On January 1, 2021, the moratorium on the collection of penalties for non-payment of housing and communal services expired. In this regard, housing and communal services suppliers have many questions: the main ones were answered by the Head of the Expert Council of the P1 Association, Elena Shereshovets, in a new video from the online magazine “Housing and communal services: dreams come true.”
The management authority can collect from local authorities an increasing coefficient for CG
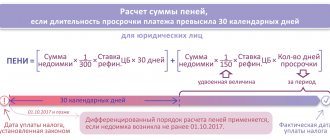
The procedure for calculating penalties for utilities
Penalties are penalties for violations of the procedure for paying utility bills and paying contributions for major repairs. The obligation to pay them occurs in two cases:
- late payment
- payment not in full
Payment of penalties is carried out in the same manner both for payment for premises and utilities, and for contributions for major repairs. The only difference is their size.
The amount of the penalty is one three-hundredth (1/300) or one hundred-thirtieth (1/130) of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation of the unpaid amount in effect on the day of payment. Considering that the refinancing rate has no independent meaning and is equal to the key rate, it would be correct to consider the penalty as one three hundredth of the key rate.
| Penalty amount for payment for housing and utilities | ||
| First 90 days of late payment | From 90 days of delay | |
| Penalty amount | 1/300 key rate | 1/130 key rate |
| Amount of penalty for making a contribution for major repairs | ||
| Penalty amount | Fixed – 1/300 of the key rate | |
Penalties begin to accrue from the 31st day of late payment.
Moreover, their size cannot be more than 1/130 of the key rate of the amount unpaid on time for each day of delay.
Rules, terms, accrual amounts
These are accrued costs for late payments that accumulate on a daily basis. The legislation, we found out, allows you to independently determine its daily value. The penalty for late payment of rent must be within the legal maximum.
Need a calculator: a reliable calculation tool
Would you like to calculate penalties for late payments? Then use such a universal and convenient tool as an online calculator. All calculations take place in rubles. “Where can I find such a calculator?” - you ask. There is a large selection of calculators on the Internet for calculating penalties. We present one of them:
The penalty is calculated by filling out all available columns on the calculator plane, such as: the debt amount, the date of its occurrence and the date of payment.
The amount of interest when there are arrears for electricity and rent
Now there is a proportion according to which the amount of debt interest depends on the duration of non-payment:
| №/№ | Time of non-payment | Amount of penalty |
| 1. | Up to three months | Equal to or less than one three hundredth of the Central Bank rate on the day the delay was detected |
| 2. | From ninety days | Equal to or less than 1/300 |
| 3. | It is illegal if the amount of interest accrued in the form of penalties exceeds 50% of the total debt | |
Information as an example: if the utility debt is fifteen thousand rubles, then the total amount of the penalty should be less than seven and a half thousand. The difficulty lies in the fact that, regardless of the presence of debt, citizens accept the services of public utilities, thereby increasing the debt “basket” and interest.
Penalties are “dripping”: when does the debt “leakage” begin?
The accrual process starts on the next day after the day determined by the final calendar point of the “payment stop”. This calendar “point” is determined in two ways:
- or a condition of the agreement;
- or regulations of the regional utility service.
A number of regional services provide a notification repayment system: interest is accrued from the next day after the debtor receives a special utility bill.
Is it possible not to pay penalties for utilities?
The obligation of citizens and organizations to pay for utilities is established by law.
If you do not make payments on time or not in full, a debt will accumulate, which can be collected in court. At the same time, the procedure for collecting debts for utility services is quite simple - the court issues a court order.
During the period of coronavirus restrictive measures, there is a widespread opinion among citizens that it is possible not to pay utility bills. This is not true. The obligation to pay for housing, utilities and major repairs remains.
Utility service providers do not have the right to demand payment of penalties (penalties) until 01/01/2021. The same rule applies to contributions for major repairs.
Thus, due to the current situation and coronavirus restrictive measures, until January 1, 2021, you do not have to pay penalties.
At the same time, the Supreme Court clarified that this right applies to debt that has arisen since April 6, 2021.
USEFUL : if you have an illegal penalty included in your receipt, feel free to request a recalculation, watch the video in what order to do this
How are fines for services calculated? Can this be done online?
Despite the fact that many citizens are accustomed to using online services to calculate penalties, you can still do it yourself:
- You just need to multiply the values on the calculator, which form the final amount of the penalty.
- It is necessary to convert the existing rate, which will be divided by 300, into a share, instead of a percentage.
- Divide it by 100.
- online
Today, you can find dozens of penalty calculator sites on the Internet. But do not rush to enter personal information into the fields. Trust the resources that are popular among citizens.
The glavkniga.ru service offers its clients the services of an online penalty calculator:
- In the “contribution” field you need to select housing and communal services.
- Indicate the date of actual payment.
- Indicate the date of deposit.
- Amount of debt (how to find out the amount of debt?).
- After clicking the calculation button you will get the result.
The sites klerk.ru and nalog-nalog.ru are no less popular. They operate according to the same instructions.
Examples
Let's give an example.
The debtor did not pay 10 thousand rubles to the management company. Exactly 30 days have passed since the payment became overdue.
In order to calculate penalties, you need 10 thousand rubles. multiply by days that correspond to the amount of delay. Let's say multiply by 20 and then multiply by 9, which is equal to the refinancing rate. Then the resulting value must be divided by 100 and divided by 300. The result is 60 rubles. This is the amount of penalties that will be charged for the entire period of delay.
10,000*20*9/100/300=60 rub.
But keep in mind that from the moment of 91 days, tariffs will rise, which means the amount of the penalty will increase.
Collection of penalties for utilities
Penalties for utilities are usually collected along with the amount of the principal debt.
To collect penalties, utility service providers or another authorized organization with which an agency agreement has been concluded applies to the court with an application for a court order or with a statement of claim in summary proceedings. A calculation of the amount of claims, the basis for such calculation (agreement) and a calculation of the amount of penalties are provided.
The court order issued by the court is sent for execution to the FSSP, where measures will be taken to search for the debtor and foreclose on his property in the event of non-payment of the debt amount voluntarily.
Why out-of-court bankruptcy will not be easy
The main difficulty of the procedure is to prove that a person does not have the opportunity to pay off his debts, say experts interviewed by RBC. This condition makes the borrower dependent on the actions of creditors and collectors, as well as bailiffs, notes Forward Legal lawyer Lyudmila Lukyanova. Extrajudicial bankruptcy is available only to those whose creditor filed a lawsuit and then sent the decision to the FSSP.
“Not all collectors turn to bailiffs to enforce a judicial act: many prefer to collect the debt by presenting a sheet to the bank. It is impossible to initiate enforcement proceedings without a statement from the claimant,” explains Lukyanova. The second difficulty of this process is the actions of bailiffs: due to the high workload, they spend a long time looking for the debtors’ property, the lawyer continues.
“Formally, bailiffs have the right not to complete enforcement proceedings for years, writing off money from meager incomes and pensions, which will mean the inability to use an out-of-court bankruptcy procedure,” agrees Mikhail Alekseev, an expert of the ONF project “For Borrowers’ Rights.” Writs of execution can be issued for individual obligations, and the collection process can proceed first for one debt, then for another. As a result, the simplified bankruptcy procedure will not be simple, RBC’s interlocutor is sure. “Especially for the poorest citizens, for whom it was supposed to be simplified,” he emphasizes.
The number of personal bankruptcies of Russians increased by 70% Finance
Alexey Yukhnin does not consider the procedure hopeless. “The point is that writs of execution do not follow the debtor for the rest of his life. Bankruptcy allows you to write off these debts,” he notes. The requirement for completed enforcement proceedings, according to Yukhnin, will be a guarantee for creditors that the debtor has no property.
Statute of limitations for penalties for utilities
The utility service provider may demand payment of penalties throughout the entire term of the contract and beyond in case of debt.
Another thing is that this debt can be collected within three years (3 years) . In this case, three years are calculated separately for each monthly payment. The statute of limitations for collecting penalties for utilities expires when the statute of limitations for collecting the principal amount of the utility payment, for the delay of which penalties were accrued, expires.
Writing off debts for housing and communal services by region in Russia: judicial practice
Judicial practice on writing off debts for services indicates that courts rarely write off debt. This is due to the lack of the correct legal position among the population and lack of knowledge of the norms of the current legislation, which allows them to protect themselves from unfounded claims from utility service providers.
The consequence of this situation was an increase in the total debt in the country, which is already calculated in billions of rubles. According to statistics from the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, the average amount of a claim in most collection cases ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles. At the same time, bailiffs in enforcement proceedings recover only 20% of all funds in such cases.
Application for write-off of fines on rent
The utility service provider may decide to write off penalties. There may be legal grounds for this or an agreement with the utility organization (agreement).
An application can be written in the following cases:
- The statute of limitations for obligations has expired
- Debtor's bankruptcy
- Purpose of restructuring (agreement with a utility company on debt repayment)
- Private, personal reasons that prevented the fulfillment of the obligation to pay for utilities - illness, disaster, etc.
- Disproportionality of penalties to the amount of debt
- Incorrect calculation of penalties
- Based on the above reasons, the penalty can be written off in whole or in part.
- Suspension of accrual of penalties for utilities
- During the period of coronavirus restrictive measures introduced throughout Russia, a Government Resolution banning the collection of penalties for utilities and major repairs came into force.
NOTE : also read additional tips on installment payments for utilities via the link on our website
Does the Criminal Code have the right to such actions?
Many residents of apartment buildings who are faced with the accrual of interest on unpaid debts are trying to challenge the legality of the accrual of penalties. This issue needs to be dealt with in more detail.
The very concept of “fine” is contained in the sources of Civil Law. In addition, other general provisions related to the calculation of penalties, the procedure for collecting them, as well as the grounds, are contained in the Civil Code.
First of all, Article 317 of the Civil Code establishes the possibility of calculating interest in principle. Article 330 of the Civil Code establishes that penalties may be applied in the field of housing legislation.
Also, Article 333 of the Civil Code also offers a penalty. As you can see, the concept of a penalty is contained in the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation , which means that such collection is permitted by law.
Reducing penalties for utility bills through court proceedings
As a general rule, if no attempts are made to reduce the penalty for utilities, then the court will, of course, take as a basis the calculation provided by the plaintiff. Therefore, I recommend filing a petition to reduce the amount with justification for the objection under Art. 333 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (more details at the link).
In such cases, according to established judicial practice, there should be a comparison of the accrued penalty with the amount of debt, when it is clearly disproportionate to the violated obligation - it is necessary to review the accrued penalties in the direction of reducing utility bills, in particular, a good example in the form of the Moscow City Court’s Ruling dated 05/06/2016 serves as confirmation in case No. 4g-4416/2016.
Other reasons for reducing penalties for utility services include:
- Other noteworthy circumstances of the case under consideration, for example, incorrect calculation of the initially indicated amounts, which led to a dispute (payments to the reserve fund for major repairs, fees for the maintenance of the common property of the house, etc.)
- Penalties should not be collected for the first month, such are the new rules for calculating fines for this category of cases
- If the defendant did not receive information about his debt, for example, the order of delivery of receipts was violated, there was no written requirement to repay the debt in the receipts provided, then all this should be used when deciding whether to reduce the amount of the penalty for a communal apartment
In addition, be sure to analyze the claim of your management company for the limitation period, because if penalties are accrued on the amount of debt outside the three-year limitation period, then you have every reason to demand that these accruals be excluded completely from the calculation of claims.
Why don’t utility companies voluntarily reduce or remove penalties if a person cannot get out of housing and communal services debt?
Everyone can find themselves in a difficult situation when various events occur in life: loss of a job, illness of a utility payer or their close relatives.
Of course, in such cases there is no time for payments that are not paramount. The question of how to avoid paying penalties for rent is the first thing that comes to mind. But the law is the law, even if it is sometimes unfair in relation to a particular citizen...
If utility companies cancel penalties without trial:
- Other residents will suffer, because they pay in good faith, and the negative consequences of delays and losses of managers, in connection with this, may hit their wallets
- Writing off penalties on rent by the head of an HOA or housing cooperative may turn against the chairman, against whom residents and employees may complain that he is reducing revenues by such actions, has entered into a conspiracy, etc.
That is why it is possible to solve the problem of reducing utility services only in court through Article 333 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Summary
The stumbling block between housing rights holders and housing and communal services is the payment of utility payments overdue. The fact is that money for calculating penalties is the only working method of motivating debtors to pay off their debts.
Energy companies, management companies and homeowners' associations have no income other than that received from residents: they depend on each payment. Having a huge debt in the homeowners' association's checking account is a direct path to bankruptcy. Debts increase like a snowball due to the accrual of penalties. Such a tragic ending for management companies and homeowners associations is not beneficial to anyone: neither the supplier nor the consumers.
If a tenant does not pay penalties on utility bills and, at the same time, ignores the “body” of the debt itself, then he faces severe enforcement by a court decision, through bailiffs. But we should not forget an important nuance: the amount of the penalty can be made much smaller or canceled altogether, if we take into account the special circumstances that we talked about.
Can penalties be assessed after the trial?
If the court has decided to reduce the amount of the fine, you should not expect that it will be possible to completely refuse to pay it. The fine will not be charged only if the statute of limitations expires or if the citizen goes bankrupt.
In all other cases, penalties will continue to be charged, albeit to a lesser extent.
Utility debts are an integral part of the lives of many citizens. At the same time, we are not necessarily talking about malicious defaulters; often among the debtors there are completely solvent people who have shown inattention or some negligence. In addition to the debt, a citizen who is overdue for payment will also have to pay a penalty, the amount of which depends on the amount of the debt and the length of the delay. If the homeowner has good reasons for refusing to pay the penalty, he can set them out in a statement sent to the Criminal Code or the court. They may be released from the fine and the need to repay the debt in the event of bankruptcy of a citizen or liquidation of an enterprise. In most situations, the court or the Criminal Code decide to reduce the fine or provide the offender with an installment plan. It will be possible to pay for utilities without aggravating your difficult financial situation.
How to calculate the amount of penalties when paying for housing and communal services
Utility debts tend to accumulate not because of the reluctance of citizens to pay, but because of the meagerness of their family budget. The economic situation in the country is extremely unfavorable; it does not contribute to a wide choice of vacant jobs with decent wages.
Considering that people need to feed their children, pay for basic household expenses and medical services, then delays in paying utility bills are quite natural.
Unpaid payments lead to the accumulation of penalties in the form of penalties. Every citizen should understand: how to calculate housing and communal services penalties, and how they can be written off, reducing the amount of debt.
How to write an application to reduce penalties
The claim to the court consists of the following parts:
- header (information about the court, the plaintiff and the defendant, in this case the Criminal Code);
- full name of the claim (“petition to reduce penalties”);
- main part (describe the plaintiff, defendant in more detail, indicate the name of the court, talk about the subject of the dispute);
- requirements (the plaintiff indicates by what amount, in his opinion, the fine can be reduced).
Documents confirming the information contained in it are attached to the claim.
Payment rules for housing and communal services
The obligation of the homeowner or tenant to pay for the provided housing and communal services is stated in Article 153 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and in subparagraph “i” of paragraph 34 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2016 No. 354.
Payment must be made on time and in full
. The deadline for paying the fee is determined in accordance with the management agreement of the apartment building or the decision of the general meeting of members of the housing cooperative.
If the deadline is not specified in these documents, then the homeowner must pay the cost of housing and communal services no later than the 10th day of the month following the expiration. This condition is specified in Part 1 of Article 155 of the RF Housing Code.
Consideration of the bill
The bill was submitted to the State Duma on June 26, 2019. registered under number 738681-7. On the same day, it was sent for consideration to the State Duma Committee on Housing Policy and Housing and Communal Services. It is not yet known when it will be brought up for discussion.
Will housing and communal services debts be written off in 2021? The new law talks about conflicts of legal norms and technical problems of write-off when there is already a court decision. Therefore, even the approval of the bill will not be the beginning of the introduction of an amnesty in cases of utility debt.
Methods for collecting debt after a court decision has entered into force
Voluntary order
The debtor may be asked to pay the debt in full at one time, or to enter into an agreement on debt restructuring (usually concluded for a period of 6 months, but can be extended). This agreement is the most advantageous option, since it allows you to pay off the debt over a certain period, in equal shares, and not the entire amount at once. The restructuring agreement form is drawn up by utility companies based on the application you submit.
Sample application for debt restructuring for housing and communal services
To the head of Management Company "Zarya" Antonov A.S. from Yakimov S.T. residential address: Mirny, st. Soyuzov 31-2 tel. 34-37-21
Statement
I ask you to consider concluding an agreement with me on restructuring the debt for the use of services (specify the type of service: heating, sewerage, water supply) for residential premises owned by me, located at the address: Mirny, st. Unions 31-2.
As of March 1, 2021, the debt is 46,341 rubles. My last payment was made in October 2021.
The reason for the lack of payment is layoff from work, difficult financial situation.
Date__________ Signature_______________
Compulsory order - with the help of bailiffs
Collection by a bailiff can be made from funds from:
- working-age population: by sending a writ of execution to the place of work (main or part-time);
- pensioners: by seizing pensions and other income;
- disabled people: debt for housing and communal services can be recovered from a disability pension, except in cases where the person is deprived of legal capacity.
Important! The amount of monthly deductions from earnings or other income cannot be more than 50% of the total monthly income.
Other measures most often used by bailiffs:
- seizure of property (including money, securities, current accounts, property in the apartment);
- seizure of seized property and sale at auction;
- introduction of restrictions on leaving the Russian Federation;
- introduction of restrictions on registration actions with property.
See what the bailiff can take away, how to find out the debt from the bailiff by last name.
How to challenge a decision to impose a penalty
Practice shows that management companies often impose disproportionate penalties that exceed any reasonable limits. If the owner of the premises manages to discover this, he can act as follows:
- request a detailed calculation that served as the basis for charging such a large penalty;
- carry out independent calculations, comparing the results with the figures indicated in the payment slip (it is permissible to involve a competent specialist from the parties, for example, a practicing accountant or lawyer);
- write a statement to the Criminal Code, pointing out the discrepancies found (you must attach your own calculations to the letter;
- draw up and send a claim to the court if the application to the Criminal Code is ignored or its acceptance is refused.
Satisfaction of the claim means that the owner will be recalculated and the final amount he will have to pay will be reduced.