It is quite easy for a creditor to obtain a court order, but it is no less easy to cancel it. So, you “got” a copy of the order, quickly wrote an objection and canceled it on the same day. What will happen next? Should you wait for the bailiffs to come and look for your property? What should the debtor do next after the court order is cancelled? Well, the FSSP will definitely not open proceedings on the basis of the canceled document. The good news is that you don’t need to make any sudden movements at this stage! Well, what will happen next?
Life after the lifting of the court order: how are events developing?
We have Art. 129 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, which obliges the magistrate to cancel orders based on an objection from the debtor in writing.
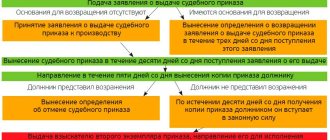
Next, the judge must issue a written ruling. It contains detailed explanations for the claimant: that he has the right to apply for collection in court.
So that you don't get confused, we will bring you up to date. Since 2021, the judicial system has:
- writ proceedings. This is an application to the magistrate for an order;
- claim proceedings. This is the filing of claims against the debtor through the district court.
So, if the collection by order does not “burn out”, then it is necessary to initiate legal proceedings - that is, go to the district court. In general, banks, microfinance organizations, collectors and other collectors prefer to first “try their luck” by order. It's easier, faster and more economical.
For example, a justice of the peace reviews documents within 10 days. The district court sets a date only for the first hearing 1-2 months after the application.
Written explanations are recorded in the resolution, which is sent to the claimant and the debtor within 3 days from the date of issuance. The debtor does not need:
- contact the lender;
- file a claim in a court of general jurisdiction;
- come to the magistrate for documents;
- repay the disputed debt.
At this stage, we wait for the lender's response and do not make hasty decisions.
A small educational program. An objection to the court order must be filed within 10 days from the date you received it by mail. It is important. If you miss these deadlines, you will have to restore them, and this is not easy. You must have a valid reason for missing. If they are not there, it will be impossible to cancel the order.
Advantages for creditors
It significantly saves their time and finances.
Namely:
— the decision is made within 5 days from the date of filing the application;
— accepted without judgment. proceedings;
- after the issuance, the claimant can receive an order from the court and immediately send the court. bailiffs;
— the state duty is lower than in claim proceedings;
— there is no need to pay for the services of representatives and transportation costs, since there are no lawsuits. proceedings.
What to do if the court order is canceled: predicting the actions of the creditor
After the court order is canceled, the creditor has several options:
Reach an agreement with the debtor out of court
For example, if your debt collector is a bank, then you have the right to listen to the following proposals to provide you with options to “get out of debt”:
- credit holidays (this option has practically not worked since the beginning of 2021);
- loan restructuring;
- refinancing.
As part of the restructuring, it is possible to agree on a partial write-off of penalties or fines. These are preferential services that help reduce a person’s credit burden.
But for this you need:
- Go to court for a claim.
- The bank prepares an application for debt collection and applies to the district court.
- Next, a hearing date is set, of which the court notifies all interested parties.
- If a person does not appear at the meeting, the case will still be considered.
- It is enough that he received the notice and was familiar with it.
But meetings can be postponed and rescheduled. For example, you notify the court that you are forced to leave the country for work. If the reason is considered sufficiently valid, the meeting will be postponed.
Why shouldn’t you count on the lender’s forgetfulness?
The third option for the outcome of events after the cancellation of the court order is similar to a rose-colored dream - the creditor is completely .... forgets about his claims. Or “scores” - it’s who likes what better.
Alas, the lender’s forgetfulness is a utopia.
The reality will be like this
What awaits the debtor? Alas, troubles
If the lender is a bank or microfinance organization
You shouldn't count on forgetfulness. These are serious organizations that are included in the monitoring and work of the Central Bank. They operate strictly following the bureaucratic requirements of the law. Each issued credit or loan is recorded in the internal register of these companies and goes through reporting to the Central Bank.
Even if your bank branch is closed, information about loans is still stored in the central database of this bank.
In rare cases, an MFO or bank can forget about the statute of limitations or miss the time to apply for inclusion in the register of creditors.
But they will never forget about your debt; this is impossible due to the total recording of relationships with individuals in documentary form.
If the creditor is an individual
For example, the alimony claimant is the ex-spouse; or an old friend lent you money, to whom you now owe money, and so on. Moreover, you should not rely on the lender’s forgetfulness. Practice shows that collection by individuals can take the form of an action-packed drama. Such creditors are ready to go all the way to the Supreme Court, the European Court of Rights (ECHR), and even the Afghan Taliban, just to get at least 50% of their money back.
The dispute that was considered in the Constitutional Court on April 26, 2021 (Resolution No. 15-P) was very indicative in this regard. The dispute arose between the parties over a debt that was outstanding by the debtor back in 1999. For all time until 2016-2017. (when the debtor began to go bankrupt) the debt increased from 700 thousand rubles to 4.5 million rubles. The creditor did not calm down until he reached the Constitutional Court and did not achieve the desired decision.
If collectors act as collectors
They use strict collection methods, that is, the debtor is processed at the highest possible speed in pursuit of debts. Of course, most collection agencies try to comply with No. 230-FZ, but still, their interest in debt collection is sometimes so high that they are ready to violate the law.
Therefore, you shouldn’t count on collector’s forgetfulness? Yes, even if they fail to collect at least 10% of the debt from you, they will certainly not forget to settle the loan debt.
How to fill out an application correctly
Drawing up a petition to review a judge’s decision is carried out according to the following rules:
- It is necessary to indicate the passport details of the objecting person on the basis of which the decision was made, and the details of the addressee, the position he holds (in a debt recovery case, the addressee is a judge).
Drawing up an application - In the application itself, you must accurately indicate the date when the court decision was made, the contents of the decision with a list of obligations. It is necessary to note compelling reasons for disagreement if it is impossible to execute the order.
- In the application, it is advisable to refer to the law - in this case it is necessary to indicate that the filing of an objection is carried out on the basis of Article 129 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- In addition to indicating the date on which the order was made, it is important to indicate the date on which the defendant received it.
- The final part of the petition must reflect a request to cancel the judge’s decision, specifying the date when the order was announced.
The application does not need to detail the reasons for the objection. It is important to note what specific decision of the judge you are going to refute: the claims of the creditor themselves, the amount of debt or the procedure for collecting it.
The application must be delivered to the court office or given to the personal assistant or secretary of the judge who made the decision. It is permissible to use postal services. However, if the letter is delayed in the mail, you will not be able to timely file a request to review the decision to repay the debt.
What to do if the court order is canceled: consequences
Often debtors understand that they need to cancel the court order, but they have little understanding of why to do it. After all, the debt will not disappear anywhere from canceling the order: creditors will continue to call, come, and demand the repayment of the overdue loan.
The debtor needs the cancellation of the court order in four cases:
- He really does not agree with the accrued amount, and is ready to challenge it in court. For example, you borrowed 200 thousand rubles, and you were asked to return the entire 500 thousand rubles. The reasons are not clear to you, or you consider them incorrect and illegal.
- He is going to seek a reduction in the amount of debt through the court. For example, through the application of the provisions of Art. 333 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It provides for the reduction of disproportionate penalties. Before the introduction of full regulation in the field of microcredit, organizations often charged hellish penalties. They sometimes exceeded the accrued interest several times. But the courts wrote them off. In particular, from 100 thousand rubles to 1-5 thousand rubles.
- He's going to bide his time to save up some money. But for what - this is an interesting question. The debtor has two reasonable options: either pay the debt or apply for recognition of bankruptcy of an individual. Both the first and second require money.
Cases in lawsuit proceedings are considered for at least 2-4 months. Therefore, stalling for time is a good solution for certain situations.
- He is going to get rid of the claims on the basis of expired statutes of limitations. This is a good move. Let us remind you that the statute of limitations in Russia for overdue loans is 3 years. If during this time the bank (or other creditor) does not go to court and does not settle the debt, it gives the debtor a chance to get rid of the problem through the application of Art. 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Accordingly, after the court order is canceled, the creditor naively files a claim. Here a smart debtor comes to the fore and submits a counter-claim about the expiration of the deadline. The court accepts it for proceedings, and the case is closed. There is supposedly no more debt. No, there is a debt, but not everything is so simple. The creditor simply lost the right to demand repayment of this debt in court.
Cancellation of a court order allows you to gain time, defend your position, raise money or get rid of the debt completely
. After canceling the court order, the debtor does not need to take active actions. Then everything depends on the behavior of the lender. If he nevertheless decides to go to court, this will play into the hands of the debtor. He will have the opportunity to get rid of the debt after the deadline has expired, save money (while the trial is going on) in order to declare bankruptcy. Also, through the court, you can reduce the debt to acceptable amounts.
What kind of document is this?
According to the Code of Civil Procedure, a court order is a single decision of a judge to collect money or to reclaim the movable property of a debtor for claims that are indisputable. Namely:
— on the collection of wage debts;
- payment for housing and communal services;
— for obligatory payments of the homeowners’ association;
- on the collection of alimony;
- in case of violation of the contract.
Moreover, the amount of debt or the value of property should not exceed 500 thousand rubles for civil cases and 400 thousand for arbitration cases.
An important nuance: a court order is not only a court order, but also at the same time an executive document. In other words, for bailiffs this order is the basis for starting enforcement proceedings.
The court order was canceled: what should the debtor do next if the bailiffs start writing off money?
When a creditor receives a court order, he has the right to appeal to the FSSP. He comes to the bailiffs and submits an order to initiate enforcement proceedings.
Let's imagine that you have written an objection to a court order. You sent it to the magistrate, who canceled the document. Copies of the cancellation order are sent to the creditor and debtor within 3 days. But bailiffs are not aware of the latest changes! They conscientiously initiate enforcement proceedings and begin various checks. As a result, the debtor’s salary is suddenly deducted.
What to do in such a situation? Of course, the write-off occurred illegally, and this error must be corrected:
- First of all, we will find out who exactly is conducting enforcement proceedings. This can be done through the official website of the FSSP by searching the bailiffs database. You can find yourself by name and date of birth: https://fssp.gov.ru/iss/ip. You will have access to the production number, contact details and name of the bailiff who is handling your case.
- Next, we contact the bailiff and inform him of the error. You will probably have to visit the branch and inform the bailiff of the magistrate's order to revoke the order. In theory, after this the bailiff is obliged to stop the proceedings and transfer the money back to the account.
- If the bailiff does not compromise and does not accept the cancellation order, we write a complaint addressed to the senior bailiff. A complaint can be submitted through the online reception of the portal, in person or sent by registered mail. At the same time, you can complain to the prosecutor's office. Such a need arises, for example, if the bailiff took note of the decision to cancel the order, but is in no hurry to close the proceedings. As a result, you suffer financially from this.
- Within 30 days, complaints are checked and the necessary decisions are made. All you can do is wait.
The main problem in the procedure and how to avoid it
The main problem in the procedure remains the problem of informing the citizen about the issued court order.
According to the requirements of the law, a copy of the order is sent to the other party via Russian Post. However, the fact of delivery at the place of registration does not guarantee receipt of the letter by the debtor, since he may live at a completely different address.
Moreover, court employees do not always adhere to the time frame for sending letters and do not monitor their receipt by the addressee.
In other words, there is a high probability that a citizen will receive a copy of the order late: after it has already entered into legal force.
In such a situation, the debtor must apply to the court with a request to restore the period for appeal.
To avoid such a situation, it is recommended to receive postal correspondence at your place of registration in a timely manner. And if you are informed about a registered letter, do not delay receiving it at the post office.
Moreover, citizens who know that there is a risk of judgment against them. orders (for example, large rent arrears), it is recommended to periodically check the websites of magistrates. Arbitration orders can be tracked on the “My Arbitrator” website. By law, they must be posted on it no later than the next day.
You can also find out about the presence of debt through your personal account on “State Services” or on the website of the Bailiff Service (FSSP).