Owners of premises in an apartment building bear the burden of maintaining the premises they own, as well as the common property of the house, and are required to pay monthly contributions for major repairs. By virtue of Article 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, property owners who have lately or not fully paid contributions for capital repairs are required to pay a penalty to the capital repair fund in the amount of 1/300 of the key rate of the Central Bank for each day of delay.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 330 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a penalty (fine, penalty) is a sum of money determined by law or contract, which the debtor is obliged to pay to the creditor in the event of non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of an obligation, in particular, in the case of delay in fulfillment. A penalty is one of the ways to ensure the fulfillment of obligations, a means of compensating for the creditor's losses caused by the debtor's violation of his obligations.
The management authority has the right to collect debt for housing and communal services in court
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Igor Borisovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in document examination.
The organization managing the house, under a management agreement, provides services and performs work for the proper maintenance of the common property of the apartment building and issues invoices to the residents of the apartment building for payment for these works and services.
Owners and tenants of premises in the house must pay for housing and communal services due to the following legislation:
- the owner bears the burden of maintaining the property he owns (Articles 210, 249, 290 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- the owner or tenant of the residential premises is obliged to pay in full every month until the 10th month for residential premises and utilities (Articles 153 - 158 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, paragraphs “and” paragraph 34 of the RF PP No. 354);
If the owners do not fulfill their obligations or do not fulfill them in full, the management authority has the right to conduct claims against such citizens, including collecting the debt through the court.
Is the debt for major repairs transferred to the new owner?
Unfortunately, the debt is transferred from the previous owner to the new owner of the property. This legal norm is enshrined in Article 158, Part 3 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. The confusion arises because, according to Art. 210 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, debts for utility bills are assigned to the citizen during whose period of ownership these debts appeared in the first place. However, Art. 158 part 3 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation separates the concept of “contributions for major repairs”, therefore Art. 210 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Accordingly, there is no point in turning to law enforcement agencies and the courts - according to the law, it is you who are obliged to repay the debt. Therefore, we recommend that you always carefully read the purchase and sale agreement (it should reflect the status of your personal account), and also require a document from the seller confirming the absence of debt. Otherwise, in the absence of caution and attention, the buyer will only find himself an additional headache.
Limitation period and actions that interrupt it
When going to court to collect debts for housing and utility services, the management organization must remember the statute of limitations: the period established by law when the management company can collect debts for services from the consumer in court. A general period of three years applies to the collection of debt for housing and communal services (Part.
1 tbsp. 200 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph.
24 resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2015 No. 43). After this period, the management authority will not be able to obtain through the court the unpaid amounts for housing and communal services from the resident of the house.
According to the general rules, a period of three years does not apply if the defendant has committed actions indicating his recognition of an existing debt (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). According to paragraph 20 of the resolution of the Plenums of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 15/17, such actions, based on specific circumstances, may include:
- recognition by the debtor of a claim for debt for housing and communal services;
- partial payment by the debtor himself or another person with his consent of the debt or penalties, fines on the debt;
- payment of interest on the principal debt;
- making changes to the contract or the defendant’s request to make them, which indicate recognition of the debt; for example, concluding an agreement on deferment or installment payment.
- confirmation of the collection order, on the basis of which funds are written off from the payer’s account, etc.
The debtor’s response to the management organization’s claim, which does not contain instructions on the recognition of the debt, does not indicate that the owner acknowledged it (decision of the Berezovsky City Court dated April 4, 2017 in case No. 2-416/2017).
Taking actions to recognize a debt interrupts the limitation period: the countdown of this period begins anew, which allows the management company to collect debt accumulated over a period of three years or more.
Can the deadline be interrupted or suspended?
The limitation period may be suspended or interrupted. In this case, it will not occur on the date on which you expect it to occur.
Most often this happens due to the debtor’s recognition of the debt. For example, in response to a complaint from the HOA or management company, the tenant responded that the debt really exists, but cannot be paid for some reason. In this case, the three-year period will begin to be calculated anew from the date of its recognition. However, this only works for those debts that have been recognized. The debtor can recognize them only for certain months.
Another example is when a debtor has paid debts for a certain period, but not in full. It turns out that you have committed actions that indicate recognition of the debt. In this case, the limitation period will also begin to run again.
Suspension of a period is a period when a period does not run due to the occurrence of circumstances provided for by law.
There are three groups of such circumstances:
- Preventing filing a claim. For example, the courts were closed due to coronavirus, and the plaintiff could not file a claim. In this case, the running of the period will be suspended for the period during which the claim could not be filed.
- Claims, i.e. when you dealt with the HOA or management company in a claim procedure. For example, they tried to resolve a dispute with the management company or HOA through the mediation procedure. The deadline is suspended for the duration of the procedure.
- Going to court. From the moment the claim is filed until the final decision on the case is made, the period is suspended.
Payment of current payments is not recognition of debt by the consumer
Separately, we should dwell on the condition of recognizing a debt upon partial repayment or repayment of interest, penalties, and fines. Since payments for housing and communal services are periodic, payment by the debtor of part or all of the periodic payment does not indicate recognition of the debt by the debtor (clause 20 of the resolution of the Plenums of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation and the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 15/17).
Consequently, payment by the debtor of current payments for housing and communal services is not a basis for refusal to apply the statute of limitations. This is only payment for services and work for the current month, and the entire period of debt and its amount have not been confirmed (decision of the Berezovsky City Court dated April 4, 2017 in case No. 2-416/2017).
Who is eligible for benefits?
The current legislation of the Russian Federation defines certain categories of citizens who can receive a discount of up to 50% when paying for major repairs. Such persons include:
- WWII veterans;
- persons injured in the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant;
- labor veterans;
- spouses of WWII veterans;
- citizens who are over 70 years old;
- families that have been assigned the status of low-income or large families;
- families raising a disabled child.
Acknowledgment of debt - only within the limitation period
In paragraph 19 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 12, 2001 No. 15, the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2001 No. 17 stipulates that when examining the circumstances associated with the commission by an obligated person of actions indicating the recognition of a debt, it is necessary in each case to establish when the debtor specifically performed the specified actions.
A break in the running of the limitation period can only occur within this period, and not after its expiration.
Consequently, the defendant’s recognition of a debt for one of the periods does not interrupt the statute of limitations for another period, if three years have already expired. The Presidium of the Altai Regional Court came to this conclusion when considering case No. 44-g-137.
The management office filed a claim against a resident of an apartment building for the collection of debt and penalties for payments for housing and communal services for the period from 04/01/2004 to 11/30/2007. The plaintiff insisted that the statute of limitations cannot be applied, since the defendant acknowledged the debt on September 5, 2007 by signing a promissory note.
The magistrate and the court of appeal agreed with the plaintiff and refused to apply the statute of limitations to the debtor. The Court of Cassation overturned the decisions of these courts, citing the fact that they did not take into account the position set out in the joint resolution of the Plenums of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 15/17.
At the time of signing the debt obligation, the three-year period for collecting the debt from the defendant for April, May, June, July, August 2004 had expired. The limitation period applies to this period.
Contacting the HOA or ERC
Where to find out the amount of debt is not specified at the legislative level. In practice, for this purpose you can use the websites of the Unified Settlement Center or Homeowners Association.
It will not be possible to indicate the exact sequence of actions, since each region has its own site structure.
On average the algorithm is like this:
- log in to your personal account;
- go to the services section;
- find an option to obtain information about debt and account balance.
Before performing these actions, you will need to clarify information about which organization is providing major repairs to the premises in which the citizen lives. The Capital Repair Fund provides such information.
Remember
When going to court to collect debts for housing and communal services, the management organization must remember the important aspects of any of these lawsuits:
- A general statute of limitations of three years applies to debts for housing and communal services, if this is stated by one of the parties to the lawsuit.
- The limitation period is interrupted if the debtor, before the expiration of the three-year period, has committed actions that indicate his recognition of the debt.
- Making periodic payments or acknowledging part of the debt for housing and communal services does not indicate that the consumer has accepted the entire debt.
- If the defendant has declared the application of the statute of limitations, the MA should clarify its claims before the court adopts the operative part of the judicial act.
Is it legal to charge contributions and does this need to be done for all residents of an apartment building?
Until 2012, contributions for major repairs were considered voluntary . Since the publication of Federal Law No. 271 of December 25, 2012, the Housing Code has clearly indicated the requirement for making mandatory payments. According to clause 6.1. Art. 2 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, public authorities are obliged to promptly provide services for major repairs of the building at the expense of contributions from the owners of the premises.
The owners, in turn, undertake to transfer monthly contributions to a fund organized for the purpose of collecting funds for major repairs (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). The following categories of persons have the exclusive right to non-payment of contributions and in the following cases (clause 2 of Article 169):
- living in houses recognized as unsafe;
- living in houses subject to demolition;
- persons living on the territory of a land plot seized in favor of the state or municipality;
- by decision of the general meeting of owners upon reaching the minimum amount of capital in the fund (clause 8 of article 170 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation);
- when carrying out major repairs, where repeated provision of relevant services is not required (clause 5 of Article 181 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
Certain categories of citizens also have the right to partial or full compensation of expenses for major repair obligations in accordance with clause 2.1 of Art. 169 Housing Code of the Russian Federation:
- unemployed citizens living alone who have reached the age of 70;
- non-working pensioners living together;
- non-working disabled people of groups I and II.
You will learn more about who is exempt from paying for major repairs and what benefits exist in a separate article.
The obligation occurs after no more than 8 months from the date of inclusion of the house in the capital repair program (clause 3 of Article 169). Work can be carried out at the expense of the funds of a housing cooperative or association transferred for the appropriate purpose (clause 4 of Article 169).
How to determine the statute of limitations on contributions for major repairs
Currently, homeowners must pay dues for major renovations. This obligation is established and legislated in Section IX of the Housing Code [1].
The section deals with the issues of performing and paying for major repairs in apartment buildings. The Constitutional Court, in resolution No. 30-P[2], confirmed the legality of establishing payments for major repairs.
Subjects of the regions of the Russian Federation have established the amount of contributions and developed programs for major repairs of houses.
In what cases is the owner exempt from contributions?
The conditions for exemption from the obligation to pay contributions for major repairs are regulated by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, according to the provisions of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the owner does not have to pay in the following cases:
- If an apartment building, part of which the owner owns, is recognized as unsafe . A conclusion on its emergency status must be issued in writing by the municipal administration of your city;
- If the property of the owner of real estate is temporarily seized from him for the needs of municipal or federal authorities. This means that during the “alienation” of the property, its current owner is completely exempt from all types of contributions, including housing and communal services, contributions for major repairs, etc. As a rule, real estate is confiscated in the event of unforeseen situations - the resettlement of refugees in your region, an increase in tourists due to any events, etc. It should be noted that the authorities most often do not touch ordinary “private traders”. This clause of the RF Housing Code applies, first of all, to hotels, hostels, property of developers, etc.;
- If the owner bought a recently commissioned house (the so-called “new building”). In this case, he is exempt from contributions for a period of one to three years, depending on the laws and regulations of his region. This information needs to be clarified with the city or regional administration. Also, the developers from whom the property was purchased are required to provide information on benefits.
About the statute of limitations for major repairs
The statute of limitations is the period of time that has passed since someone's rights were violated. The expiration of the period entails the loss of the opportunity to file a claim in order to restore violated rights. This period is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
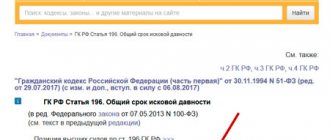
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation[3], the general statute of limitations for major repairs is three years from the moment when the management company or regional operator learned about the non-payment of contributions by a citizen. This happens the next day after the due date for paying the fee for the billing month.
When purchasing premises in an apartment building, the new owner must make sure that the previous owner paid contributions for major repairs. Otherwise, the old debts will have to be paid by the new owner.
The transfer of debt is regulated by Part 3 of Article 158 of the RF Housing Code[4]. Consequently, the management company will be able to recover unpaid payments for major repairs from the new owner of the premises.
When filing a lawsuit against a homeowner, the organization acting as the plaintiff most often demands payment of the amount of contributions for the maximum possible period of time, as well as the amount of penalties accrued on overdue contributions. It is possible to partially reduce the size of such a claim.
A citizen who has not paid contributions for major repairs for more than three years has the right to declare in court that the statute of limitations has expired. The court may reduce the amount of the penalty by ordering contributions for the last three years to be paid. The amount of the penalty is collected in proportion to the amount of contributions awarded for payment.
It should be remembered that when a citizen submits an application to miss the statute of limitations on debts for major repairs, he must make sure that it is recorded in the minutes of the court hearing.
The court will accept an application for expiration of the statute of limitations if the owner:
- did not recognize debts for major repairs;
- did not make payments to repay the debt;
- did not sign debt reconciliation acts with the management company;
- did not sign documents acknowledging the debt.
From what moment does the countdown begin?
The statute of limitations begins to count the day after the defendant is late in payment. For example, he was supposed to pay on August 3 and did not fulfill this obligation. In this case, the period will begin to count from August 4.
We remind you that if several payments are not paid, then the statute of limitations for each of them will begin at a different point.
For example, payments for August, September and October are missed, and the due date is the 5th of each month. In this case, the deadlines will begin to be calculated from September 6, October 6, November 6, respectively.
Penalties for violation of payment deadlines
The legislation provides for the liability of citizens in case of incomplete or untimely payment of contributions for major repairs.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Igor Borisovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in document examination.
Part 14 of Article 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation [5] establishes the norms by which citizens are obliged to repay debts and pay penalties. The collected amount of penalties goes to replenish the fund's reserves and will be used exclusively for the purpose of major repairs of houses.
Formula for calculating penalties: P = N * StR / 300, where
N – the amount of unpaid contributions transferred not on time or not in full,
StR – refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
If the refinancing rate changes, the calculation is made at the rate in effect on the date of interest payment.
Owners who consider the assessed contributions to be incorrect have the right to go to court. It is necessary to take into account that payments for major repairs are regulated at the level of federal laws. Recently, judicial practice has not been in favor of citizens.
Organizations that take into account the capital repair fund have many methods for claiming unpaid contributions. In pre-trial proceedings, the supply of water and electricity to debtors may be cut off.
If debts are not repaid after a court decision, then bailiffs can seize movable property. If the amount of debt exceeds 10 thousand rubles, travel abroad is limited.
Methods for checking debt
Often, tenants or even new apartment owners discover that there is a debt for major repairs at their address. Often, along with this debt, there are other types of debt - for housing and communal services, garbage removal, etc.
New owners or tenants, of course, do not expect to see a large amount owed. However, often the previous owners leave behind an extremely unpleasant “tail” in the form of an extra several tens of thousands of rubles of debt.
And it would be nice if the previous residents at least left receipts. But in most cases they are simply not found anywhere - neither in the house itself, nor in the mailbox.
There are several ways to find out your debt online:
- You can view your account status through the State Services service;
- On the website of your Unified Settlement Center, which is responsible for servicing your home;
- Through a personal appeal to the Capital Repair Fund or the Homeowners Association.
In all of the above cases, searching for your home is possible by address, personal account or by an already generated receipt. Let's take a closer look at how to find out the status of your account depending on the method.
Through State Services
The convenience of this method is that the entire procedure is done online - you will not need to go anywhere, collect documents, etc. It is enough to have a registered account in the State Services system, access to the Internet and the address of your home. So, how can you find out the debt for major repairs at an address? Follow our instructions:
- Go to the State Services website at https://www.gosuslugi.ru
- If you do not have your own account, you will need to register on the resource. To do this, click on the “Personal Account” button in the upper right corner, then click on the “Registration” button. You will need to enter your passport and contact information. Next, an SMS message with a verification code will be sent to your specified mobile number. Confirm ownership of the number, after which registration will be completed;
- Next, click on the “Service Catalog” button at the top of the site. Find the section “Payment for housing and communal services” ( https://www.gosuslugi.ru/10373/1 ). Click “Get a service”, enter your address, after which the system will automatically display the status of your account: existing debts, accrual dates, division of payments into categories, etc. In addition, right here you can pay off your debt by paying with a bank card, e-wallet or other way.
Thus, you only need a personal account on the State Services website. In this case, your personal account number will not even be needed - you only need the address of the apartment or house.
On the website of your URC or HOA
The method is very similar to checking your balance through State Services - everything is done via the Internet in a couple of clicks. In addition, checking the balance through the website of the service organization well answers the question “how to find out the debt for major repairs on a personal account”, because in this case, to check the debt you will not need anything other than a personal account.
The algorithm of actions is as follows. First, you need to find out which company is doing the major renovation of your home. To obtain this information, you can contact the Capital Repair Fund.
Next, go to the website of your URC or HOA. You will first need to go through the registration procedure - as a rule, they only require an email, a password for a new account and a personal account number. You will receive an email with a link inside - you need to follow it to confirm. After confirming your email, you can already track the status of your balance.
The design and functionality of the site directly depends on the URC or HOA, so it is impossible to give universal instructions. Try to find the section “Balance”, “Amount to be paid”, “Pay for major repairs”, etc. As a rule, this is where information is located for the user about the amount of debt and the date of its occurrence.
In person at the FKR or HOA
Unlike all previous methods, personal application requires time and a small package of documents, without which the center employees will refuse to provide information. You need to take with you:
- Certificate of registration of ownership or other document confirming your right to housing;
- Internal passport of the Russian Federation. It is especially good if it has a stamp indicating permanent registration at the address about which you want to receive information.
The addresses of the FKR or HOA can be found using online maps like Google Maps or Yandex Maps. Only the person who is registered in the housing space on a temporary or permanent basis, as well as the owners of this housing (even if there are many owners, and each has only a small share of the housing) can apply to the FKR or HOA.
FKR or HOA employees are required to provide you with all the necessary information on the day of your application. In practice, the client is informed about the status of his personal account immediately after checking the documents, i.e. The entire operation takes no more than 20 minutes.
Attention: the seller is obliged to give the buyer, upon purchase and sale, an original certificate of absence of debt on utility bills, because otherwise, if there are still debts for major repairs and housing and communal services, the new owner of the property will have to resolve the issue independently. Perhaps even through litigation, which is confirmed by extensive judicial practice in resolving housing disputes. Therefore, when buying an apartment, be sure to ask the seller for the appropriate certificate.
How to write off debt for major repairs?
Contributions for major repairs are mandatory, so it is impossible to write off the debt for major repairs. However, if the case goes to court and the statute of limitations expires for individual payments, you can declare this in court and then the court will not collect the debt beyond the statute of limitations.
In addition, the legislation contains provisions when contributions for major repairs are not subject to payment, for example, if the house is recognized as unsafe and is subject to demolition. In this case, it is necessary to inform the capital repair fund that the contributions are not payable and ask to cancel the corresponding debt, or wait for the lawsuit and object to the claim for collection of the debt for capital repairs.
In addition to the debt for major repairs, a person may be charged penalties for late payment of contributions for repairs. In this case, the question arises: is it possible to write off penalties for major repairs? You can contact the capital repair fund with a request to write off penalties, however, most likely the applicant will be denied this. When going to court to collect penalties, the debtor may claim that the plaintiff missed the statute of limitations or ask to be exempted from penalties, since he did not receive, for example, payment slips for the payment of contributions.
In addition, from 04/06/2020 to 01/01/2021, no penalties will be charged for late payment of contributions for major repairs.
Calculation procedure
For payments for major repairs, the limitation period is calculated separately for each payment. For example, the debtor did not pay in January, February and March of the current year. The statute of limitations will expire at different times for each payment. It turns out that if payments are not paid for a long time, then some payments may expire at the time the plaintiff goes to court, but some may not.
The formula for calculating the statute of limitations is simple. It is necessary to determine the start date of the period, add to this date the duration of the period for payment, and the next day after this date the period will be considered missed.
Example: the debtor did not pay the next payment for major repairs, which was due on 08/05/2021. Accordingly, the statute of limitations for this payment will expire on 08/05/2024, and on August 6 the defendant will be able to claim that the statute of limitations has passed. But for the next payment, which should have been paid before 09/05/2021, the statute of limitations will only expire on 09/05/2024.
Application for cancellation of a court order for major repairs
When collecting debt on contributions for major repairs, first the plaintiff applies to the court with an application for the issuance of a court order. The debtor learns that a court order has been issued much later if he receives a court order from the court, and sometimes at the stage of enforcement proceedings.
After the debtor has learned about the court order for major repairs, he has 10 days to file an application with the court to cancel this court order. In this case, in the application to the court it is enough only to indicate that the debtor objects to the court order issued against him.
Of course, you can give specific reasons why the debtor objects, but you don’t have to give them. It is important to indicate in the application when the debtor became aware of the court order.
According to current practice, as soon as the court receives an application to cancel a court order, the judge makes an appropriate determination and cancels the order. There were cases when the court canceled court orders even after several years, since the debtor became aware of the court order after a long time.
USEFUL : for more information about the procedure for canceling a court order, follow the link
Using State Services to obtain information about debt
The easiest way to find out whether a citizen has made contributions for major repairs is by using the State Services portal. The main advantage is that the information is provided remotely, meaning there is no need to visit authorized companies and submit an application.
The check is carried out online 24 hours a day. The main requirement for obtaining information is the presence of a registered entry on the portal.
The algorithm of actions looks like this:
- open the official website of State Services;
- register if the citizen has not previously created an account on the portal. To do this, you need to go to your personal account and click on the “Registration” button. Then the person enters the data of the act through which the identity and SNILS are verified. After receiving the SMS code on your phone, you will need to enter it for identification;
- pass authorization. To do this, enter your cell phone number and password. SNILS can also serve as an identifier;
- go to the “Services” tab, select the line “Apartment, land and construction”;
- open the item “Payment for housing and communal services”;
- click on the “Get service” button;
- enter your home address.
Next, the system displays payment data for the payment in question. If a citizen has a debt, this is reflected in the response to the request. The date of accrual of the debt and the category of payment are indicated.
You can also pay your accumulated debt online. To do this, you need to use a card issued by a banking organization or an electronic wallet.
How to win a court case for major repairs?
Victory in court in a dispute related to major repairs depends on the participant in the process and on the validity of the claims.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Igor Borisovich
Lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: criminal law. More than 3 years of experience in document examination.
If the capital repair fund goes to court, then in order to win the dispute it is necessary to correctly pay for the capital repairs, file a pre-trial claim, make sure that the house is subject to major repairs, and correctly identify the defendant in the case.
In order for a citizen to win in court regarding major repairs, he needs to give arguments why he is not obliged to pay contributions for major repairs, if any. Provide documentary evidence that, for example, the house is recognized as unsafe.
Check the calculations of the capital repair fund for the correctness of the calculation of contributions and, if errors are identified, provide the court with reasoned objections in this matter.
In any case, if there is no reason not to pay contributions for major repairs, then the person is obliged to pay them, and if the requirements of the capital repair fund are justified and proven, it is almost impossible for the defendant to win in court in such a dispute.
How to check debt
By checking the amount of debt for major repairs in a timely manner, a citizen will protect himself from possible unpleasant surprises in the future, for example, when buying an apartment. You can find out the debt for major repairs in the following ways:
- through Internet resources. To check the amount of debt online, you should go to the official web page of the service organization that is assigned to a particular house. This should contain complete information about the services that the company provides, as well as the amount of expenses for performing certain works. If funds to pay for major repairs are accumulated in the account of a regional operator, then all the required data can be clarified on the website of a certain government agency. Also, thanks to the information provided, it is possible to track your own payments to the capital repair fund for any month. Please note that in order to gain full access to the portal information, user registration will be required;
- by personally contacting the managing organization or division of the regional fund. The address of the company that is responsible for spending the funds paid for major repairs is always indicated on monthly mail receipts. The address can also be found on official Internet resources. It is advisable to find out in advance the reception hours of citizens at the organization: by phone or on the website.
- study the receipt. The settlement line contains a section on the amount of unpaid debt. Usually the total amount to be paid is written here. But as with any payment document, the receipt may contain inaccuracies. Therefore, if you discover a debt, you should contact the management company for clarification.
What happens if you don’t pay into the capital repair fund?
For improper fulfillment of obligations to make contributions for the maintenance of residential premises, the following types of liability are provided:
- Court order (Chapter 11 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The debtor is sent an order demanding reimbursement of the amount of debt at the corresponding request of the collector.
- Court decision (Chapter 16 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The debt is collected by a court decision at the stage of completion of the claim proceedings in the event of an appeal against the court order.
- Accrual of penalties for major repairs (clause 14.1 of Article 155 of the RF Housing Code). If there are no payments within the period established by law, the amount of debt increases by a certain percentage for each day of delay.
- Fine . An additional measure of liability within the framework of a court decision in conjunction with the recovery of the principal amount of debt in case of malicious evasion of obligations.
- Seizure of property (subclause 7, clause 1, article 64 of Federal Law No. 229). During enforcement proceedings with the participation of bailiffs, property valued at the total amount of the debt is confiscated from the debtor. Subsequently, the property is sold at open auction, and the proceeds are sent to the claimant to pay off losses.
- Seizure of property (subclause 7, clause 1, article 64 of Federal Law No. 229). Another penalty in enforcement proceedings involving bailiffs. The property is seized for the benefit of the capital repair fund until the debt is paid.
- Seizure of accounts (subclause 7, clause 1, article 64 of Federal Law No. 229). A measure of collection in enforcement proceedings with the involvement of bailiffs, expressed in the freezing of the debtor's active bank accounts or withholding funds in favor of repaying the debt.
- Restriction on travel (subclause 3, clause 1, article 64 of Federal Law No. 229). Bailiffs have the right to issue a ruling on a temporary restriction on crossing the border of the Russian Federation if the amount of debt exceeds 30 thousand rubles.
Enforcement proceedings with the participation of bailiffs are initiated at the request of the management company or upon the fact of a court decision at the request of the claimant (clause 1, clause 5 of Article 30 of Federal Law No. 229).
As an enforcement measure, the debtor does not have the right to evict from the residential premises . The presence of debt for major repairs acts as an unofficial encumbrance in the case of the sale of an apartment, since the transaction is accompanied by the provision of a certificate from the BTI. This circumstance will adversely affect the cost of housing and buyer confidence.
You will find all the details of whether it is possible not to pay contributions for major repairs in an apartment building in another material.
How are debts calculated and late payments calculated?
Debts are collected by court order or decision. As a preliminary measure, at the pre-trial stage, penalties are added to the amount of debt.
Liability for non-payment before trial
According to clause 14.1. Art. 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, in case of failure to fulfill obligations to pay contributions, penalties are initially charged . The accrual is made after 31 days following the due date for payment of the contribution established in the region. Penalties are collected both in case of complete evasion of payments and partial evasion.
The formula involved in the calculations is VP = TD x (KS/300) x DP , where:
- VP - the amount of the penalty taking into account the number of days of delay;
- TD - the body of the debt or the amount of the principal debt;
- KS - key rate established by the Bank of the Russian Federation;
- DP - number of days of delay.
A penalty is charged for each day of delay in the amount of one three hundredth of the Bank's rate. According to Government Decree No. 1340 of December 8, 2015, from January 1, 2021, the key rate is used for calculations instead of the refinanced one.
Penalties are included in the body of the contribution and are reflected in the column of the receipt for major repairs . Payment is made monthly. If payments have not been made in full, then the entire amount of payment is recognized as the body of the debt; if partially, part of the unpaid amount is recognized. The amount of the principal debt involved in the calculations increases daily in proportion to the duration of the delay.
Example. On February 1, 2021, the owner of an apartment with an area of 30 sq.m., living in a region with an established rate of 15 rubles/sq.m., did not pay a fee of 450 rubles. From March 2, the accrual of penalties begins according to the following calculations: 450 x (7.25/300) x 1 = 10.875 - the amount of the penalty for 1 day of delay. Starting from March 3, the body of the debt will be increased by this amount, and 2 days will be accepted as the number of days of delay.
Can the fund sue non-payers?
In case of improper fulfillment of obligations to pay contributions for major repairs, including repayment of penalties, the management company has the right to go to court with a demand to collect the amount of debt from the owner of the residential premises. This requirement is implemented on the basis of a court order or court decision if the applicant provides evidence of unlawful evasion of obligations.
If you refuse to make contributions, what are the consequences?
The party that has formed and maintains the capital repair fund has the right to send to the court a demand for the issuance of a court order to collect the debt (Article 122 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). The application is considered in the magistrate's court if the amount of the debt does not exceed 50 thousand rubles (subclause 1, clause 1, article 23 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation), otherwise in the district court. The applicant submits a written application in accordance with Art. 123-124 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation with the condition of providing documents confirming the debt.
In the absence of grounds for refusal listed in Art. 125 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, a court order is issued within 5 days from the date of application and contains (Article 127 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation):
- number and date of issue;
- name of the judicial authority;
- information about the judge;
- details of the claimant: place of registration, name of the legal entity;
- known information about the debtor: place of residence, name, place of work, place and date of birth;
- a law allowing the execution of the claimant's demands;
- amount to be recovered;
- the amount of the fine or penalty;
- the amount of state duty, which is compensated by the debtor;
- details of the applicant's bank account for transferring funds;
- debt formation period.
We do not recommend completing the documents yourself. Save time - contact our lawyers by phone:
8 (800) 350-14-90
The order is issued on a special form in 2 copies signed by the judge. A copy is sent to the debtor's address. The decision is made without the participation of the owner and can be challenged within 10 days from the date of notification of delivery or from the date of expiration of the storage period for postal correspondence (Article 128 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
If no objections are received, the claimant is given a second copy of the order with an official seal, which acts as a writ of execution. At his request, the document is sent to the bailiff.
In a separate publication, we will tell you whether you can refuse to make contributions and how to do this legally.
Is it legal or not to appeal a collection order?
According to Art. 129 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, in order to cancel an order at the stage of enforcement proceedings, the debtor must apply to the magistrate’s court, which made the decision, within 10 days from the date of receipt. It is necessary to submit a written application requesting cancellation and indicating objections: Disagreement with the amount of the debt, complete disagreement with the debt, etc.
Upon review, the judge issues a ruling to cancel the order . At the same time, the creditor retains the right to present claims in the manner of claim proceedings, where the debt, in the event of a positive decision of the court, is collected on the basis of a court decision. Copies of the document are sent to the parties no later than 3 days from the date of issue.
You can challenge a court order after 10 days if the debtor proves that he could not go to court for good reasons or due to inadequate notification due to circumstances beyond his control. In this case, it is necessary to file a petition to restore the deadline.