Let's start with the fact that a disabled person is a person who has a health disorder with a persistent disorder of body functions. Such a violation is caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects. It leads to limitation of life activity and causes the need for social protection of a person (Article 1 of the Law of November 24, 1995 No. 181-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 181-FZ)).
A person recognized as disabled is issued a certificate confirming the fact of disability, indicating its group. Along with the certificate, he receives an individual rehabilitation program.
Disability and its group are determined by special federal institutions - the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (hereinafter referred to as ITU). A citizen can be referred to such a bureau by:
- an organization providing medical and preventive care, regardless of its organizational and legal form;
- body providing pensions;
- social protection body.
A certificate confirming the fact of disability is issued in a certain form. It was approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated November 24, 2010 No. 1031n.
Checking the certificate and IPR
First, you need to check the disability certificate and individual rehabilitation program (hereinafter referred to as IPR) of the disabled person for the presence of signatures and seals. These documents must be signed by the head of the ITU bureau where the employee underwent the examination, and certified with the seal of this bureau. After checking the documents, copies of them should be kept in the personal file of the disabled employee.
The IPR is of a recommendatory nature for a disabled person. He has the right to refuse one or another type, form and volume of rehabilitation measures, as well as the implementation of the program as a whole (Article 11 of Law No. 181-FZ). Therefore, an employee can only bring a disability certificate to work in order to receive general disability benefits provided for by the Labor Code.
The IRP of a disabled person includes certain types, forms, volumes, terms and procedures for the implementation of medical, professional and other rehabilitation measures. Their goal is restoration, compensation for impaired or lost body functions, restoration, compensation for the abilities of a disabled person to perform certain types of activities (Article 11 of Law No. 181-FZ).
Attention
Refusal of a disabled person from the IRP as a whole or from the implementation of its individual parts relieves the employer of responsibility for the implementation of such a program. At the same time, a disabled person does not have the right to expect to receive compensation in the amount of the cost of rehabilitation measures provided free of charge (Article 11 of Law No. 181-FZ).
IPR of a disabled person must be implemented regardless of the organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership of the employer. This means that everything will need to be done to create the working conditions for the employee that are prescribed in his IPR.
You will also need to make a note about the completion (or non-compliance) of specific rehabilitation measures. The mark must be certified by the signature of the responsible person, for example, the head of the company, personnel officer, accountant, and the seal of the organization.
Legal dismissal
The recognition of an employee as completely incapable of work in accordance with a medical report is a circumstance in which the employment contract is subject to termination. Reason – clause 5 of part 1 of Article 83 of the Labor Code.
The classifications and criteria used when conducting MSE are determined by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 23, 2009 No. 1013n.
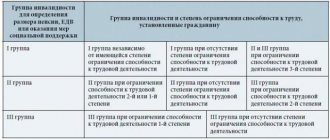
Let’s say an employee is recognized as disabled with the ability to work 3rd degree. Ability to work – the ability to work in accordance with the requirements for the content, volume, quality and conditions of work. Limitation of the ability to work of the 3rd degree implies the inability to do any work or its impossibility (contraindicated). This degree of limitation of one of the main categories of human life activity belongs to group I disability. In this case, the employment contract with such an employee can be terminated on the basis of clause 5 of part 1 of Article 83 of the Labor Code.
Limitation of the ability to work 1st degree assumes that the employee is able to work under normal conditions with a decrease in qualifications, severity, intensity or a decrease in the volume of work. As well as the employee’s inability to continue working in his main profession while maintaining the ability to perform lower-skilled work under normal working conditions. This degree of limitation corresponds to disability group III.
Limitation of the ability to work 2nd degree implies the ability to perform work in specially created working conditions with the use of auxiliary technical means or with the help of other persons. This degree of limitation corresponds to disability group II.
We hire a disabled person
This means that if an employee is recognized as a disabled person of group II or III, then he can be dismissed at his own request on the basis of Article 80 or by agreement of the parties on the basis of Article 78 of the Labor Code.
Transfer to another job
An employee recognized as disabled can continue to work, but only under the working conditions recommended for him in the IPR. In this case, two options can be provided for the IPR. The first is a change in working conditions without changing the terms of the employment contract. The second is a change in the terms of the employment contract, including transfer to another job.
Changes to the terms of the employment contract must be formalized by agreement.
If it is not possible to create for a disabled person the conditions specified in the IPR, the employee must be transferred to another job.
If such a possibility exists and the employee has given his consent, a transfer agreement should be concluded with him. It will also be necessary to issue a transfer order in Form No. T-5. These unified forms were approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1.
The transfer of an employee to another job is reflected in section III of his personal card in form No. T-2*.
How to prepare documents for the dismissal of a disabled person of group 3 for medical reasons
Dismissing a disabled person of group 3 due to medical indications under clause 8, part 1, art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, draw up standard documents on dismissal. In particular, issue a dismissal order, make an entry in the work book (if it is maintained) and information in the information about labor activity (part 4 of article 66, article 66.1, part 1 of article 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 4 Rules for maintaining and storing work books).
Additionally, take into account the nuances associated with the wording of the grounds for dismissal in the order, work book and information about the employee’s work activity. We'll talk about this in more detail below.
The transfer did not take place
If there is no suitable vacancy or the employee refuses to transfer, the employment contract with him is subject to termination. In this case, clause 8 of part 1 of article 77 of the Labor Code is indicated as the basis for dismissal.
There is no need to notify the employee of dismissal in advance in such a situation.
However, the right of all workers to receive, within a reasonable time, information about the termination of their employment is provided for by paragraph 4 of Article 4 of Part II of the European Social Charter, ratified by Law of June 3, 2009 No. 101-FZ. Thus, having decided to dismiss a disabled employee, he should still be warned in advance. Before the expiration of this warning, the employer is obliged to remove the employee from his previous job. During the period of such suspension, wages are not accrued (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
An employee’s application is not necessary to issue an order to terminate an employment contract. It is issued on the basis of a medical report. The employee must be familiarized with the order against signature. If it is not possible to bring the order to the attention of the employee or the employee simply refuses to read it under signature, a note about this must be made on the order.
By the way, at the employee’s request, he will need to provide a certified copy of the dismissal order.
The day of termination of the employment contract in all cases is the last day of work, with the exception of cases where the employee did not actually work, but retained his place of work (position). This means that the employment contract is terminated on the day specified in the dismissal order, even if the employee was suspended from work on that day.
Attention
The establishment of working conditions for disabled people in collective or individual labor contracts that would worsen the situation of disabled people in comparison with other employees is not allowed. We are talking, in particular, about wages, working hours and rest periods, the duration of annual and additional paid leave, etc.
On the day of termination of the employment contract, it is necessary to make a settlement with the employee, including paying compensation for unused vacation. Deduction for unworked vacation days for the employee in question, if the vacation was provided to him in advance, is not made.
Severance pay is paid in the amount of two weeks' average earnings.
If the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts must be paid no later than the next day after he submits a request for payment.
On the day of termination of the employment contract, the employee is issued his work book. The following entry should be made in it: “Dismissed due to the employer’s lack of work required in accordance with a medical certificate issued in the manner established by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, paragraph 8 of part one of Article 77 of the Labor Code.” It is this option for filling out a work record that is provided for in paragraph 5.2 of the Instructions for filling out work books (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69).
If it was not possible to issue a work book on the day of termination of the employment contract (for example, the employee was not at the workplace), the employee must be notified of the need to appear for the work book or agree to have it sent by mail. From the date of sending this notification, the employer is released from liability for the delay in issuing the work book.
Conditions under which severance pay is due
In order for the right to severance pay to arise, the reason for terminating the employment contract is important. If a person leaves on his own initiative, he is not entitled to any compensation. But if the employer did not find a suitable place for an employee with a disability (it is even more harmful to health) or he refused the transfer voluntarily, the company is obliged to pay severance pay.
IMPORTANT!
Some employers seek to terminate the contract with employees who become disabled by agreement of the parties. In this case, you should carefully read what amounts and in what amount the management of the organization offers. Because the money will be paid under a separate agreement, and not as compensation guaranteed by law.
Annual leave
In general, the annual basic paid leave is 28 calendar days. Disabled people are granted annual leave of at least 30 calendar days (Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 23 of Law No. 181-FZ). Moreover, such extended leave is due regardless of whether the employee was disabled during the entire working year for which he was granted leave or not.
It should be borne in mind that if, after establishing disability, an employee resigns, then compensation for vacation must be paid to him in proportion to the time when he was recognized as disabled.
Let's say that part of the working year for which leave is granted falls during the period when the employee was not yet disabled. Then for this part he is granted leave at the rate of 28 calendar days per working year. And for the part that falls on the period after the employee was recognized as disabled - at the rate of 30 calendar days per working year.
Taxes on payments
If the employee does not have any debts, he is entitled to the entire amount that was obtained in the calculations, since personal income tax is not taken from it. If the employer has a writ of execution and payments are made according to it, another part of the debt will be withheld from the severance pay.
IMPORTANT!
Neither income tax nor insurance contributions are transferred if the amount of severance pay does not exceed three times the average monthly earnings (paragraph 7, paragraph 1 and paragraph 3, Article 217, paragraph 2, paragraph 1, Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraphs 2 clause 1 article 20.2 of Law No. 125-FZ “On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases”). If the benefit is higher due to an agreement between the parties or a collective agreement, mandatory payments are withheld and transferred to the budget.
Vacation at your own expense
Unlike other employees, a disabled employee has the right not to ask, but to demand leave without pay; it is impossible to refuse to provide it. Moreover, based on a written application, a disabled employee can apply for unpaid leave of up to 60 calendar days a year (Article 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us note that the issue of the specific time for granting a disabled person leave at his own expense is still decided by agreement of the parties. After all, the Labor Code does not establish the employer’s obligation to provide such an employee with unpaid leave at the exact time he insists.
How to offer a group 3 disabled person another job that is not contraindicated for him
If you have a job that a group 3 disabled person can perform taking into account his state of health, offer it to the employee (Part 1 of Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It is advisable to do this in writing, for example in the form of a notice. We recommend that you draw it up in two copies: give one to the employee, and on the second, which will be kept by you, ask the employee to sign for receipt of the notice and familiarization with it. This way you will have proof that you have not violated the requirements of Part 1 of Art. 73 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Reduced operating time
For disabled people of groups I and II, a reduced working time is established - no more than 35 hours a week while maintaining full wages (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 23 of Law No. 181-FZ). The duration of daily work (shift) for disabled people must correspond to the issued medical report, for example, IPR (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To indicate shortened working hours in the time sheet in form No. T-12 or T-13 and use: - or the letter code “LC”; – or digital code “21”.
Consent to overtime work
Involvement of disabled people in overtime work, work on weekends and at night is permitted only with their consent and provided that such work is not prohibited for them due to health reasons.
A disabled person cannot be involved in overtime work, work on weekends and non-working holidays, as well as night work, if this is directly contraindicated for him for health reasons according to the IPR submitted by him. In it, the ITU institution specifies the working conditions of a disabled person.
Let’s say a disabled employee did not want to use the IRP at the place of work and brought the employer only a certificate of disability, where restrictions on overtime work and other restrictions are not recorded. Then such an employee, with his consent, can be involved in overtime work, work on weekends and non-working holidays, and night work.
In what cases is it possible to dismiss a disabled person of group 3 for medical reasons?
Consider dismissing a group 3 disabled person for medical reasons if he has provided you with the necessary medical documents. This could be, for example, a certificate of disability of the employee, an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program (IPRA), a medical certificate issued to the employee based on the results of a professional suitability examination.
After receiving such documents, check whether the work the employee is performing is really contraindicated for him. The fact is that disabled people of group 3 do not have as many contraindications as, for example, disabled people of group 1.
For example, a disabled person of group 3 is contraindicated from working as a loader if the medical report states that he is prohibited from work involving manual lifting and moving heavy objects weighing more than 5 kg.