The concept of “intellectual property” was not clearly formulated until the end of the twentieth century; it was used by lawyers and economists only as theoretical reasoning. However, in 1967, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) was approved in Stockholm. Since that time, the concept began to actively develop, including all new results of mental human labor.
With the active development of the Internet and social networks, we are increasingly faced with violations of property rights to text, photo and video content. Creators often do not know how to post materials online in such a way that no one can appropriate them. If you are faced with the appropriation of your copyright laurels by someone else, seek advice from competent lawyers specializing in such issues.
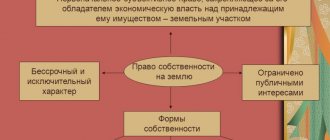
What is intellectual property
According to the definition of WIPO (in English this abbreviation looks like WIPO), intellectual property is the right to the results of the creation of the human mind. Art. 1225 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation reveals this definition, clarifying that, in addition to the results of mental activity, this concept also includes means of individualization. Both are protected by law.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation also adds signs of intellectual property to the definition for a more correct interpretation and determination of whether a specific item belongs to the concept. These are the signs:
- Intangibility. It is necessary to clearly understand that if a thing exists, it is material, and the rights to it are also regulated by law. However, the methods of owning and disposing of creative objects differ from the manipulation of property in the classical sense. It is intangibility that allows this to be realized.
- Absoluteness. The author is always opposed in law to everyone else. And the absence of a ban does not give the right of ownership and use to other people.
- The immaterial is embodied in the material. For example, an idea becomes a text. Music - a record. However, ownership of a material reflection of a work does not give rights to intellectual property.
- The object must be classified as a given type of property at the legislative level , that is, it must be prescribed in legislative acts.
The last point is rapidly losing its relevance with the advent of ever new means of individualization. Such as, for example, a domain name or nickname, avatar. However, at the moment in Russia it is possible to protect rights only to objects prescribed in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
In the Internet
Protecting intellectual property on the Internet is a particularly complex area. Today there is no mechanism that would work successfully. All attempts by the state to eliminate “piracy” end in failure.
There are certain features of protecting intellectual property on the Internet:
- It is often impossible to locate the person who infringed the rights.
- There are no ways to completely block access to a site with controversial materials.
- It is extremely difficult to collect compensation from violators.
Legal protection and protection of intellectual property on the Internet is currently carried out according to the following scheme:
- The copyright holder can contact the site owner personally and ask to remove the controversial content.
- In case of refusal, you can file a lawsuit.
- The authority makes a decision on the need to remove the content, otherwise blocking will follow.
- If the site does not carry out the sentence, then access to it is limited in the territory of the Russian Federation.
But it is important to consider that blocking occurs exclusively for users from Russia. The decision does not apply to other countries. This fact makes it impossible to completely restrict access.
Users can access the portal from a foreign server using VPN and other methods. The resource loses part of its audience, but still remains accessible.
There are currently too many issues of legal protection of intellectual property on the Internet. It is not so easy to destroy “piracy”; users will always come up with new methods to circumvent the prohibitions.
Types of intellectual property
As noted earlier, in Russia only those enshrined in Art. 1225 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. All others cannot be recognized as such, and therefore their protection at the legislative level is not implied.
Copyright. This is a legal term that gives authors the right to the works they create. In addition to literary works (texts, stories, novels, plays, and so on), copyright includes such objects as musical works, paintings and sculptures, films and videos, computer programs and databases, advertising products, maps and drawings.
Copyright arises automatically when an object is created. They remain with the author throughout his life. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation reserves the right for each person to make claims if it is established that materials or part of them have been used by other people without reference to the author or without officially issued permission.
Related rights. As the name suggests, these include rights related to copyright. What we mean here is the ability to manage intellectual property for performers, creators of phonograms, arrangements, remixes, publishers, translators, and so on.
Related rights arise according to rules similar to copyright. However, it is worth remembering that their appearance is possible only if the consent of the author has been given. For example, reproduction of a musical work is possible only if there is a license agreement. In its absence, such actions will be interpreted as a violation of copyright.
The exception is works of folklore. Related rights to them can be acquired without additional documents. Also exceptions are works whose authors are no longer alive (in the absence of legal successors), since with the death of the creator, copyright ceases to be valid unless its transfer has been formalized.
Patents. This concept implies the right to any invention. At the same time, the creator has a legislatively enshrined opportunity to decide who, how and when can (or, conversely, cannot) use his invention. What is important to society is that in exchange for patent rights, the creator shares detailed technical documentation on the creation and operation of the device.
In patent law, in turn, there are three types of intellectual property:
- Inventions. These can be not only technical structures, but also biological derivatives: substances or strains of microorganisms, chemical formulas, genetic structures.
- Utility models. This must be a new and industrially applicable object, a certain technical solution that relates to a specific technical device.
- Industrial designs. This concept means an artistic and design solution for a product, which determines its future appearance and user characteristics.
Non-traditional intellectual property. This is a general group that includes objects that are not subject to copyright, related rights and patents. These include:
- know-how (the right to trade secrets);
- breeding achievements (rights to new plant varieties);
- topographical objects (geographical names, names of places of origin).
Personalization means. As the name suggests, these are any objects that allow legal entities, goods, and services to stand out from the background of identical ones. This group includes:
- Trademark. This concept means a distinctive designation that allows one to identify a specific product among a mass of similar ones.
- Brand name. Allows you to identify the entire enterprise as a whole. Often has nothing to do with the products manufactured or services provided.
- Name of place of origin of the goods. Provided with a certificate obtained as a result of state registration.
For each type of intellectual activity, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation has its own chapter, which describes in detail all the procedures relating to the acquisition, protection and preservation of rights.
Signs
The key features of personal non-property rights are the following:
- Lack of material character. There is no monetary content and no possibility to evaluate the rights in any equivalent value. No remuneration. This feature prohibits other persons from taking measures to collect from an object that has personal rights.
- Individualization of personality.
- Impossibility of alienation and transfer in any other way. There is a group of special objects. These include health, life, inviolability of personal and private life, honor and dignity, family and personal secrets, results of intellectual activity and others.
Intellectual Property Protection
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation implies some features of the procedures for assigning and protecting intellectual property rights for each group of objects. However, there are also general methods that apply to any case. These include:
- recognition of rights - including procedures for securing the right to a specific object;
- suppression of violation - cessation of unlawful use;
- compensation for losses - including payment of lost premiums;
- seizure of counterfeit goods – both physical and from consumer access;
- publication of the court decision.
If violations of intellectual property rights are established, the law provides for punishment in the form of civil, administrative and criminal liability.
Most often, fines are imposed during the proceedings. However, plagiarism and illegal use of copyright or related rights are subject to criminal liability, including imprisonment.
Sources:
Link to the website of the World Intellectual Property Organization
Peaceful resolution of the dispute
Methods and measures for protecting intellectual property suggest another way. You may not file a claim and try to reach an amicable agreement with the other party. Lawyer Goloveshkin will help you with this.
How the whole process goes:
- Initially, the lawyer prepares documents and forms a legal position.
- Contacts the other party.
- Arranges a meeting.
- All parties to the dispute gather at one table.
- The lawyer talks about the claim and suggests ways to resolve it.
- There is a discussion of the nuances.
- Often it is possible to reach a common solution.
What can we agree on?
- On the complete cessation of use of the disputed object.
- On the continuation of its use, but with payment of remuneration to the owner.
- About compensation for violation.
Protecting a company's intellectual property through peaceful negotiations is preferable to litigation. Lawyer Goloveshkin recommends starting from this stage. It is possible to avoid a lengthy process and save time.
If negotiations fail, you can always go to court. Therefore, you have nothing to lose in the future.
Types of non-property rights to personal integrity of a citizen
Moral legal powers in this context relate primarily to life, health and movement, as well as related capabilities. In accordance with article number 150 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, life has intangible value and is one of the priority objects of civil rights protection. It is the Civil Code that first of all guarantees the inviolability of life.
According to the provisions of article number 1085 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, cases of physical injury to citizens of the country are punishable by law and require compensation for lost income that the citizen could have received while remaining in health. Also, the guilty party is obliged by law to reimburse the costs necessary for treating the victim, purchasing medications, providing the necessary outside care, undergoing a course of sanatorium treatment, and so on. The law itself establishes the amount and scope of compensation in such cases based on the provisions of the Civil Code. In addition, the imposition of specific liability may be carried out in accordance with the contract. For example, paragraph three of article number 1085 provides for the inclusion in the employment contract of conditions for compulsory medical insurance of employees with payment of associated expenses by the employer. In turn, article number 1093 states that the reorganization of a legal entity entails the transfer of the rights and obligations of this legal entity to the legal successor.
A similar category of rights includes freedom of movement, determination of place of stay and permanent residence. According to article number 22 of the Russian Constitution, absolutely all people have the right to make their own decisions regarding these issues. The protection of this legal power is carried out by the Civil Code of the country, article number 150 in particular.
Types of non-property rights to the inviolability of a citizen’s life
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the right to personal and intra-family secrets, private documentation, and home is protected:
- Personal and family secrets. This legal authority is determined on the basis of Articles No. 23 and 24 of the Russian Constitution. Protection of material wealth is carried out in accordance with Article No. 150 of the Civil Code. This article defines a ban on the collection, storage and distribution of any information that affects the private life of a person without first obtaining consent from that person. At the same time, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for relevant norms regarding the protection of personal life with the involvement of third parties. Thus, doctors, lawyers, notaries, bank employees, etc. are obliged to preserve the confidentiality of clients (patients) without disclosing it.
- Private documentation. The legal foundations of the Russian Federation and archives determine the status of preservation and protection of private documentation belonging to a citizen as property and on the basis of a procedure determined by law, classified as archival documents. This right applies to documents that contain private information. The owners of such documents can be all citizens of Russia, including senders who used the services of the postal operator. The right to private documentation also affects the privacy of telephone conversations. The basis for its occurrence is the conclusion of an official agreement with the appropriate content between the client and the specialized organization. As for private documentation, the right to its inviolability arises from the moment the documentation was given an objective form. Moreover, from the point of view of its content, this right gives citizens the legal authority to make changes or additions to documents, determine the procedure for processing these documents, request a refund, and so on. When sending documentation by post, service employees are responsible for the safety of information. Thus, any violations require payment of compensation.
- Housing. The home of a citizen has absolute inviolability based on the provisions provided for in Article No. 25 of the Constitution of the country. This article defines a ban on the entry of third parties into a citizen’s private home without first obtaining consent from the residents. The exception is those cases in which entry into a home is conditioned by a court decision or other conditions provided for by Federal legislation. Housing becomes inviolable due to the conclusion of a rental agreement, joining a cooperative, acquiring ownership rights, and so on. Both owners and tenants, as well as family members living with them, can be considered as holders of the right to inviolability of the home. The obligation to respect the right to privacy also applies to employees of hotels and inns, and so on.