Construction of waste incineration plants will increase the price of metro travel Business
In accordance with Art. 8.2 of the Code of Administrative Offences, throwing waste in the wrong place entails an administrative fine for officials - from 10 thousand to 30 thousand rubles, for legal entities - from 100 thousand to 250 thousand rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days. But it is extremely difficult to prove that companies dump their waste in residential containers.
Read on RBC Pro
What tax innovations have the authorities prepared for src=»https://s0.rbk.ru/v6_top_pics/media/img/5/36/756337447457365.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»1536″ height=»960″[/ img]Swimming shallow: how does the thinking of a leader differ from the thinking of a performer
The Russian insurer is going for an IPO with a valuation of up to $1 billion. What is important to know
“Commodity prices could collapse”: Cathie Wood on risks in stock markets
In December 2021, Minister of Natural Resources Dmitry Kobylkin demanded that regional heads take measures to stabilize the situation in the waste management industry and prevent waste operators from going bankrupt due to non-payments. According to him, the level of non-payments by legal entities for waste removal reaches 70%. Last week, the minister called for “paying increased attention to the collection of payments from legal entities,” noting that the department is “working on a mechanism for introducing serious sanctions” against “evaders.” He did not disclose the essence of the sanctions.
In order to prevent disruption of the implementation of waste reform indicators, the Ministry of Natural Resources held a series of meetings from February 13 to 19 with the participation of the Russian Environmental Operator (REO, reform operator), regional authorities from Yakutia to Dagestan and operator companies, it follows from the department’s reports. Representatives of Dagestan at one of these meetings told Kobylkin that even though the territory has the lowest tariff in Russia, the collection rate for waste removal from the population is 50-60% of the planned amount, from legal entities - 25%. Governor of the Kemerovo region Sergei Tsivilev also outlined the problem of the high share of unconcluded contracts for waste removal between legal entities and regional operators.
What kind of document is this
At first glance, nothing has changed for the average citizen. The contract for the removal of MSW is concluded in a standard written form in several copies. Before signing an agreement, citizens or organizations producing waste must complete simple steps:
- Determine the hazard class of MSW: from 1, the most dangerous, to 5, non-hazardous.
- Obtain a certificate for the required waste hazard class. Typically, this is done by the regional operator himself or his authorized representative. The certificate is an annex to the agreement.
- Determine the owner of the MSW. According to the new provision, before shipment it is the owner of the container site, and after that it is the regional operator.
- Enter into a contract.
It is important to understand: the document regulates all relations of a citizen or organization producing MSW, and can serve as confirmation of correctness in court when resolving controversial issues. An agreement drawn up outside the legal framework is declared illegal.
Is it necessary to enter into an agreement?
Since 2021, all citizens and organizations producing MSW are required to enter into an agreement for the removal of MSW. At the same time, the residents of the apartment building do not personally sign the document: the management company or the HOA does this on their behalf.
The private sector litter law should be interpreted correctly. The homeowner must now contact an authorized organization and, after submitting documents for the house, enter into an agreement.
This obligation today follows from the interpretation of the owner of MSW. Until January 1, 2021, the owner of waste generated by residents was the local administration. And therefore, citizens had the right to throw away household waste free of charge in exposed containers.
From January 1, 2021, the owner of MSW is recognized as the owner of the territory where the waste collection site is equipped. And if it is located in the local area, then the resident himself must pay for the garbage.
Fines due to lack of agreement
For the absence of an agreement for the removal of MSW, you will have to answer according to the law:
- For unauthorized desire to remove garbage and the creation of spontaneous landfills, burying solid waste in the ground, dumping it into water bodies, citizens are subject to fines of 1,000-3,000 rubles.
- If an individual entrepreneur does not have the required document, his activities may be suspended for a period of up to 3 months.
- For systematic refusals to sign an agreement, a legal entity producing MSW is punishable by a fine of up to 300 thousand rubles. If an individual does not want to enter into an agreement, he will face a fine of up to 5,000 rubles.
(All data on fines and sanctions are current as of 03/03/2019).
It is important to understand: such measures are designed to rid the area of spontaneous waste dumps, improve the environmental situation in the regions and stabilize the movement of waste flows.
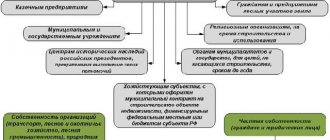
With whom is it concluded?
The parties organizing waste removal may be:
- Regional operator for MSW management. In this case, the document is signed directly.
- An organization (legal entity) authorized by the registrar. This representative is able to remove waste of all 5 hazard classes. The list of categories is specified in the company's license.
- Individual (individual entrepreneur). These performers are given the right to work only with waste of hazard class 5.
It is important to remember: before concluding an agreement, you should ask what information the regional operator provided to the Housing Information System and who are its authorized representatives for the removal of MSW.
Basic Concepts
The legislation, which we will discuss below, uses the following concepts:
- Solid household waste - it is the waste of the population generated as a result of life activities, that is, cooking, cleaning and minor repair work, cleaning of house and common areas, things and furniture that have become unusable. Solid waste is also waste from heating devices, garbage from yards (leaves), etc., generated both from residential premises and from public buildings (hotels, kindergartens and schools, catering organizations).
- Municipal solid waste in accordance with Art. 1 of the Law on Waste is waste from residential premises due to consumption by individuals. In addition, MSW also includes goods that have lost their consumer properties due to people using them in residential premises for personal and domestic needs, as well as garbage from cleaning the territory of settlements (street waste, garbage after being in public areas, beaches).
Essentially, the types of waste are similar. In relation to legislation on waste management paid for by citizens, it is necessary to take into account the waste that is generated directly as a result of meeting household needs. Thus, citizens pay for the removal and disposal of MSW - municipal solid waste (household waste). Read more about calculation, payment and other issues of MSW management.
Question: Many people are interested in whether construction waste falls under the concept of MSW.
The purpose of such a question is clear. When paying for a waste removal utility service, the consumer believes that the remaining building materials should also be removed as part of the service provided. This is wrong. Garbage after renovation is not included in the concept of MSW, so citizens are required to remove it themselves; containers near our houses are intended only for household waste resulting from human activity.
Preparation of contract
It is important to draw up a bilateral agreement correctly: otherwise, the document will be declared invalid.
The document must indicate:
- The name of the company or person providing the service, with all details (legal address, tax identification number and bank details).
- Name of the organization or full name of the person applying for the service.
- Description of exported MSW with mandatory indication and confirmation of class.
- Exact schedule for removal of MSW.
- Planned volume of collected waste. In this case, the container and its capacity in cubic meters must be indicated.
- Indication of the exact address of the site from where MSW will be collected.
- Time during which waste removal services will be provided.
- Price of the service and payment procedure.
Separately, the contract specifies the rights and obligations of the parties.
It is important to remember: the contract for the removal of MSW is urgent, that is, it begins to be valid from the moment it is signed by the parties and ends at the moment specified in it.
What else is required to conclude an agreement for the provision of garbage and municipal solid waste (MSW) removal services?
But before concluding an agreement, it is recommended to study the annexes to it. For legal entities providing waste removal services, this is a license for the right to carry out this type of activity (the company must provide the type of activity code to the State Information System for Housing and Communal Services), registration documents.
Officials on behalf of the customer (in the case of removal of MSW from the sites of apartment buildings) sign an additional agreement. It confirms the intentions of the parties to enter into an agreement and necessarily includes a waste collection schedule and a transport route. These documents are required for verification carried out by Rospotrebnadzor.
Interesting: if residents of the private sector independently remove solid waste to places specially designated for waste collection and provide a receipt indicating the time, class and volume of waste removed, then they will not be punished for not having a waste removal agreement.
Procedure for notifying purchases in the UIS
Before signing the contract, the institution places a notice of the planned purchase in the Unified Information System. The document must be published at least five days before the conclusion of the contract.
The notice states:
- name of location, postal address, contact number and email, responsible officer of the customer;
- brief terms of the contract, including the name and description of the subject of the auction;
- size, requirements for security for the execution of a contract and the procedure for its provision (if security must be used under Article 96 of Law 44-FZ).
When generating planning documents and tender notices in the Unified Information System, the customer must enter the code from OKPD2. Depending on the specifics of the buyer’s activity, the following codes are used:
- 11.29.000 – “Services for the collection of other non-hazardous waste that is not suitable for reuse”;
- 11.21.000 – “Services for the collection of non-hazardous municipal waste that is not suitable for reuse.”
How construction waste is removed
According to the established classification, construction waste is classified as categories 3 and 4 of MSW. And for proper disposal, you should contact an organization that has the appropriate permit to work with these classes of solid waste.
The law allows you to dispose of construction waste yourself.
But for this, a number of conditions must be met:
- Properly sort and pack waste.
- Provide transport with a loader (transport must have a license to carry out such work).
- Prepare a package of permits (usually it consists of 8 pieces).
- Deliver solid waste to a specialized landfill.
- Pay (and, if necessary, provide Rospotrebnadzor) with a receipt indicating the cost of disposal.
Obviously, it is easier to conclude an agreement with a licensed organization for the removal of a certain volume of construction waste. In this case, the citizen will save time and get rid of the risk of being fined for unauthorized actions .
Who should enter into a waste removal agreement and make payment?
From January 1, 2021, the following categories of citizens are required to enter into a waste removal agreement:
- Residents of apartment buildings (a management company or HOA enters into an agreement on their behalf).
- Villagers.
- Individual entrepreneurs producing waste.
- Legal entities whose activities generate solid waste.
- Members of gardening associations (the agreement is concluded on their behalf by the board).
- Owners of private houses.
All these categories, regardless of whether they themselves entered into an agreement or through a legal representative, are required to pay for the removal of solid waste at the tariff established in the region.
Residents of apartment buildings receive a payment receipt indicating the MSW removal service. In most gardening associations, payments are included in the amount of membership fees and are not included in a separate column. The remaining categories fill out a receipt with the specified details of the service provider and pay at the bank or using an online payment service.
❓ Is it possible not to pay if you haven’t signed the contract?
Clause 8.17 of Rules No. 1156 established that it is enough for a regional operator to publish both in the official media and on its website an appeal to consumers about concluding a standard agreement.
Mikhail Suvorov
Leading lawyer of the Legal.Center portal. Experience – 26 years
Ask a Question
If the consumer has not sent any documents to the regional operator within 15 working days, then the contract is considered concluded and comes into force on the 16th working day.
Regional operators carefully implement this clause. Therefore, even if a citizen does not have a signed paper agreement in hand, payment for services for the removal and disposal of MSW will still be charged .
How to calculate the statute of limitations when dividing jointly acquired property: the position of the RF Armed Forces
Read
Who owns the meters located at the entrance?
Read
Is it possible to reduce waste from the “private residential sector”?
Residents of private homes can reduce the amount of waste they produce.
To do this, you should follow simple rules:
- It is recommended to compost food waste (vegetable peelings, leftover food). In 3-4 years they will turn into valuable organic fertilizer for flowers, lawns and beds.
- Eco-friendly products are in fashion. 10 chickens will help you cope with uneaten food and reward you with fresh eggs.
- Cut tree branches need to be chopped using a shredder. The resulting wood chips are an excellent mulch for the garden.
- The foliage harvested in the spring will rot well in the ground. At the same time, the soil will be saturated with nitrogen.
- The trunks of cut trees are useful for preparing aromatic shish kebab. And this wood burns perfectly in a sauna stove.
- Metal waste can be recycled and you can get some money for it in addition to the family budget.
Village residents are concerned about the question: is it necessary for everyone to enter into a contract for garbage collection in the private sector? Yes, every homeowner is required to pay for the disposal of solid waste based on an agreement.
But the Territorial Public Self-Government will help reduce the costs of MSW removal. The initiative group will conclude a collective agreement on behalf of several owners. Combining several rural streets or alleys will allow you to place 1 large container instead of several small ones.
It is important to remember: taking care of the cleanliness of the surrounding area is a common task. And reducing the amount of garbage thrown away will free the container from overflowing.
The obligation of citizens from January 1 to enter into an agreement for garbage removal will make it possible to clear the territory of the regions from spontaneous landfills and avoid an environmental disaster.
Garbage removal agreement (2 videos)
Federal law on garbage collection from 2021
Back in 2021, President of Russia V.V.
Putin instructed the prosecutor's office to regularly and thoroughly check the implementation of legislation on waste management. Especially in the field of livestock farming and hazardous production, where compliance with disposal rules is especially important. In the May decrees, the President, in a separate paragraph, indicated the need for the complete elimination of unauthorized landfills by 2024. In pursuance of the order of the first person of the state, prosecutors are filing claims against the administration for the liquidation of small and large landfills in cities, which are satisfied by the courts. In addition, back in 2021, changes were made to the Waste Law on the need to separate waste into food and toxic. But until now, the idea of multi-colored containers has not yet become widespread. It should be noted that with new changes in the legislation on waste removal, the introduction of separate waste collection is becoming more active, including in the private sector.
Today in Russia there are several legal acts that jointly regulate waste issues:
- Federal Law “On Licensing of Certain Types of Activities” dated May 4, 2011 No. 99-FZ, to which, with the exception of the general rules for the validity of licenses and the frequency of inspections of licensees, no significant changes have been made over the past year. This law approves the requirements for the activities of organizations related to the disposal of waste of hazard classes 1-4.
- Federal Law “On Environmental Protection” dated January 10, 2002 No. 7-FZ, to which some amendments were made in 2021 on the creation of an automatic system for monitoring emissions and discharges of pollutants that negatively affect the state of the environment.
- Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population” dated March 30, 1999 No. 52-FZ, according to which, starting from 2021, sanitary protection zones are established by the federal supervisory authority, and the regulations on sanitary protection zones are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Along with the above, the main one in the area under consideration is the federal law “On production and consumption waste” dated June 24, 1998 No. 89-FZ (many call it the law on garbage removal). It regulates the rules of accounting, regulation, reporting and delimitation of actions during waste removal. Changes to this law were made twice in 2021 - in July and December, and came into force in January 2021. Based on the law, the Russian Government Resolution No. 1156 dated November 12, 2016 “On approval of the procedure for handling municipal waste” is in force, which reveals details rules of law and rules are established.