Procedure for canceling a court order
This procedure must be carried out by the same judge. This distinguishes it from a court decision, which can be overturned by a higher court (read about the procedure for appealing a court decision). Unlike a court decision on the basis of which a writ of execution is issued, this document has legal force.
Court orders are issued based on:
- notarized transaction;
- an agreement concluded in writing;
- protest of the bill.
- alimony;
- arrears on taxes and other obligations to the state;
- accrued wages that were not paid.
So, you have received a court order, what to do next?
- Decide whether you agree with the requirements for you specified in the court order, for example, to collect tax debts.
- If you do not agree with the court order issued against you, prepare objections regarding the execution of the court order (hereinafter referred to as objections to the order).
- Submit your prepared objections to the order to the judge who issued the order. Do not forget about the 10-day period during which the debtor has the right to file objections to the order.
- Check with the court when you will be able to receive information about the decision made on your objections.
- Obtain a court ruling to cancel the court order or to refuse to satisfy the debtor's request to cancel the order. Although, if you file objections within the established time frame, the judge will have no reason not to cancel the order, which is discussed in more detail below in the material.
USEFUL: watch the VIDEO - how to cancel a court order, write your question in the comments of the video to receive FREE legal advice
Objection to an application to reverse the execution of a court decision
The party to the court case who received the application for reversal has the right to submit to the court its objections regarding the stated requirements. Failure to provide a response will result in the court deciding the case based on the available materials and, most likely, taking the applicant’s side. The ability to provide feedback is enshrined by the legislator both in the arbitration process (Article 131 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation) and in the civil process (Article 149 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation), the main thing is that the counterarguments presented are justified and provable (Article 65 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and 56 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). An objection to the application is submitted to the court in writing with the obligatory indication of the court and the case number. It is better to disclose your position on the case to the other party in advance, in order to avoid postponement of the court hearing.
The main arguments in the objection to the application for a reversal, depending on the specific circumstances of the case, will be information about non-fulfillment or partial execution of the decision made, about an incorrect calculation of the debt, as well as that a reversal is not required in connection with the voluntary transfer of funds. In case of voluntary return of previously collected amounts, a decision in favor of the applicant may lead to his unjust enrichment.
Deadline for canceling a court order
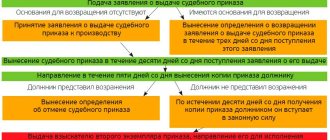
The debtor's party has the right to appeal the document in writing within 10 days from the date of receipt of the court order by filing an objection with the court that sent the judicial act to him.
In this case, the court order on the loan or other grounds for issuing it is canceled, and the creditor is informed of the possibility of filing a claim. If the debtor does not raise objections, the claimant is issued a court order with a stamp, which the claimant presents to the debtor through the bailiff service or directly to the bank (if credit institutions with accounts of the debtor are known).
How does the issuance of a court order affect it?
Taking into account the latest changes to the provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation under Federal Law-100 dated 05/07/2013, the answer to the question of whether a court order interrupts the statute of limitations is unequivocal - it does not interrupt. The amendments approved only one case of interruption of the IDA, when the obligated person takes actions indicating recognition of the debt (partial payment, written response to the claim indicating the debt, etc.).
In accordance with the law and practice of law enforcement, summarized by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the implementation of defense in court in the form of a joint venture is a special case when the limitation period is suspended; after a court order, it does not begin to run again. The legislative justification is as follows: according to Art. 204 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the LED does not flow from the moment of going to court. This rule applies throughout the entire period of defense in court. Suspension is important, since a court decision can be made not only positive or negative; the dispute often does not reach a resolution by the court on the merits and remains without consideration. If the claim is left without progress and then returned or immediately returned, the rule of suspension does not apply, since in fact no defense of the right took place.
SP is a type of defense in court, so similar rules apply to it. This is confirmed in paragraph 18 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 43 of September 29, 2015. The generalized practice of law enforcement is of particular importance when canceling a joint venture.
Restoring the deadline for canceling a court order
If for some good reason you missed the deadline for filing objections to the order and canceling it, then you can always go to court at the same time as filing the objections with a petition to restore the corresponding procedural deadline, justifying and documenting the validity of the missed deadline.
Next, the court will decide whether the reasons for missing the deadline are valid or not.
If you received a court order 2 months after it was issued, and the date of receipt can be seen on the envelope in which you received a copy of the court order, indicate in your objections when you received a copy of the order and attach a copy of the envelope. Reinstatement of the deadline is not required in cases where it is possible to accurately determine the moment the debtor received the relevant order, and the deadline begins to count from the moment the debtor receives a copy of the order.
PLEASE ATTENTION: on the dates on the envelope, since there may be different situations and the envelope may lie in the mail for a long time and, accordingly, the stamps on the envelope may indicate dates when you have already missed the deadline and they will not confirm the fact that you filed a complaint within the established time frame.
It should be noted that in the Plenum the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation) indicates the possibility of filing objections outside the relevant period, but the debtor
- must indicate the circumstances that prevented the timely submission of objections;
- the specified circumstances must have existed during the period when objections could be submitted,
- and objections must be sent by the debtor no later than 10 days from the moment when the relevant circumstances ceased.
Consequences
If the order is canceled due to objections received within 10 days, it will not actually enter into force. Therefore, there will not be any significant consequences for the parties in this case. The claimant will be able to file a claim, and the debtor will present his response in the trial.
If an order that has already entered into force and issued to the claimant is cancelled, the following consequences occur:
- all enforcement measures and restrictions imposed by bailiffs or other authorities are subject to cancellation;
- the arrest of accounts and cards is lifted;
- the employer stops deducting wages;
- the debtor will be able to apply for the return of funds withheld under the canceled order.
According to Art. 43 of Law No. 229-FZ, the bailiff is obliged to terminate the proceedings if the executive document was canceled, i.e. court order. At the same time, seizures of property and accounts, restrictions on travel outside the Russian Federation and on the right to drive transport will be lifted. If the claimant subsequently submits a writ of execution, the proceedings will be initiated anew.
The debtor can also apply for the return of funds actually withheld under the canceled order. The money will be returned to the FSSP deposit within 30 days according to the details specified in the application.
After the order is cancelled, the claimant may file a claim in court. To do this, you need to take into account the limitation periods provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For the period from the filing of an application for the issuance of an order and its cancellation, the statute of limitations is suspended. If a dispute arises about the timing, the claimant must submit an initial application with the date of registration in the magistrate's court.
After canceling the order, the debtor can submit it to the FSSP unit where the proceedings are being conducted. The bailiff is obliged to stop the proceedings within 3 days, and also:
- revoke documents for retention from the debtor’s place of work;
- cancel the seizure of bank accounts and property;
- cancel the search for the debtor and his property;
- remove restrictions on travel and the right to drive transport.
A copy of the decision to terminate the proceedings will be sent to the claimant and the debtor.
Appeal against the cancellation of a court order
The Procedural Code does not provide for an appeal against a ruling to cancel a court order. The fact that the ruling to cancel the order cannot be appealed was also indicated by the RF Supreme Court in its Plenum. By canceling the order, the judge explains to the claimant only his right to file the same claim in the manner of claim proceedings.
Debtor's complaint if the order is not canceled
If you filed an objection to the court order and it was not canceled, look at the grounds for refusing to satisfy your objections.
In fact, the only reason for refusing the debtor to cancel the order can only be missing the deadline for filing objections; in this case, the arbitration court, by ruling, returns the relevant objections to the debtor without even considering them. The magistrate may make a ruling refusing to satisfy an application to cancel the order.
A complaint against a court ruling, taking into account the grounds for its issuance, can be filed with a higher court through the court that issued the order (magistrate, arbitration court of first instance), in which you should indicate to whom it is sent, set out in the complaint all the circumstances of the current situation and indicate , what you are asking, namely, to recognize the determination to return or refuse to cancel the order as illegal, or simply cancel it, as well as cancel the court order.
ATTENTION: if the debtor missed the deadline and the court order entered into force, then he has the right to appeal such a court order in cassation under the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
In this case, the cassation appeal is filed directly with the cassation court, i.e. to the regional court. The details are standard; it is necessary to indicate to whom the complaint is addressed, from whom it is being submitted and who the claimant is.
Indicate what you are filing a cassation appeal against, for example, a cassation appeal against the court order of the magistrate of the Chkalovsky judicial district dated November 11, 2018 in case No. 2-5463/2018.
Directly in the text of the complaint, state all the circumstances, namely, when, by whom and what application was considered, what decision was made on it (a court order was issued), when you received the corresponding order, when you filed objections, including with a petition for restoration of the period by which the court made a decision on your objections. The complaint must allege procedural violations.
Grounds for cancellation
In Art. 129 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation states that if objections are received from the debtor in a timely manner, the judge is obliged to:
- cancel the order by issuing a ruling;
- send the determination to the parties within 3 days;
- notify the claimant that he can present the same demands in a lawsuit.
What arguments and evidence must the debtor present in order to obtain the cancellation of the order? The Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation does not provide a list of grounds on which the court must cancel a previously issued order. In fact, it is enough for the debtor to notify the court of his objections without disclosing the reasons and arguments for such a decision. Even if the received objections do not indicate reasons and grounds at all, the judge will cancel the order.
The claimant will also not be able to appeal the cancellation determination if he is not satisfied with the debtor’s explanations. In this case, a dispute arises between the parties, and it can only be considered in a lawsuit. When filing a claim, the claimant must indicate that he previously filed an application for the order, but the document was canceled. This will allow the debtor to collect the state fee if it had to be paid to issue the order.
How to write an application to cancel a court order?
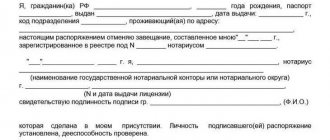
You can get a positive decision on canceling an order by filing an application to cancel a court order containing the following elements:
- court address details;
- Full name (name) of the debtor and the claimant or authorized representatives, indicating the place of residence and location of the parties;
- number of the canceled order;
- the reasons why the debtor objects to the execution of the document, as well as references to partial or complete failure to comply with the above requirements;
- evidence that serves as a basis to challenge such a document;
- list of attached documents;
When is it impossible to return the written-off money?!
In accordance with Part 3 of Art. 445 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, in exceptional cases, it is impossible to return the written-off money, since the reversal of the court decision is possible only if the plaintiff provides false information. Collection cases fall into this category:
- alimony;
- on labor disputes;
- remuneration for the use of exclusive (copyright) rights;
- compensation for harm to health;
- compensation for the loss of a breadwinner.
In addition, the reversal of the execution of a court order has its own characteristics related to the provision of the right to the plaintiff, after the order is canceled, to apply to the court on the same grounds with a statement of claim. If such a claim is accepted for proceedings, the court will refuse to reverse the judicial act, therefore, it becomes impossible to return the written off money, even by canceling the court order, until the court makes a decision on the filed claim.