific person who was there in the most difficult times, provided assistance, supported, the will was disputed by relatives who did not help during their lifetime. Upon death, they receive most or all of the inheritance.
This process is especially difficult in the segment of any type of business, when you have to wait six months before you have the right to change or adjust anything in a company that has been left without management. The new law on inheritance is designed to simplify the work procedure of notaries and ensure control over the execution of the last will of the testator.
What other changes in legislation are planned?
The new legislation on inheritance is expected to be further refined and additional clauses will be added, for example, such as:
- introduction of a single tariff for notary services for registration of inheritance;
- preparation and issuance by employees of notary offices of a special certificate of inheritance rights, which will indicate not one, but several successors at once.
The resolution with amendments and additions should be issued on June 1, 2019.
The adoption of this bill will enable testators to enter into an inheritance or joint agreement.
Inheritance contract
In this document, the testator will be able to stipulate special conditions that the successor will be obliged to fulfill after receiving the inheritance, for example, to care for the deceased’s pets, preserve and increase his collection, etc.
Features of the inheritance agreement:
- can be concluded with both an individual and a legal entity;
- the testator has the right to indicate in the will the person who will control the actions of the successor. If the condition set by the deceased is not met, the heir is deprived of the property bequeathed to him in court;
- an inheritance agreement, like a foundation, helps the successor to enter into inheritance rights immediately after the death of the testator, and not after 6 months, as in other cases;
- an agreement can be concluded even with a minor with the consent of his parents or guardians;
- if the list of property to be inherited contains real estate, the agreement must be notarized and officially registered;
- if the testator has elderly parents, children or disabled people as dependents, they retain the right to an obligatory share in the distribution of the inheritance;
- If someone’s rights were violated during the preparation of an inheritance agreement, they can be challenged in court both during the life of the testator and after his death.
It happens that a citizen draws up both a will and an inheritance agreement, then the property is distributed according to the latter document, since it takes precedence over the will.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
If the testator suddenly changes his mind, he can subsequently draw up a new will, where a separate clause will stipulate that the inheritance agreement drawn up earlier is now invalid.
Joint agreement
A joint agreement is drawn up by a married couple.
It may include not only common property, but also valuable personal belongings of each spouse. It specifies the shares transferred to the heirs. The document must be certified by a notary, and video recording is allowed during its conclusion in order to prevent forgery and deception. Only spouses who are legally capable and in a legal union can enter into a joint agreement. If the marriage is dissolved before one spouse dies, the will is considered invalid. After the death of one of the testators, it is no longer possible to change anything in the agreement.
All amendments to the law are being introduced to simplify the procedure for obtaining an inheritance and reduce the number of controversial situations leading to litigation. It is important that these changes and additions work not only on paper, but also in real life.
Dear readers, the information in the article may be out of date, take advantage of a free consultation by calling: Moscow +7
, St. Petersburg
+7 (812) 425-62-38
, Regions
8800-350-97-52
Basic principles of inheritance distribution
After the opening of the inheritance, the inheritance is distributed either by law or by will.
In law
If a will has not been drawn up, then according to the law there are 7 main stages. Close relatives and family members have priority rights. The clarity of the transfer of rights from one queue to another and their composition are shown in the picture diagram.
In addition to these main lines, there are additional branches of the right of representation, when the heir by law dies at the same time or before the testator, and his share is inherited in turn.
By will
In the case of a will drawn up and certified by a notary, the deceased can bequeath all property to any of his relatives or strangers. But part of the property is a mandatory share if there are applicants for it. The following are entitled to the obligatory share:
- disabled elderly parents;
- minor unemployed children;
- disabled dependents who have lived with the testator for at least one year.
Attention! In the Civil Code, disabled people of groups 1-3 are considered dependents. Unemployed relatives do not fall into this category.
Third stage
According to the law, heirs of the third stage include full and half-blood brothers and sisters of the testator's parents - his uncles and aunts.
As for cousins (first cousins), these citizens can inherit only by right of representation.
Heirs of the fourth to eighth order
Further, the inheritance queue according to the law is distributed as follows:
- The fourth stage includes great-grandparents.
- to the fifth - children of natural nephews and nieces (great-great-grandsons and granddaughters, or “great-nephews”), as well as siblings of grandparents (great-uncles and grandmothers).
- to the sixth - children of cousins' grandchildren and granddaughters (great-great-grandsons and great-granddaughters), as well as children of cousins and children of great-uncles and grandmothers.
- to the seventh - stepsons and stepdaughters (if they were not adopted), stepfather and stepmother.
- to the eighth - disabled heirs of a citizen who were dependent on him for at least a year, regardless of whether they lived with him or not.
Heirs of the eighth line can present their rights and inherit according to the law together with the heirs of that line who are called to inherit immediately after the death of a citizen, since they have the right to an obligatory share in the inheritance in accordance with Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Entry into inheritance according to the new rules
The innovations in the law on wills are reduced to a simplified registration procedure, which came into force in September 2021. A new concept “Inherited Fund” (NF) has appeared.
The changes affected parts 1-3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Creating a fund eliminates the six-month waiting period.
Unfortunately, today not all legal sources of information adequately explain its purpose and main functions. The result is confusion and substitution of legally significant concepts.
According to the new law on wills, any citizen can create his own NF, with the help of which the deceased’s business, his property, and various types of savings will be managed.
- It is created by the testator at the time of drawing up the expression of will, in which he describes in detail who will be at the head of the organization and manage its activities after death.
- The creator himself approves the Charter.
- Managers are appointed, the role of each person in the organization is outlined, with a detailed description of how to dispose of the property.
- Methods of replenishment and volumes of assets are indicated.
- The validity period of the Fund is established. The execution of the will of the deceased is controlled by the administrators.
Important! All instructions are mandatory. Correction is possible only through the courts, and in very rare cases.
Expert opinion
Romanov Igor Severinovich
Lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in developing legal documentation.
The Foundation, having the status of an organization, also becomes a co-heir with management rights. The rights to the received material assets are claimed:
- creditors of the deceased;
- relatives specified in the will and members of the obligatory share.
This approach preserves assets and the ability to continue the family business if close relatives are unable or refuse.
Fee when registering an inheritance
Another pressing question is how much tax will the successor have to pay to the treasury after he legalizes the right to the property of a deceased relative?
Let’s clarify right away: they pay for the inheritance not taxes, but duties. The tax was abolished in 2006. However, the difference is more relevant for the Federal Tax Service than for the payer.
The state inheritance tax varies in size: 0.3% of the value for close relatives (the first two orders), 0.6% for all others. The following are exempt from duty:
- Persons permanently residing in inherited real estate.
- Minor heirs.
- Incompetent citizens.
- Some preferential categories (veterans, etc.).
If you still have questions on the above topic, the lawyers of the prav.io site will be happy to answer them. Free and paid consultations and assistance in paperwork are available.
Operating principle
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right.
The testator decided and outlined all organizational issues with the NF during his lifetime. After his death, the notary is obliged:
- within three days, submit an application to the Ministry of Justice to open an NF, providing a will as confirmation;
- according to Art. 1154 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, issue all documents of the NF that confirm its legal status within the period specified by law.
According to the new law on wills, the NF must ensure the growth of the estate by applying effective management. Profits from activities are distributed according to the will. The circle of persons was approved by the testator, among whom there may be relatives of any level of relationship, organizations, and employees of the company.
By the way! If the will specifies an unaddressed charity, then the board of trustees independently decides who to pay the money to.
Rights and obligations of heirs
The beneficiary claiming the property acquires rights and obligations. The basic principles are as follows:
- there is no opportunity to repay your debt at the expense of the Fund;
- existing rights are not inherited or alienated;
- receives funding according to the terms of the expression of will;
- complete openness about the activities of the NF;
- challenging management only in court;
- lack of rights to sole management;
- has the right to vote in the election of a manager;
- control over the implementation of significant transactions is allowed.
The experience of hereditary funds was adopted from foreign experience. If the testator during his lifetime does not give instructions to open an NF, then all business assets are frozen for six months in accordance with existing legislation. During this time, there is a high probability of losing everything.
Before the President signed the law, business representatives organized Funds abroad, withdrawing assets. Now business remains in Russia, jobs are created and the opportunity to develop our own economy.
It is still unknown how the law will show itself in Russian realities. What’s new in inheritance is no longer needed by ordinary Russians, but by business representatives, since they manage the main assets.
There are unresolved tax issues and how to prevent double payments.
Inheritance contract
As a norm of law, an inheritance agreement is an alternative to a will and will come into force in June 2021. It can be concluded with individuals and legal entities.
The contract specifies the conditions that must be met after entering into inheritance rights. This could be caring for cats and dogs, erecting a monument and other tasks.
They are also mandatory.
You should know! If someone's rights were violated when drawing up an inheritance agreement, then it is disputed in court even during the life of the testator. And after his death by a person whose rights were violated. Mandatory shares are preserved both in the will and in the inheritance agreement, which has priority over the will.
What is the essence of the new law?
The inheritance bill regulates the procedure by which real estate is transferred from a deceased citizen to his relatives or other people named in the testator's will.
According to the new legislation, the heir has the right to abandon property in favor of a third party, and this person can be any person, even if he is not a relative or close acquaintance of the testator. This rule of law is noted in Article 1158 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Previously, a person who refused an inheritance could not decide to whom to transfer it and the property was distributed among the next heirs. The only requirement for a third party, limiting his entry into inheritance rights, is the following - previously he should not have been deprived of property rights by the testator due to unworthiness of his lifestyle or behavior.
In order not to rewrite the will every time the composition of the property changes, when drawing it up, you need to use the following phrase - “all the property that will belong to me at the time of death.”
A testator can leave the same piece of property, for example, an apartment, to several successors. If the will does not indicate the share of each of them, the property is divided equally among all heirs.
Who will be affected by the new law?
As you can see, the changes affect the interests of people who decide to formalize a will properly and redraw the order of inheritance. The new law on inheritance in Russia in 2021 allows you to freely dispose of your wealth.
A document certified by a notary allows you to transfer the right to own property to anyone. But there is also a mandatory share that will be claimed by:
- Minor children (in the absence of official employment).
- Elderly parents of retirement age/
- Disabled dependents (they must live with the author of the will for at least a year).
What documents are required
Documents for registration of inheritance can be divided into two categories:
- Those that are presented at the first visit and writing an application for acceptance of the inheritance or refusal of it.
- Those required to prepare a certificate of inheritance.
First of all, the notary must bring the documents necessary to register the inheritance. Namely:
- Passport/passports (in addition, the notary may ask for TIN and SNILS).
- Death certificate.
- A certificate from the housing authority about the composition of the deceased’s family (to make it clear whether the heirs lived with him or not).
- Documents confirming family ties.
- Will (if there is one).
The need for subsequent documents depends on the nature of the inherited property. What documents may be needed to register an inheritance? Those that confirm the testator’s right to this or that property, or its very existence:
- Real estate purchase and sale agreements.
- Cadastral and technical passports.
- Banking agreements.
- PTS/STS for transport.
- Property valuation acts, etc.
The notary will definitely tell you what he needs to draw up a certificate of inheritance. If certain papers are missing, the notary may request additional information.
New opportunities for heirs and testators
One of the key tools in the updated legislation is a joint will. Previously, such a concept did not exist in domestic law.
This type of will allows spouses to agree in advance on the fate of their property by documenting their intentions. The number of court proceedings will be reduced - this is the main advantage of the new Inheritance Law 2021.
The tool that appears will distribute everything in its place. The death of spouses will not lead to conflict between their relatives, and the courts will not be overloaded with lawsuits. It should be remembered that the joint paper does not affect the mandatory share, so the interests of young children, the elderly and dependents will not be infringed.
Inheritance contract
Another tool that appeared thanks to the edition approved in June. Now the applicant can agree with the testator on counter actions for the transfer of property. The parties sign the document, notarize it and enjoy life.
Foreign experience served as the basis for the creation of inheritance funds relating to business assets. When opening such a fund, an entrepreneur freezes all assets for six months. The heir receives certain rights and obligations:
- lack of possibility of alienation;
- prohibition of sole management;
- financing;
- openness of activity;
- voting for the manager;
- control of serious transactions.
As you can see, the new Law on Inheritance in Russia 2021 expands the boundaries of possibilities for ordinary citizens and, in some cases, simplifies doing business. The existence of inheritance funds in the Russian Federation will slow down the outflow of capital abroad, since company owners will receive an important tool.
True, there is a risk of losing all assets during the six-month freeze. Perhaps legislators will make amendments and eliminate this shortcoming.
The legislation of the Russian Federation on inheritance has undergone some changes in recent years, provoked by modern legal realities. The inheritance procedure is a complex process, so each stage must be clearly regulated at the legislative level.
What will the law on inheritance of the Russian Federation be like in 2021, what has been adopted new in this area in recent years and what changes can be expected in the future?
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
Legacy fund
The updated legislation introduced a new concept that came to Russia from Europe - an inheritance fund. The testator can establish a legal organization that will manage his property and assets after he dies.
The testator has the right to draw up the charter of the organization, appoint people responsible for conducting business, and the method of distribution of profits. The will specifies the list of heirs who will receive income from this fund, as well as the amounts due to them.
Previously, such a procedure was possible only abroad, and many large entrepreneurs specifically transferred their business and money abroad to take advantage of this opportunity. In addition, previously it was possible to officially enter into inheritance rights only 6 months after the death of the testator, which greatly interfered with the work of large companies that were left without an owner for a long period of time.
When registering an inheritance fund, these deadlines change. Within three days after the death of the testator, the notary must write an application to the Ministry of Justice regarding the opening of an inheritance fund, presenting the client’s will to confirm his authority.
Immediately after this, the business and assets of the deceased are transferred to the management of the people who were noted in the will as the managers of this fund.
Thus, after the death of the owner, the property is not squandered, but is collected in a fund and distributed as the testator wanted. This rule of law was created mainly for rich people with large businesses.
However, small, individual entrepreneurs can also exercise their right to create an inheritance fund.
Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation
— contact the on-duty lawyer in the online chat on the right or call:
+7
— Moscow and region.
+7
— St. Petersburg and region.
8
- Other regions of the Russian Federation
You will not need to waste your time and nerves
- an experienced lawyer will take care of solving all your problems!
What regulates
The hierarchy of legal acts of the Russian Federation is headed by the Constitution. The most important document of the state does not directly relate to the inheritance procedure, but it establishes the basic rights of citizens associated, among other things, with this process.
The procedure for accepting an inheritance is directly considered by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, and issues of taxation, fees, duties and benefits are regulated by the Tax Code of Russia.
The actions of notaries during the procedure for registering an inheritance are provided for by the law “Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on notaries.”
Expert opinion
Romanov Igor Severinovich
Lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in developing legal documentation.
More highly specialized issues that are not considered by civil law are additionally regulated by decisions of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation.
Purpose
The legislation is designed to streamline the process of receiving property by heirs, provide for possible options for accepting property and provide maximum assistance in resolving disputes that arise between successors.
The provisions of the laws protect the rights and interests of heirs, establish the necessary list of documents for receiving an inheritance, determine the actions of officials in the inheritance process and the size of shares due to various categories of persons.
You can find out how to draw up an agreement on the division of property here.
Is the inheritance procedure mandatory?
Along with the inherited property, the heirs also receive a number of obligations.
This applies to both loans and debt obligations. And therefore, many are in no hurry to receive an inheritance. There are cases when expenses exceed property income.
There are several ways to refuse an inheritance.
In the first case, you need to take only two actions:
- Write a statement of refusal.
- The application must be submitted to a notary. You also need to have with you a passport and a document confirming the death of the person giving the inheritance. The right to inheritance is not restored after filing an application.
There is another technology . It consists in the fact that the recipient of the inheritance ignores the fact of transfer. It is important not to accept actual inheritance.
Even if a person is already using inherited property, he can refuse it. This can be done within six months.
The right to inherited property may be taken away from these persons:
- The person neglected his duty towards the one who gave the inheritance;
- A person with malicious intent falsified a fact and a document, exerted pressure on a non-dead person;
- If the parent who gave the inheritance was deprived of parental rights.
Entry procedure
To inherit an apartment, house, vehicle, or other valuable things, it is necessary to follow the legal order. The sequence of actions includes:
- after receiving information about the death of a relative, a potential candidate should contact a notary office (regardless of the place of residence of the deceased);
- when visiting a specialist, he needs to have a package of documents that are required to establish the grounds for entering into an inheritance;
- Conduct a property assessment by contacting the appropriate organization (market, cadastral or inventory);
- pay the state fee (calculation of the cost depends on the valuation of the property);
- after 6 months from the date of death, you should contact the notary again in order to obtain a certificate confirming the right to inheritance.
Important ! If the relative who received it plans to privatize the property and make transactions with it in the future, an obligatory step is to contact the registration chamber to enter information into the state real estate register.
From this moment on, it will include a new owner who, at his own request, has the right to dispose of it - sell, exchange, donate, bequeath, rent.
People with rights to inherited property
There is a certain queue for accepting inherited property. It is established by Articles 1142–1145 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. First of all, the closest people, relatives, children, spouses receive inherited property. Article 1116 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that the list of those receiving an inheritance may include:
Relatives who have rights to inheritance are:
- Husbands (wives), children.
- The property can be accepted by the grandmother or grandfather on either side.
- Uncle or aunt, if they died along with the giver of the inheritance.
- Child of an uncle or aunt.
- Their children.
- Great-grandfather or great-grandmother.
- A cousin, grandson, brother or sister of a grandfather or grandmother.
- Great-great-great-grandson, uncle or aunt, nephew.
- A child of the inheritor who is not related by blood.
- A disabled person who was dependent on the person who gave the inheritance.
- State organization. It happens that there is no claimant to the inherited property. Then the property values go to the state or municipal property.
Remember
- The first priority heirs are parents, children and spouse.
- All children of the testator, incl. illegitimate and adopted children have equal rights to inheritance.
- If the testator's child dies earlier, his right to inheritance passes to his grandchildren.
- The property is divided equally between all candidates. Grandchildren who inherit the share of their deceased parent divide this share among themselves.
- The surviving spouse should contact a notary and allocate a spousal share in the amount of 50% of the property acquired during the marriage before dividing the inheritance.
- Cohabitants and former spouses can only claim a share of the inheritance as a dependent.
- Disabled dependents of the testator will inherit first if they confirm this status.