Municipal property is another type of property ownership adopted at the legislative level in Russia. It has much in common with state ownership rights. Municipal ownership includes property bases managed by rural or urban settlements, other municipalities and entities. The owner, on behalf of these entities, carries out a set of management actions regarding the movable or immovable fund. Local government regulates, manages and controls the activities of facilities.
Municipal property is property owned by a specific government body. It can be considered using the example of government medical institutions, universities, public utilities and other institutions. Ownership of municipal property is carried out by local government. The city, population, republic can use, manage and own the object. Moreover, the property is used to meet the needs of Russians who live in the territory of the municipal area.
Subjects of municipal property rights
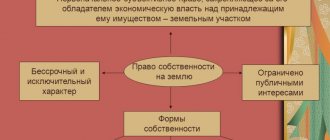
Based on the basic provisions of Article 214 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it can be argued that land and other natural resources that are not under the control of private individuals belong to state property. And the management of these resources is carried out by government bodies, which perform all necessary actions on behalf of the Russian Federation.
Thus, all resources that have material or intangible value are distributed among several subjects of property rights. And one of these entities is the state. It is worth noting that the entire volume of property that has been registered is owned and managed by the state, in turn, divided into several types.
Firstly, these are federal resources that are under the control of federal government structures. All resources that belong to urban and rural entities are controlled by municipal authorities.
The right of state and municipal property is regulated in accordance with current civil legislation.
All issues that affect municipal property belonging to specific administrative entities are considered in Article 215 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on its key provisions, the municipalities themselves will act as subjects of municipal property. Thus, control over resources will be distributed between authorized municipal authorities, local representative authorities and municipal enterprises and other entities that own certain material assets, and which keep records of them and rationalize the use of this property.
Characteristics of municipal property
Use and disposal of the mun. property objects are carried out only on behalf of the municipal formation. Thus, local government bodies have the right to provide municipal property facilities for a short-term or permanent period to both individuals and legal entities. In some cases, property may be transferred to the state authorities of the Russian Federation (various subjects of state power of the Russian Federation), and other local government bodies.
Property can be transferred to individuals or legal entities
The rights of local authorities also include the ability to alienate property and carry out transactions in accordance with federal law. At the same time, representative bodies approve the procedure for managing and using municipal property objects, and executive authorities are actually the owners, users and managers of such property, including through objects and vesting powers in the relevant bodies.
Note ! However, the Law of the Russian Federation of October 6, 2003 does not include the population among the subjects of use and disposal of municipal property.
In turn, the legislative power does not interfere with the resolution of emerging issues and problems (except those that directly relate to the budget) through a referendum of local significance. Property objects owned by local government authorities may be transferred in accordance with the agreement to bodies of territorial public self-government. Fully organized municipal property is entered into the general register of local government.
Note ! The right and obligation to form such a register (tasks of the person responsible for the register) belong to bodies of special competence, which were determined on the basis of a decision of a representative body of local government.
Local authorities can carry out various transactions regarding such property within the framework of federal legislation
The authorized body must:
- within a month, enter information on transferred property objects into municipal ownership into the unified register;
- within a month, send an official letter to the administration, a specific ministry, or department stating that this enterprise or institution has become municipal property;
- promptly accept all information and changes relating to municipal property objects.
For specific objects transferred into the ownership of the municipal government and entered into the appropriate register, the competent authorities for regulating all property issues and tasks are obliged to:
- draw up, on the basis of the legislative framework, the constituent documents of municipal institutions, enterprises and other objects, the authorized capital of which includes financial investments that constitute municipal property;
- on the basis of a standard provision approved by government bodies of the Russian Federation for the regulation and control of property objects, approve charters and conclude agreements (contracts) with the main managers of enterprises and institutions that are municipally owned;
- re-register lease agreements, rental agreements, and use of municipal property facilities.
Competent authorities are required to prepare all necessary documents and control property objects
Amendments to the unified register of municipal property are made by the relevant competent authority for the management of municipal property in accordance with:
- by order of a higher authority;
- by order of a higher authorized body (committee, fund) for the regulation and control of property objects;
- act of receipt of the object;
- property purchase and sale agreement;
- court decision;
- other regulatory act in accordance with current legislation.
A note on the inclusion of a property object in the unified register of municipal property or removal from it on the grounds specified in the legislation of the Russian Federation must be made by the competent authority for control over the property object within three days before the decision is made.
Note ! When maintaining a unified register, special attention is paid to the above-mentioned decisions of the competent authorities (most often this is a municipal financial department, a committee for the control and development of property objects and other authorities authorized under the legislation of the Russian Federation).
Property objects are registered in a special register
An equally important difficulty becomes the question of the boundaries of the “inviolability” of property objects of municipal ownership when re-registering property from municipal to other public property (for example, into the state property of the Russian Federation or a constituent entity of the Russian Federation). Municipal property, qualifying in accordance with legal characteristics as a type of public property, at the same time has some individual characteristics associated with the subjective right to local self-government.
The system of transfer of property objects from municipal to federal and state ownership of the Russian Federation provides for the mandatory consent of the local government body for a transfer of this nature. All disputes about the right to ownership of property objects (about the legally justified location of specific property in the possession of constituent entities of the Russian Federation or in municipal property) are resolved in court in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Note ! This legal provision was introduced in the Ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation No. 542-O dated December 7, 2006. The significance of this issue is supported by the Constitutional jurisprudence of the Russian Federation.
In connection with the above, it can be noted that municipal property contains a large network of property objects for both economic and social purposes. The quality of life of the population depends on the effective sale of such property.
Types of municipally owned objects
The right of municipal property belongs to the category of public law. This is an independent form of property rights, which provides that in the process of managing certain resources, the interests of local representative authorities and the population of the municipality are taken into account.
The exercise of municipal property rights occurs with the active participation of the authorities of specific administrative entities, and taking into account the interests and demands of local residents.
The following may act as an object of municipal property:
- securities and funds owned by public entities;
- monuments of historical and cultural significance (except for those objects that are recognized as national treasures);
- household items used by government agencies;
- vehicles, as well as industrial and production equipment that is used by enterprises under the control of self-government bodies;
- different forms of real estate, namely residential premises, land, industrial buildings and much more.
The right of municipal ownership of land also has some features. In particular, the municipality cannot control those resources that are classified as property of regional or federal significance.
Distinction between the treasury and the “distributed” property of the municipality
In accordance with the current norms of civil legislation, municipal property is divided into two main categories:
- resources that are assigned to certain enterprises and departments of municipal importance, and that use property to conduct certain economic activities. In this case, income from the use of property will belong to the enterprise minus taxes and other fees;
- resources and values that make up the coffers of administrative education. In this case, the treasury will consist of those funds that are available to the local budget and the property that is not under the control of municipal production structures.
Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that the total mass of property of the municipality consists of several parts that practically do not interact with each other. Recognition of the right of municipal property is based on the fact of the presence of certain values that will be objects of protection from irrational and illegal use.
The objects of municipal government property can only be those property values that are necessary to resolve issues of a local nature.
The procedure for the formation of municipal property
Municipal property has a certain independence from state property, and therefore has a public-state character. It is created by municipal authorities, or the upper echelons of government, by transferring property to the disposal of the municipality. The financial component consists of the local budget, as well as taxes and fees. The legislation also notes the possibility of commercial acquisition of municipal property, i.e. purchase, exchange or gift. It is also possible that municipal property may be exaggerated when municipalities are united, thus the property of each of them passes into the common property of the newly formed municipality.
Bodies exercising owner rights on behalf of municipalities
In accordance with civil legislation, municipal property is under the control of structures that are in one way or another connected with the representation of interests of national importance at the local level.
Based on the basic provisions of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the management of local property is carried out by those structures that are registered with the authorities and are authorized by law to perform duties of this nature.
Thus, municipal resources that have material values are managed through:
- enterprises and institutions to which certain resources are assigned, and whose registration is confirmed in municipal structures;
- local government bodies, which have the right to manage certain values, guided by the interests of the administrative entity and local residents;
- elected authorities, that is, government structures that represent the interests of the state locally and are elected through elections with the participation of the population of the administrative unit.