In addition to the detailed rights of citizens and legal entities in relation to property rights, the Russian Federation distinguishes the right to own and dispose of property for state entities.
Property of public legal entities - what does it mean and what legal aspects apply to the property rights of these entities?
Public legal entities
The concept of public legal entity (PLE) is often found in legislative acts, but its interpretation is often ambiguous.
Indeed, the term is used in the Civil and Budget Codes of the Russian Federation when clarifying aspects of the participation of PPOs in civil legal relations, but does not have a clearly defined wording.
In legal practice, public legal entities are understood to be some constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
According to Article 124 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the list of subjects of civil law includes not only citizens and legal entities, but also the state.
Subjects of civil law relations are divided into several categories:
- State (Russian Federation);
- Subjects of the Russian Federation:
- republics;
- autonomous regions;
- autonomous okrugs;
- the edges;
- regions;
- cities of federal significance.
- Municipal entities (urban or rural settlements and other territorial units prescribed in Article 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Any of the listed entities territorially, legally, legislatively and constitutionally has a special public status and is considered a public legal entity.
Powers of the state over private land plots
Unlike other objects of property rights, land is immutable and unchangeable. As property, it cannot be destroyed or otherwise removed from civil circulation. For this reason, the state retains some of its powers in relation to plots that are used by private individuals.
For these purposes, the state uses the following mechanisms:
- registration and re-registration of land plots;
- control over the reclamation state of farmland;
- bringing the perpetrators to justice;
- requisition of land holdings.
In addition, legislation in the field of nature conservation and ensuring the preservation of land is improved every year, and more and more responsibilities and duties fall on the owners.
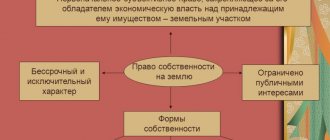
Ownership
Article 212 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation gives PPO the right of ownership on an equal basis with other entities, unless otherwise established by law.
Ownership, management and disposal of property by subjects are recognized and protected by the Constitution if it meets several conditions:
Property relations of public legal entities are regulated in the same way as those of civil entities and legal entities.
What is the property of public legal entities in simple language and by what rules is it established? In accordance with subsection 3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the definition refers to property (objects of civil rights) owned by state entities.
There is a strict hierarchy in the definition of property rights. The right of ownership in the Russian Federation (in its composition and in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation), as well as in municipalities, arises on the basis of Federal Law No. 52-FZ of November 30, 1994 and Art. 218 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Property rights of state public legal entities
The legal basis for the right of state property is enshrined in Art. 214 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to the law, state property is property that:
- is property of the Russian Federation (federal property);
- is the property of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (property of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation).
The property rights of state public legal entities are assigned to unitary enterprises and institutions . The responsibilities of enterprises include ownership, management, use and disposal of state property on the basis of economic management or operational management (Articles 294, 296 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The list also includes the treasury, which consists of funds from the federal budget and budget funds (treasury) of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The state has the right to own all types of federal property, including limited and withdrawn from circulation.
There are a number of objects of civil rights that are legally assigned to state public legal entities by Resolution of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation No. 3020-1 dated December 27, 1991 (as amended on December 24, 1993, hereinafter referred to as Regulations*).
Federal public property includes the following property:
- land not owned by citizens, legal entities or municipalities;
- subsoil and fossil resources;
- forest fund;
- water resources (including territorial waters);
- resources of the continental shelf and marine economic zone;
- railways;
- production facilities for the production and use of nuclear and radioactive materials (nuclear plants, nuclear weapons);
- historically significant objects on the federal balance sheet;
- objects of cultural heritage of federal significance;
- mints and other enterprises for the production of state signs, etc.
The listed objects are withdrawn from circulation and cannot belong to private or legal entities. The state has the right to dispose of property in accordance with its own needs, taking into account the benefits received by interested parties.
Property of municipal public legal entities
The municipal form of ownership is regulated by Art. 215 Civil Code of the Russian Federation . The property rights of this subject of civil legal relations extend to objects of civil rights that belong to public legal entities on the basis of municipal property rights.
Property is assigned to municipal enterprises with the rights of economic management or operational management (Articles 294, 296 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The Regulation* classifies the following objects as the property of municipal public legal entities within the framework of the responsibility of the local executive authority:
- housing and non-residential stock;
- urban engineering infrastructure facilities;
- educational and healthcare institutions;
- social facilities, etc.
Property also consists of local budget funds and other funds not distributed between municipal institutions and enterprises (municipal treasury).
Public property management
Like any property, the property of public legal entities can be used to benefit the owner. The exercise of property rights occurs through the participation of these entities in civil legal relations (Article 124 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Property management is carried out in accordance with Art. 125 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is performed as follows:
- Management of federal property. The rights to manage property of state public legal entities (the Russian Federation and constituent entities of the Russian Federation) are exercised by federal government bodies (Articles 71-73 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation).
- Municipal property management. The rights to manage property of municipal PPOs are exercised by local government bodies and persons whose competencies comply with the requirements of Art. 125.
Since the property rights of state and municipal PPOs are built on the principle of separate property, these entities are not liable for each other’s obligations (Article 126 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Legal status of land owner
In a general sense, the status of a user differs little from the owner of a land plot. However, in a legal sense, cases are allowed when users may be persons who do not have the right to own property. In turn, the owners always have all the rights of users, unless by agreement or legal requirement they have granted these powers to other persons.
Unlike persons who have exclusive rights to use the site, the owner has the right to:
- sell or donate a plot;
- rent it out;
- used as collateral for debt obligations.
But due to the specifics of the property - land, the owner is assigned the same responsibilities as those defined by the Land Code for users of land plots.
Unlike users, who bear responsibilities individually and only for their own actions, owners are also responsible for the actions of those persons for whose use they provided the land.
Thus, along with a wider list of powers, owners also receive more responsibility.
Transfer of ownership rights of public legal entities
In accordance with Art. 217 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, property rights of state and municipal owners can be transferred to civil and legal entities. This right is especially often of interest to potential land owners.
The transfer of objects is carried out in accordance with privatization laws. Privatization is limited for some legal entities and non-profit organizations.
In addition to land plots, as part of privatization you can purchase:
- enterprises;
- industrial and civil buildings and structures, including unfinished ones);
- shares of open joint stock companies.
How to transfer the property of public legal entities into private and how to buy a land plot? The procedure for acquiring and terminating ownership of state and municipal public legal entities is regulated by the relevant articles of the Civil and Land Code (unless otherwise provided for by law for property).
Features of land acquisition
Civil legal relations in relation to such part of the property of public legal entities as land are additionally regulated by the Land Code.
In 2021, rights to a land plot owned by state or municipal property can be acquired as follows:
- erect a residential building or other permanent structure on leased land;
- organize a peasant farm on leased land in a rural settlement;
- win a tender for the sale of land plots.
To make sure that the land is owned by a public legal entity, you need to find a plot free from development, but formed in accordance with the requirements of the Land Code of the Russian Federation (Article 11) on the cadastral map of RosReestr.
If the information on the electronic resource does not correspond to reality, accurate information can be obtained by requesting an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
The property rights of public legal entities are clearly regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation. The property of the PPO is the property of the state, its subjects and municipalities, which the owners have the right to dispose of in the interests of the public-territorial collective.
The procedure for managing public objects of civil law relations in the Russian Federation is determined by the Civil and Land Codes, as well as relevant laws and regulations.
Responsibilities of a land user
Land, unlike other objects of property rights, is a natural resource, which determines its special legal status. In this regard, the legislation assigns certain responsibilities to users of land plots, which ensure the preservation of the land as part of nature and the rational exploitation of the capabilities of individual plots.
Among the responsibilities, the Land Code identifies:
- Ensuring the targeted use of land resources in accordance with the rules established by government agencies and the law.
- Ensuring the safety of engineering signs and other distinctive devices installed by employees of public services and private cadastral engineers.
- Periodic or continuous implementation of measures to ensure the safety of the environment, especially fire safety measures.
- Payment of land tax established by law.
- Compliance with construction standards and the general urban planning plan when constructing buildings on the territory of one’s site.
- Prevention of land pollution, land reclamation depletion, and reduction of fertility.
Land legislation contains many rules aimed at limiting the rights of users in relation to their lands. Thus, the norms of the Land Code are aimed specifically at ensuring the preservation of the original properties of the country’s land resource for the benefit of future generations.
Rights and obligations of participants
Public lands may, in some cases, be provided for use by citizens and legal entities (on the basis of lease, permanent perpetual use or ownership). Moreover, the specific set of rights and obligations of these persons will directly depend on the specific right on which he receives the property. General rights include:
- the ability to use the land at your own discretion (including growing various plants, raising animals, and engaging in other types of economic activities);
- the right to erect buildings on it;
- the opportunity to carry out entrepreneurial activities;
- the right to transfer land for use to third parties (but not always).
It is worth considering that all these rights are limited by the type of permitted use of the site, which the owners must take into account when operating it.
For example, if the land is intended for agriculture, but does not allow the construction of residential buildings, then it will not be possible to build them legally. Therefore, the main responsibility of each owner is to use the public land provided to him only for the intended purpose.
Other responsibilities may include:
- compliance with the law when operating the allotment;
- payment for it (if its provision was not free of charge);
- granting the right to limited use of land to other citizens (that is, easement) in cases established by law;
- ensuring the safety of individual objects located on the territory of the allotment (if they are subject to special protection);
- other duties established by current legislation.
When allocating a plot of land on a lease or free use basis, this transaction must be documented with the help of an appropriate agreement. It is in this document that the mutual rights and obligations of both parties will be officially established.
Drawing up an act of transfer of a land plot to a land donation agreement will help protect your rights. Large families can receive land on preferential terms. Read more about this in our article. To carry out land surveying, you will need to collect a package of certain documents. You will find the list here.
Participation in property turnover
Participation in property circulation implies the use of property that is publicly owned for its intended purpose.
PPOs take part in privatizations and can seize or confiscate property for the needs of the state. PPOs must necessarily serve the interests of the country and act as a customer for various services.
Public legal entities have a legal right to participate in the authorized capital.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages include the following:
- protection from fraudsters
- no taxation;
- replacement of property in case of loss;
- possibility of property improvement through a social tenancy agreement.
Disadvantages include:
- a citizen does not have the right to give, sell, or dispose of property;
- a citizen has no right to contribute as collateral for a mortgage loan;
- a citizen may lose the right to use property.