Home / Labor Law / Labor Code
Back
Published: 08/07/2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
4160
Labor legislation provides special benefits for pregnant workers, including those who wish to continue working. The preferential organization of labor activity also includes a shortened day - work according to a special work schedule established for preferential categories of workers.
Any working woman can take advantage of this privilege while waiting for the birth of her baby.
But it should be remembered that the reduced work time is not set automatically (due to pregnancy) . The employee will have to take the initiative and contact the head of the enterprise, organization or institution with a corresponding written request.
- What does the law say?
- Which pregnant women are entitled to the benefit?
- Establishment rules
- Registration procedure
Standard working hours for pregnant women
The Russian Labor Code establishes equal working hours for all categories of employees. The standard rule sets it at 40 hours per week. Such a time exists for government and budget employees. However, this time may be reduced for a pregnant employee. This abbreviation has some features that should be specified in more detail:
- The law does not establish a specific limitation on time reduction for such employees. Therefore, the reduction is determined by the employer in agreement with the employee. This is a general compromise solution that should not infringe on the interests of the employer and employee;
- This is an employee's right. Therefore, the employer or organization cannot restrict it. The employer is obliged to provide a reduction in time at the request of the employee;
- The employer cannot establish a reduction in time on its own initiative. This is the same restriction as the refusal of an employee to satisfy her application. Reduction is possible only if there is her application and not otherwise;
- The only basis for reducing the working hours of a pregnant employee is the very fact of her condition, certified by a doctor’s certificate.
Thus, reducing the length of a working day or shift is an unconditional right of the employee and cannot be limited by the organization.
Working hours for a pregnant woman - Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Working hours for pregnant women are set in the same way as for all other employees. Its reduction is possible only at the request of the employee. It becomes the basis for the employer to limit the length of the working day.
In this case, the period does not matter. The medical condition of her health also does not matter. Therefore, the law does not link the reduction in the length of the working day to these concepts. The key and only basis is medical fact. Nothing more is required.
Working hours for pregnant women
As stated above, the law does not establish specific restrictions. It fixes only their types:
- Reducing the duration of a work shift. At the same time, the work week remains the same;
- Reducing working days while maintaining the same shift length.
The choice of one option or another depends on the employee and the characteristics of her professional functions.
A pregnant woman visiting a doctor during working hours
The question of whether an employer is obliged to allow a pregnant woman to see a doctor during working hours is very relevant, because visits to the doctor and hospital are required regularly. And often it is simply impossible to postpone them.
The law requires employers to allow women to see a doctor or hospital. At the same time, they must provide supporting documents. That is, a visit to a doctor or hospital must be confirmed by appropriate medical certificates.
Application of a pregnant woman to reduce working hours
Such a statement is mandatory for execution in any organization, regardless of its organizational and legal form. At the same time, you need to understand that a decrease in working hours will inevitably lead to a decrease in wages, so you should use this right carefully.
Practice shows that employers reduce the working day by 1 hour. As a rule, this suits both parties. The woman receives additional time with a slight loss in wages. She has such a right from the moment the pregnancy status is medically determined. In order to exercise the right, you must apply to management.
If you have questions, consult a lawyer
Leaves to the hospital
The Ministry of Health established Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2012 No. 572n “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care in the field of obstetrics and gynecology”, that during the entire period of pregnancy women must visit:
- obstetrician-gynecologist - at least seven times;
- therapist - at least twice;
- dentist - at least twice;
- otolaryngologist and ophthalmologist - at least once;
- other specialists - according to indications.
You can go to the hospital on weekdays from the earliest stages of pregnancy. The Labor Code does not limit the number of visits to the doctor.
An employer should not force an employee to go on vacation or take days off without pay. The pregnant woman will continue to be paid the average salary Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Rights and guarantees for employees in position
Expectant mothers who are officially employed have the opportunity to receive certain benefits:
First of all, it should be noted that the employer does not have the right not to hire an employee for a suitable position who is in a position solely because of her condition. The second important right for a woman during pregnancy is the opportunity to receive maternity leave.
An employee does not have the right to demand that her employer maintain her previous salary if she has signed a part-time agreement.
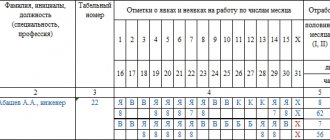
Recording hours worked on a timesheet
The legislator does not establish a minimum limit for part-time work for a pregnant woman. As, in fact, the “ceiling”.
The time of completion of the mandatory medical examination is also noted on the report card on the basis of a supporting document.
A special cipher is used for this.
It would be correct for a pregnant employee to notify her superiors in advance about her possible absence and obtain a doctor’s certificate, which is then provided to management.
Ban on dismissal
An employer, with all its desire, cannot, Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, fire a pregnant woman, even if she skips work without good reason. The maximum that a manager can do is issue a reprimand or reprimand.
A pregnant woman can be fired without consequences in two cases:
- If an individual entrepreneur or company ceases to exist.
- If the employee is working as a substitute and the contract expires. But the employer must offer Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation another vacancy. Moreover, you need to show all the options that exist in this area, even if the position is lower and the salary is lower. An employer can offer a place in another city or region if this is provided for in an agreement, labor or collective agreement.
If an employee's fixed-term employment contract expires, she can ask to extend it until the end of her pregnancy. If desired, the employer can include maternity leave in this period. In response, the woman must provide a certificate from the hospital every three months, proving that she is still pregnant. As soon as the boss finds out about the birth, he can terminate the contract.
A pregnant woman can leave work of her own free will. And at the same time not work for two weeks.
Shorten a pregnant woman's working day in three simple steps
A pregnant woman needs to initiate the establishment of part-time work.
The most effective way to convey your desire to the employer is a written statement. A pregnant woman must submit an application to the employer, which reflects
- desired length of working time;
- type of part-time work (part-time or part-time work week);
- the date from which the woman wishes to reduce her working hours.
The application must be accompanied by a document confirming the fact of pregnancy, for example, a certificate from the antenatal clinic.
The employer and the pregnant woman must reach an agreement on working hours.
The duration of part-time work and which party determines it is not established by law. Apparently, everything should be achieved by agreement of the parties. It is not clear what to do if the parties cannot agree, and the law obliges the employer to reduce the working day of a pregnant woman.
When the parties agree among themselves, it is necessary to conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract, since the working hours are its essential condition.
The employer must issue an order
The employer must issue an order regarding the establishment of a part-time working day and familiarize it with it against the signature of the employee.
As you can see, it is not difficult for a pregnant woman to shorten her working hours. The woman herself needs to remember that payment will be made in proportion to the time worked or depending on the amount of work performed.
The Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, in Resolution No. 1 of January 28, 2014, clarified a number of issues regulating the peculiarities of the work of women, persons with family responsibilities and minors. The explanations are given taking into account the practice and questions that arise in courts when considering labor disputes on similar topics. The clarifications of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation will ensure uniform application of labor legislation by courts and put an end to long-standing disputes between employees and employers.
Advertisement _ No. 1
2. An employment contract, the end of which occurred during the employee’s pregnancy, generally needs to be extended until the end of the pregnancy. Moreover, in the case of the birth of a child, the need for dismissal is indicated not within a week after the child’s birthday, but on the last day of maternity leave. Reason: Clause 27 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1
3. The employment test is not imposed on pregnant women, women with children under the age of 1.5 years, as well as persons under 18 years of age. This rule also applies to other persons raising children under 1.5 years of age without a mother.
If such employees were subject to probation, then termination of the employment contract with them based on the test results is unlawful. Ground: Clause 9 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1
Work and leave to care for a newborn child
In order to have the opportunity to care for a newborn child until he reaches the age of three, an employee of the enterprise must submit a corresponding application.
She has the right to take leave for this entire period of time. Division is allowed between the following persons:
- baby's dad;
- grandmother grandfather);
- relatives;
- guardian.
If it is decided that one of the listed people will care for the newborn child, then they have the right to work part-time or a week. It is also possible to determine the place of work at home. Such persons must retain the right to receive benefits.
When caring for a baby, the position held (workplace) must be retained by these persons. This time period is included in the employee’s work experience and should not be interrupted.
The procedure for making state benefits and their amounts are determined by law.
What benefits are provided?
The Labor Code protects the rights of expectant mothers, including those who get a job during pregnancy.
Basic labor benefits for pregnant women:
Employment of pregnant women occurs without a probationary period (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employer cannot refuse a job to an applicant because she is pregnant. Moreover, he cannot ask questions about her situation. The only reason for refusal to work is an insufficient level of qualifications for the position. If the reason for the refusal was a fictitious excuse, the woman can ask for a written answer and contact the labor inspectorate with it. Identification of an unreasonable refusal to provide employment will entail sanctions. An employer cannot fire a pregnant employee, including under Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (for violating the schedule, absenteeism, etc.). The employer is obliged to provide a pregnant woman with light work upon presentation of an appropriate medical certificate
It is important that the certificate indicates specific restrictions on work activity. The employee is exempt from work on weekends and holidays, as well as on night and overtime shifts. A pregnant woman can take annual paid leave at any time. Even if it was not her turn, or she did not work for a certain period
For example, you can take a vacation before the start of maternity leave or immediately after it. Light work for pregnant women according to the Labor Code in 2019 implies a ban on working on a rotational basis (Article 198 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). A pregnant woman has the right to be excused from work duties on weekdays to undergo a scheduled examination. In the case of a difficult pregnancy and frequent examinations, it is necessary to take the appropriate certificate from the antenatal clinic and register it with the human resources department. If necessary, the employee may leave the workplace. Regardless of how many hours per day are actually worked, the employer is required to retain earnings for the entire day. In addition to the lunch break, the expectant mother has the right to receive short breaks during the working day. It is prohibited to transfer a pregnant woman to another position without her consent. An employer is required to provide a pregnant employee with paid maternity leave. The duration of the leave depends on the course of pregnancy and the complexity of childbirth.
Benefits may also be provided to the husband of a pregnant employee. Regardless of his length of service, he can take advantage of annual leave during his wife’s pregnancy and childbirth.
What to do if the employer refuses to accept the application?
If the employer, for any reason, refuses to alleviate the situation of a pregnant employee, then the latter has the right to file a complaint with the labor inspectorate.
If the check does not bring the desired result, then the only option left is to file a claim in court. There is no state fee for consideration of such cases.
The main thing is to remember that the employee’s work shift should not be cut short without permission, without notification and an appropriate decision from the employer.
Leave for pregnant women before maternity leave: how many days are required?
Shortened working hours for pregnant women
Home Rights of pregnant women and young mothers The presence of pregnancy is not a basis for denying a woman employment. When deciding whether to hire a person, only her business qualities and qualifications are subject to assessment. If they do not meet the requirements, then only in this case the employer may not hire a pregnant woman. When hiring, employers do not have the right to demand from a woman a document confirming that she is not pregnant, as well as any assurances or receipts that she is not planning a pregnancy in the near future. This contradicts the requirements of Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the list of documents that must be provided for employment. If a pregnant woman is hired, the employer does not have the right to set a probationary period, send her on business trips, or involve her in overtime work. An employer does not have the right to dismiss a pregnant woman on his own initiative, regardless of the grounds for absenteeism, failure to fulfill official duties, staff reduction, etc. The only exception is the complete liquidation of an enterprise, when the activities of the organization as a legal entity are terminated, when an individual entrepreneur ceases operations, for example, due to with the expiration of the state registration certificate. During pregnancy, in accordance with a medical report, a pregnant woman should have production standards at the enterprise reduced or she should be transferred to light work that excludes exposure to harmful factors. At the same time, she must retain the average salary for the position in which she worked before the transfer.
Changes in the law for pregnant women
There are several changes to the legislation. For example, the list of persons who can receive maternity payments has been increased. Now foreign citizens and close relatives of the employee can receive these funds. The maximum payment level has increased to 755,000 rubles.
Also among the latest changes:
- the use of female labor in hazardous industries is limited, and therefore pregnant women are transferred to easier work, where there is no danger to the development of the child;
- after 2014, the labor version of the pension was replaced by an insurance one, which led to full enrollment in the maternity period;
- since 2012, if there are small children, 4 additional days off can be provided per month, which are paid at the general rate.
The main changes took place in 2012-2015. At present, there are no plans to introduce various amendments.
Registration procedure
The following stages of shortening a shift or work week can be distinguished:
- A pregnant woman turns to the antenatal clinic for a certificate of status.
- Contact the company's HR department.
- Submitting an application in writing (a medical certificate is attached to the application).
- Leaving the resolution on the application.
- Preparation of an additional agreement to the employment contract in two copies and its signing by the employer and employee.
- Issuance of an order regarding changes to the work schedule.
The order also requires a statement of the procedure for changing the calculation of wages.
Application example
The application is not standardized and can be drawn up in free form. However, it must contain all the necessary information. When compiling, you can use the following example as a guide:
To the director of Orion LLC, V. B. Zaitsev, from project manager E. I. Sidorova.
statement.
I ask you to reduce your work shift by 1-2 hours due to pregnancy on the basis of Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To confirm pregnancy, I enclose a certificate dated 09/08/2021 with registration number 0667785.
/Sidorova/ Sidorova E.I.
At the end of the application, a signature and date of preparation must be affixed. The exact content of the document depends on the wishes of the employee. For example, it may require a four-day workweek with an additional hour reduction in shifts.
ATTENTION! The document is drawn up in two copies. One of them remains in the personnel department, the other is in the hands of the employee
The second copy bears a mark indicating registration of the application in the appropriate journal. This is necessary to confirm that the paper has been submitted.
The application may contain additional requirements. For example, if an employee does not want to reduce her shift until her pregnancy is over, she can ask for a change in her work schedule for a few months or weeks.
What are the working conditions
Features of the structuring of the conditions suggest that the employer will perform a number of positions.
The Labor Code in 2021 describes light work for pregnant women as such that it excludes the possibility of:
- actions related to carrying heavy loads;
- occupying a position on an assembly line;
- emotional and psychological stress;
- the presence of harmful, toxic substances in the environment.
But depending on the field of professional employment, positions may vary slightly and have their own characteristics.
In the field of trade
In this case, harm at the place of employment is associated with positions that are present in trade.
For example, when a woman is engaged in sales of household chemicals. Despite the relative safety, it is worth limiting the influence of fumes of this kind.
The same goes for hard work. Often, a salesperson's job involves moving large volumes of goods during the working day.
A prescription in this area can be obtained from a doctor. You should describe to him the features of the work and he will identify the presence or absence of negative factors.
Video: transfer to light labor
In medicine
This area involves contact with the same chemicals. They have the greatest impact on laboratory workers. After all, when conducting research, chemicals, solutions and antiseptics are used.
The revision of the conditions may consist of a transfer to a different work procedure. For example, for general filling out forms and documentation. Which is much more favorable than the constant influence of drugs.
In banks
There is only one risk in this area - interaction with computer technology. The issue of the impact on health has not been fully studied.
In this regard, processing information on a computer and using printers/scanners falls within the scope of the employer’s decision.
He may, at his own discretion, shorten a woman's tenure in such work. The medical responsible person also prescribes the provisions separately.
He has the right to set a limit of working with equipment within three hours a day. Then the employer will have to transfer the pregnant woman to other conditions and replace the remaining hours with other actions. They do all this in the standard manner.
The obligation to create special conditions for women expecting a child falls on the employer. He must take all actions to establish comfort in the workplace.
At the same time, the law stipulates that the woman herself must begin the process. But the employer does not have the right to refuse her this point, as well as to fire her or terminate the agreement with her.
Prohibited activities
The Labor Code prohibits pregnant women from performing the following types of work:
- night shift;
- being at a height;
- recycling;
- lifting heavy objects;
- carrying heavy objects (maximum weight allowed is 5 kilograms);
- long standing;
- bending or pulling;
- contact with radiation and toxic substances.
If a woman suffers from toxicosis, she should not work where there is an accumulation of various odors. They contribute to the deterioration of well-being. It is also necessary to limit and reduce the duration of work associated with vehicles and computers. For example, while a child is pregnant, you cannot perform the duties of a driver and controller.
Responsibilities of the Chief
Every boss must fully respect all rights of the employee. The Labor Code provides for updating the work schedule of the expectant mother, taking into account her wishes. In addition to updating the schedule and reducing hours, additional considerations must be taken into account. benefits provided to pregnant women who are officially employed.
The manager will be required to thoroughly comply with all Labor Code norms and rules regarding expectant mothers specified in legislative acts.
Any refusal will be considered an illegal act.
Even if the employee’s desire has a negative impact on her work, it cannot become a reason for refusal. In such situations, the boss and employee try to find a compromise. Usually, during maternity leave, girls hire a temporary worker who will perform her duties temporarily.
The schedule of a pregnant girl should not contain a number of requirements:
- Night shifts should not be included in the schedule of a pregnant woman, who may refuse them in accordance with Art. 96 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Working on weekends and holidays is also prohibited for pregnant women. The boss must comply with these rules specified in Article 112 of the Labor Code of Russia;
- A pregnant employee can work overtime if she wishes, but should not perform additional work. work and work overtime, which is noted in Art. 99 TK;
- Pregnant women should not work on shifts, this is stated in Art. 298.
general information
Legislatively shortened working hours are regulated by various articles. For example, Article 92 of the Labor Code of Russia provides for the introduction of a reduced schedule for:
- certain groups of budget employees, in particular doctors and teachers;
- minor workers;
- disabled people, with the exception of the third group;
- citizens who work in dangerous conditions.
At the same time, reduced work time means establishing less time in comparison with general labor standards without reducing wages . That is, a reduction in the general level of production standards.
ATTENTION! Part-time work is controlled by the provisions of Art. 93 of the Labor Code of Russia, and sets working hours less than those determined by generally accepted standards for the duration of a shift in particular, and the work week in general.
This is the basis for the new procedure for paying employees working in a similar regime - their wages are paid based on the number of hours worked, or the volume of work done.
Shortened working hours for pregnant women
Everyone knows that discrimination against women in the workplace is a fairly common phenomenon. Some employers even force a woman to take a pregnancy test before hiring her. Such actions are illegal and are prosecuted by law. The main thing is to know this and understand that the owner does not have the right to refuse to hire a pregnant woman at any stage.
In various ways, not only bosses try to harass a pregnant woman at work, but also colleagues, to whom some of the responsibilities are transferred. If you need to negotiate amicably with employees, then only knowledge of labor law works with your bosses.
Any pregnant woman, regardless of whether she feels well or not, should be transferred to light work, but with the written consent of both parties. In this case, wages remain the same. Even if the enterprise does not have a position to which a woman can be transferred, the unnecessary burden is removed from her. But are pregnant women's working hours reduced?
Not everyone knows that a reduced (shorter) working day for pregnant women is provided for by law. This issue is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article No. 93. This regulatory document states that, at the request of the woman herself, the owner (director, manager, etc.) is obliged to transfer the woman to part-time or weekly work, regardless of the form of ownership of the enterprise.
Women of Ukraine are also protected by law, because according to the Labor Code, Article 56, they have the right to a reduction in both the working day and the week. In addition, according to paragraph 9, Article 179, a woman on maternity leave has the right to take work home, if possible, and at the same time receive child benefits and wages.
If the employer refuses this, then the woman can file a corresponding application in court and win it, after which her rights will be restored, and a fine will be imposed on the owner. Many do not bring the matter to trial and ultimately agree to reduce their working hours for pregnant women.
What should a working day be like for pregnant women?
There are three types of time reduction:
- Part-time work for pregnant women.
This means that a woman will work several hours less per day (there is no clear figure, it all depends on the agreement between the parties) - Partial work week.
The length of the working day remains the same, but instead of five days, the woman will work for three. - Mixed type of reduction of working time (day, week) for pregnant women.
Both days (three instead of five) and hours (five instead of eight) are shortened. In order to switch to reduced working hours, you must write an application, sign a bilateral agreement and attach a doctor’s certificate confirming your pregnancy. Unfortunately, as the time decreases, the salary also becomes less (proportionally), which is stipulated by law. But light work is paid at the same level.
Working hours for pregnant women
When an employer hires a pregnant employee, the working hours may be immediately agreed upon.
It may be incomplete, just like a part-time working week. The law defines the following categories of persons who have the right to ask for a day or week to be shortened:
- pregnant employee;
- mother (father) or legal guardians who have a child under 14 years of age;
- parents or legal representatives who have a child with a disability under 18 years of age;
- persons who care for close relatives.
An employee working according to such a schedule receives payment for his work equal to the volume done for this time. Working in this manner cannot affect a person's right to have leave. It must also be paid.
Also, such working conditions do not entail restrictions when calculating length of service. The time may be reduced from eight to six hours. At the same time, the working week is not shortened. An employee can also work full time, but not all days of the week. For example, not from Monday to Friday, but from Tuesday to Thursday.
The establishment of a part-time work week (day) is carried out in the following order:
- Obtain a document from a medical institution that confirms pregnancy.
- Prepare an application requesting a reduction in working hours due to necessity. In it you can express your wishes on exactly how to shorten it. For example, add a day off and reduce the working day by several hours.
- Submit your application to the HR department. It is recommended to prepare your appeal in two versions. One option to keep for yourself. It can become an evidence base in the event of a dispute.
- Sign the order after reading it.
- Read the additional agreement, which is drawn up as a supplement to the current employment contract. After that, you need to put your signature on it. It is recommended that the employee keep the second copy.
Part-time working hours can be established indicating a certain period. It is also installed without specifying this period.
Features of a shortened day for pregnant women
The provisions of Art. 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the possibility for pregnant employees to demand that the employer provide them with a shortened working day. At the same time, the employer under no circumstances has the right to refuse the employee to fulfill her demands. An employee can ask the employer to change the duration of individual shifts or all work shifts as a whole, or to change the length of the working week. In this case, it is possible to demand a simultaneous reduction in both the time worked during a shift and the number of total working days per week.
Since working time in this case is recorded in accordance with the time worked, the employer has every right to proportionally reduce the wages of a pregnant employee, as well as any other employees working in accordance with such a regime.
Important fact
The reduced working hours regime, both for pregnant employees and for other employees, can in no way affect the payment of bonuses and other allowances, if any, for employees in similar positions working a full schedule.
Info
As soon as an employee of a medical institution records this fact and provides a certificate, the employee can exercise her right.
It is important to note that in order to reduce the length of the working day, a pregnant woman is not required to provide any additional documents or doctor’s recommendations or prove the fact of poor health. All you need is a standard certificate and an application addressed to the manager
Pregnant women should remember that the right to change the working hours arises regardless of whether the employer is a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur. It also applies to government agencies.
The procedure for remuneration for work during pregnancy.
With a shortened day, your salary may decrease. This action is carried out in accordance with the principles of payment calculation (hourly, based on performance).
If earnings depend on the hours spent at work, then a decrease in income is directly related to a decrease in working hours. If a pregnant woman receives income that depends on the result, then the woman has the opportunity to keep the income to the family budget in full when developing the norm.
By the way, the latter can also be adjusted at the request of the employee in the situation.
The benefit does not affect the amount of vacation pay and maternity benefits. However, changing the schedule may have a slight impact on the indicated amounts.
The fact is that when calculating maternity benefits, average earnings over the last 24 months are taken as a basis.