Requirements for the content of a statement of claim for recognition of ownership rights Sample statement of claim for recognition of ownership rights What evidence is needed to file a claim for recognition of ownership rights in court State duty for recognition of ownership rights Jurisdiction for recognition of ownership rights
A claim for recognition of property rights must meet the requirements established by the civil and civil procedural legislation of the Russian Federation.
First of all, you need to decide on the grounds that will serve as your “support” in achieving a positive result. Section 2 of the first part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as other federal laws and by-laws will help you with this.
This stage should be approached very carefully, since an incorrect basis for establishing ownership will lead to partial or complete refusal to satisfy the stated claims.
Ownership rights can be recognized for such types of property as:
- Land plot
- Building, house, apartment, garage
- Unfinished construction projects
- Unauthorized construction
- For a share in the property
- Car and other vehicles
This list of claims is the most common and is not exhaustive.
Lawyer for property rights in St. Petersburg. Tel.+7 Telephone consultation
When is an application needed?
The need to go to court arises when recognition of the right is required:
- in the order of inheritance in ambiguous situations (in case of ambiguous interpretation of the will, in disputes between heirs, in case of incorrect or untimely execution of documents);
- for an apartment in a new building on the basis of an investment agreement or an agreement on shared participation in construction, when the work is completed and paid for, but the developer does not issue the documents necessary to register ownership (Articles 208, 218 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- if previously executed documents contain errors, typos, absence of important data and other inconsistencies with legal norms;
- due to the loss of title documents;
- in connection with an invalid transaction;
- if the documents have not been drawn up, but the fact of long-term (more than 15 years) conscientious use of this real estate has been established - acquisitive prescription (clause 1 of Article 234 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- other reasons.
The rules establish:
- Federal Law No. 220-FZ of June 23, 2016.
- Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-05-06-03/21270 dated 03/19/2020.
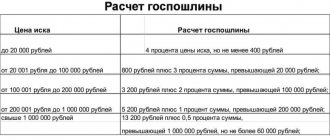
State duty for recognition of property rights (in cases considered by courts of general jurisdiction)
Property is subject to assessment, and the law says that state fees for this category of cases must be paid based on the value of the object to which rights are claimed (the price of the claim).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation refers to a norm that precisely establishes how the amount of state duty is calculated for claims of a property nature - clause 1, part 1, article 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of calculating state duty. The cost of the property is 3,000,000 rubles. The state duty is: 13,200 rubles (amount up to a million rubles) + 2,000,000 rubles. x 0.5% = 23,200 rubles
How to compose it
The Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation contains recommendations for drawing up claims, requirements for filing, and rules for filing a lawsuit (Articles 131, 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation). For a claim to an arbitration court, additional requirements are determined by Art. 125, 126 APC. If a document is not drawn up according to the sample, it will not be accepted for consideration by the court. A claim filed with the court for recognition of ownership of an apartment contains the following information:
- full name and address of the court;
- information about the plaintiff and defendant: full name, registration, contact details, identifier (SNILS, INN, passport details, etc.); if the defendant is an organization, its name and address;
- information about violated rights and a list of requirements presented to the defendant;
- a list of grounds for filing a claim and a list of evidence supporting these grounds;
- the cost of the claim;
- a list of attached documents indicating the number and date of each, including a document confirming payment of the fee;
- plaintiff's signature.
Claims for damages
- Claims for compensation for damage caused as a result of an accident (insurance compensation, insurance payment) filed against the insurer under compulsory motor liability insurance
- Claims for compensation for damage caused as a result of an accident, brought against the tortfeasor (the culprit of the accident, and not the insurer)
- Claims for compensation for health damage caused as a result of an accident at work (occupational disease)
- Claims for damages in connection with the death of a breadwinner
- Claims for compensation for damage caused by flooding of premises
- Claims for damages caused by dog attacks and bites
- Claims and compensation for damage caused by illegal actions of the bailiff
- Claims for compensation for moral damage
Features of the motivational part
This part of the claim is drawn up in any form, but with precise, succinct, logical and consistent content. These are important conditions for satisfying a claim for recognition of ownership of an apartment. In accordance with Part 4 of Art. 92 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, the reasoning part of the statement of claim sets out the rationale for filing an application to secure the claim and the interim measure that must be taken. The reasoning part must contain an indication of the plaintiff’s requirements to the defendant and legislative arguments for satisfying the claims, i.e. references to laws and other regulatory legal acts. In the claim, it is important to clearly and briefly describe what the violation (or threat of violation) of rights is, what the defendant must do in a claim for recognition of ownership of the object in order for the said violation to be eliminated.
In addition, in his claim, the plaintiff is obliged to prove his claim, refer to the circumstances on which he bases it, provide appropriate arguments and evidence confirming these circumstances (documents, written testimony of witnesses, etc.).
To make your claim more convincing and help solve the problem, study court decisions on similar cases. The database of judicial practice in ConsultantPlus will help you find them (get free access to it by clicking on the link below). The database contains decisions of all Russian courts, and the search is as simple as in Yandex. Be sure to refer in the text to those cases that the court decided “in your” favor.
Claims for compensation for damage caused by flooding of premises
(see claims and comments on the topic)
Statement of claim for compensation for damage caused by flooding of the apartment due to the fault of the management company
Statement of claim for compensation for damage caused by the management company (sample)
Statement of claim for compensation for damage due to flooding of an apartment (we recover the cost of restoration of the apartment, legal costs - state fees, costs for legal assistance, costs for the services of a damage appraiser)
Statement of claim for compensation for damage caused by flooding of an apartment
Statement of claim for the recovery of funds in compensation for damage caused by the flooding of the apartment when extinguishing a fire in the apartment above
Statement of claim for compensation for damage caused by flooding of the apartment (cost of restoration of the apartment, cost of damage assessment services, interest, and other expenses)
Sample statement of claim for recovery of damage caused by flooding of an apartment and recovery of lost profits. Demands are made for the recovery of an amount amounting to the material damage of the plaintiff - the owner of the apartment, as well as lost profits, amounting to the funds not received by the plaintiff from the transfer of the apartment for rent to a third party
A sample statement of claim for recovery of damage caused by flooding of an apartment occupied by the plaintiff under a social tenancy agreement. The tenant's demand: to recover from the defendant, the owner of the apartment above, the material damage caused by the flooding of the apartment.
Sample statement of claim for recovery of damage caused by flooding of the tenant's apartment (under a social tenancy agreement). The plaintiff’s (tenant’s) demands are to recover the cost of restoration of the apartment and the cost of the property that became unusable as a result of the flooding of the apartment.
Sample statement of claim for recovery of damage caused by flooding of non-residential premises. As a result of the flood, both the non-residential premises of the plaintiff - walls, floors, ceilings - and equipment, as well as goods located on the premises, were damaged.
Sample statement of claim for recovery of damage caused by flooding of non-residential premises - office. The plaintiff, the owner of a non-residential premises, asks to recover damages caused by damage to the non-residential premises as a result of flooding (flooding), which occurred through the fault of the owner of the apartment located on the floor above.
Which court should I go to?
Depending on the status of the plaintiff and the value of the apartment, a claim for rights to real estate is filed with an arbitration court, a district court of general jurisdiction, or a magistrate.
Court determination scheme
IMPORTANT!
A claim for recognition of ownership of a real estate object is filed at the location of this object.
It is possible to submit statements of claim in the form of electronic documents (Federal Law No. 220-FZ of June 23, 2016). But even in this case, the jurisdiction of the claim for recognition of property rights remains, depending on the status of the plaintiff. The application is submitted on the official website of a particular court. The list of all courts is presented in the state automated system of the Russian Federation “Justice” https://sudrf.ru. This service is available only to owners of an enhanced qualified digital signature.
Claims for damages in connection with the death of a breadwinner
(see lawsuits and article on this topic)
Statement of claim for compensation for damages in connection with the death of a breadwinner who died while performing work duties (for the recovery of a monthly payment of sums of money constituting the average earnings of the deceased breadwinner).
Statement of claim for compensation for damages in connection with the death of a breadwinner who died at work as a result of an accident (for the recovery from the employer of the deceased in favor of his wife of a monthly sum of money for the maintenance of the child until he comes of age.
A statement of claim for compensation for damages in connection with the death of a breadwinner as a result of poor-quality medical services provided to a medical institution.
Statement of claim for compensation for damage as a result of the death of the breadwinner at work (for the recovery from the employer in favor of a dependent (for example, a minor child) of money to compensate for the damage caused by the death of the breadwinner on a monthly basis).
Statement of claim for damages in connection with the death of the breadwinner, funeral expenses and compensation for moral damage. The breadwinner died while performing his job duties.
Results of the trial
In case of a positive outcome through the court, the plaintiff receives recognition of ownership by the court. A document about this decision may become the basis for solving the problem that resulted in going to court.
Thus, both the authorities registering property and the notary will be obliged, upon presentation of a document with a court decision, to fulfill the initial requests of the plaintiff. In disputes with a person claiming ownership, the court’s decision will also be a significant argument in favor of the plaintiff .
Who to include as parties
The parties to the process are the plaintiff and the defendant. They may speak in person or through representatives. If a representative is involved in the case, his powers are confirmed by a power of attorney. The plaintiff is the person whose rights have been violated. In most cases, this is a citizen.
The defendant can be a citizen, legal entity or government body if they committed a violation of the rights of the plaintiff. For example, if a government agency has not issued a certificate of ownership, it is a defendant in such a case.
Please note! If the development company has not issued documents for the house, it will be the defendant, and the third party will be the institution that exercised control over the construction of the house.
Unauthorized construction
The recognition of ownership rights to illegal construction is regulated by Article 222 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, although in this part the legislation has undergone significant changes.
In particular, recognizing ownership of “samostroy” is now much more difficult than it was before. There is a chance to receive not documents for the house, but a decision on demolition, if the illegal building is found to not comply with safety standards.
At the same time, the legislation understands illegal construction as buildings that fall under at least one of the criteria listed below:
- construction was carried out on a site not allocated for construction or on an illegally occupied site;
- the structure was erected without permission, without permission from the relevant authorities, without a design and in violation of town planning rules.
A structure erected on a site not allocated for construction will not be considered illegal if the owner of the structure was not aware of the existing restrictions.
The chances of legalization (recognition of ownership of a house) increase in the presence of the following circumstances:
- the house was built without a permit or design, but on a plot of land that is either the personal property of the owner of the house, or in his lifelong possession, or in perpetual lease, provided that the intended purpose of the land allows the construction of residential buildings on it;
- the house does not violate anyone’s rights and does not pose a threat to the life or health of its residents:
- the building is designed and built taking into account technical standards and safety standards;
- an illegal structure, built in violation of safety standards, was improved by the owner and brought to the level of compliance with building regulations.