Legislation
04.01.2021
82051
Author: Anastasia Volkova
Photo: pixabay.com
Inheritance is a concept that should not be judged by foreign films and TV series. It is better to refer to the main legislative acts of your country. Issues of inheritance law in Belarus are mainly regulated by the Civil Code of the Republic of Belarus.
We have tried to simplify the legal language and cover the basic facts about inheritance below. So what is it, who has the right to it, how to receive an inheritance?
Inheritance - procedure
The inheritance procedure in the Republic of Belarus takes place on the basis of the contents of the will and state legal acts.
Moreover, according to the law, the procedure occurs in the absence of a will. It should be noted that sometimes a will may not apply to all the property of the deceased; in such cases, it is distributed to them outside the framework of the will on the basis of legislation. There are some restrictions related to the right of inheritance. For example, a legal entity cannot be an heir. It is worth considering that the right of inheritance is not affected in any way by the legal capacity of the heir, however, only a fully capable person can draw up a will.
There is a list of rights that are inextricably linked with the personality of the deceased, and therefore cannot be transferred to a third party:
- Participation in commercial organizations and legal entities;
- The right to compensation for harm to health or life;
- Alimony rights;
- Rights to pension payments and other benefits;
- Moral rights that have nothing to do with property.
By taking ownership of the rights to property, the heir also assumes the obligations associated with the property. The heir receives at his disposal the rights of the deceased testator, which do not terminate at the time of the death of the latter.
Cost of registration of inheritance
The cost depends on the specific situation, in particular on the list of notary services. One base amount is charged for:
- consultation on inheritance issues;
- preparing and drawing up an application for inheritance;
- issuance of a certificate of inheritance rights to first-degree heirs (if they have documentary evidence of kinship).
0.25 of the base value is charged for drawing up and sending each request, notice, letter and other documents required to perform a notarial act. However, you can collect the necessary documentation yourself.
Entry into force of inheritance
The moment of opening of the inheritance is the day on which the testator is recognized as dead. Sometimes such a decision is made for missing people after a certain period of absence of the citizen. The death of the testator is registered on the basis of the death certificate. The inheritance is opened at the last place of residence of the testator. If this place cannot be determined, then by the location of the property that is inherited by third parties.
The list of heirs includes relatives of the deceased who are alive at the time the will is opened or were conceived during the life of the testator and were born after the inheritance was opened.
Basic terms
Inheritance is the transfer of inheritance from a person who has died (testator) to other people or organizations (heirs).
Inheritance – property (for example, a car, an apartment as an inheritance) and some other inherited rights (for example, intellectual) and obligations.
Heirs are capable persons who can receive the property of the deceased.
Acceptance of inheritance is the official procedure of consent to the transfer of property.
The day of opening of the inheritance is the date of the person’s death or its recognition (if he was missing).
The place of opening of the inheritance is the last registered address of residence or registration of the testator. If it cannot be set, the location where the inheritance object is located.
An escheat inheritance is property that passes to the state because there are no heirs by will or law.
Civil Code on Inheritance
The current civil code most clearly and broadly forms the circle of heirs under the law; it quite accurately sets out the principles of the order of succession under the law. There are only 6 priority levels. The legislation reveals the principles of inheritance by right of representation. We are talking about the case when the heir is a deceased person, in which case his inheritance is divided among his heirs in proportion. Within one turn, the heirs divide the property equally, but the heirs by right of representation divide their total share among themselves. If there are 4 heirs of the first priority and 3 by right of representation, then the latter will divide among themselves ¼ of the entire inheritance.
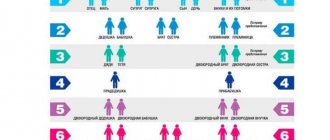
1. Heirs of the first stage:
Spouses, children and parents. Grandchildren and their direct descendants assume rights by right of representation.
2. Heirs of the second stage:
Siblings and brothers. Nephews can claim inheritance by right of representation.
The third line is the relatives of the deceased. Heirs of the fourth stage are siblings of the testator's parents. By right of representation, cousins of the deceased may claim the inheritance.
According to the law, dependents who were supported by the deceased may be eligible for inheritance. There is a rule for dependents - they must be supported by the deceased for a period of at least one year.
Disabled dependents are also affected by how close they lived to the deceased. According to the law, they can claim no more than 25%, which is distributed within their queue. There is another category of dependents. These are those persons who are not included in the circle of heirs, but were still dependent on the deceased for at least a year. The same rule applies to them as for the first category described above.
Rules for inheriting property after death
It is necessary to enter into an inheritance within 6 months from the date of death of its owner. If during this period the heir specified by the will or law dies, the time is extended for another three months.
Depending on the situation, any person has the opportunity to renounce his rights in favor of another relative or the state. For example, if the costs in this case exceed the cost of the property received.
It is impossible to refuse part of the inheritance. Just as you cannot obtain rights only to certain items from the general list. Inheritance or refusal is carried out in full.
You cannot inherit only the material things of the deceased. All non-property obligations, such as payments under a loan agreement or debts for utilities, also pass to the new owner. Any citizen can inherit the property of a deceased person, regardless of their state of health. Whereas for writing a will, legal capacity is one of the most important conditions.
Will and inheritance
A significant difference from inheritance by law is that when inheriting on the basis of a will, the shares of the inheritance are distributed strictly at the discretion of the will-maker, that is, everything depends on the will of the testator.
The will of a person must be expressed directly by the testator himself; no intermediary participation in this case is appropriate.
Moreover, it is important to know that the legislation of the Republic of Belarus does not provide for the drawing up of joint wills for several persons; a will can only be an individual expression of will.
A will is a transaction drawn up unilaterally; there is no need for the expression of the will of the heirs. However, if the testator entrusts a certain person with the execution of his will, then he must obtain consent from such person to such an assignment. Such consent is confirmed in writing: either in a receipt attached to the will, or in the form of a signature in the will.
It should be noted that there is a principle of freedom of will. The principle is interpreted as follows. The testator has the right to dispose of his property in full and has the right to bequeath his property to any person without any explanation or interpretation, this is his right. The testator has the right to make sure that any of his legal heirs or all legal heirs together will be deprived of the inheritance. However, such a right does not apply to those heirs who can claim the inheritance by right of representation.
Sometimes, not simple inheritance is practiced, but inheritance with the fulfillment of an important condition for the testator. An example of this is the following condition in the will: the son receives ownership of his father’s car from the moment the former marries. There is also a situation in which the heir can receive an inheritance only if the entire inheritance or part of it fulfills the testator’s instructions; this may be for some generally beneficial purpose, for example, a charitable donation. Also, one of these conditions may be the maintenance of the testator’s pets after his death.
In some cases, the testator indicates a reserve heir who can assume his rights in the event that the heir refuses the inheritance or, due to force majeure, is unable to assume his rights.
Rules that may limit the freedom of a will include:
- The rule on compulsory share in the inheritance, which restricts the heirs from disposing of the property that they received as an inheritance on their own, that is, transferring it to someone, also includes the principle that the testator cannot fix for the heir what is obviously problematic in fulfillment of the condition;
- There is a concept of a mandatory share. Such a share is received by the children of the testator who are minors or disabled, or by spouses and parents who are also disabled. The persons described above receive by inheritance 50% of the share that would belong to them if inherited by law.
It is important to take into account the requirement that if the testator somehow stipulates the receipt of an inheritance for the heir who has the right to an obligatory share, then this condition only affects the heir’s receipt of that part of the inheritance that goes beyond the obligatory share.
Types of inheritance
The Civil Code of Belarus defines two types:
- inheritance by law;
- inheritance by will.
The first option applies when a person did not leave behind a document in which heirs are registered. In this case, they are appointed in accordance with the order established by law.
If there is a corresponding document, the inheritance under the will comes into force. This is an expression of the will of a capable citizen, which is drawn up personally (without representatives). The document can only indicate the property that belongs to the testator. The will must be in writing and certified by a notary or other authorized person. The cost of registration with a notary is 1.7 base units (49.3 BYN in 2021).
In Russia, there is the term “inheritance agreement” - a document that specifies the heirs and the conditions for the transfer of inheritance. In Belarus, the only legal document is a will. It differs from an inheritance agreement in that the will usually does not stipulate certain conditions that the heirs must fulfill.
Who can claim the inheritance?
If there is an inheritance under a will, then the property of the deceased is received by those indicated in the document. It does not matter whether the marked people were related. Moreover, not only individuals, but also companies, public organizations - any legal entities can receive an inheritance after death under a will.
How is it determined to whom property or non-property rights are transferred? There is a clear sequence:
- heirs of the 1st stage - children (including adopted ones), wife or husband, parents;
- 2nd stage - blood brothers or sisters, as well as their successors (nephews and nephews);
- 3rd – grandfather or grandmother on the side of both parents;
- 4th – brothers or sisters of the deceased;
- heirs of subsequent orders are other relatives (great-grandfathers and great-grandmothers, cousins, nephews and nieces, etc.).
For example, an elderly man died and left behind a private house. If he did not have a wife and children, they will turn to their parents. If the parents are no longer alive, the house will be inherited by the brothers and sisters. All this is provided that no will was made.
An important addition - disabled family members (children, spouse, parents) must become heirs, even if they are not indicated in the will.
Who cannot receive an inheritance?
In some cases, even the will of the deceased, written on paper, has no force. They will not be able to receive property:
- people who killed the testator or attempted his life. However, an exception is possible - if the will was written after the attack or attempt;
- people who, through illegal actions, forced a will to be written in their favor.
By law, parents who have been deprived of parental rights cannot accept an inheritance. And also people who were obliged, in connection with a court order, to support the testator, but did not do so.
From the point of view of legislation, such heirs are called “unworthy”.
Inheritance – terms and procedure for entering into inheritance rights
You can receive inheritance rights within 6 months after the death of the testator. This can be done later, if other heirs to whom the property has passed do not object.
During the same period - 6 months - you can refuse the proposed rights. Why is this necessary? As mentioned earlier, inheritance is not only about property, but also about the responsibilities that come with it. For example, an unpaid loan for an apartment or car. If you don’t want to pay off your debts, you shouldn’t accept the “gift.”
At the same time, the heirs are not responsible for obligations not related to property. For example, you do not have to pay alimony or compensation for damages.
How to enter into an inheritance?
- It is necessary to contact a notary located at the place where the inheritance was opened.
- At the office you need to fill out an application and attach the relevant documents to it. An alternative option is to send the application by mail. In this case, the application must be certified by another notary. The application must indicate: last name, first name and patronymic and address of the applicant, details of the deceased person, place and date of opening of the inheritance.
- The notary will review the documents and after some time notify the heir that he can receive a certificate of right to inheritance.
- After this, you can re-register the property.
To obtain a certificate you will need to pay:
- heirs of the first stage - 1 BV (base value) in the amount of 29;
- second stage – 2 BV (58 BYN);
- third stage - 3 BV (87 BYN), etc.
What documents need to be submitted to a notary?
List of documents for obtaining a certificate of inheritance:
- a document confirming the identity of the heir - preferably a passport;
- certificate confirming the fact of death;
- if inheritance is valid by law, then documents confirming the relationship are required (marriage or birth certificate, etc.);
- if there is an inheritance under a will, then the will itself is needed;
- documents confirming property rights to inheritance.
This is a standard list, but depending on the situation, other documents may be needed.
If some documents are missing, the notary has the right to make an independent request to the authorized bodies in order to prepare a package of documents for a certificate of inheritance.
What does the law say?
- SECTION VI of the Civil Code of the Republic of Belarus;
- Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus 1145 December 27, 2013 On approval of notarial tariffs for performing notarial actions and providing legal and technical services.
Is it possible to challenge a will?
A will, like any other agreement or transaction, can be challenged in court. This can only be done after the will has been opened.
In what situations can a document be declared invalid?
- if it is proven that the will was drawn up under duress. For example, the testator was blackmailed or threatened;
- if facts are provided that the testator was incompetent at the time of writing the will (mental problems, alcohol or drug use).
The limitation period is three years. It starts counting from the day when the person learned or should have learned that his rights were violated.
Popular questions
What to do if there is no will?
If there is no such document, the heirs are determined according to the order determined by law. First we will consider – children, spouse, parents; then brothers or sisters.
What to do if the heirs are unhappy with the distribution?
You can contact the court - both before receiving an official certificate of the right to inheritance in the Republic of Belarus, and after.
What should I do if I missed the deadline for accepting the inheritance?
The first option is to reach an out-of-court agreement with the other heirs to whom the property went. If they don't mind, then you can accept the inheritance later. The second option is litigation.
What can you pass on as an inheritance?
Owned property, bank accounts, some rights, for example, intellectual rights. Along with the above, debts may also be transferred, for example, a loan for an abandoned apartment. Alimony, rights to receive a pension or other social benefits, and other personal non-property rights are not inherited.
Where to go to register an inheritance?
To register an inheritance, you need to contact the notary office at the place of residence of the deceased.
How to register an inheritance for children?
If you need to leave an inheritance to your children, you must draw up a will with a notary. This procedure will cost 1.7 base units (49.3 BYN). Otherwise, after death, the property will be transferred in equal shares to the first priority heirs - wife/husband, children and parents.
How much will the procedure for accepting an inheritance cost?
The work of notaries in Belarus is regulated by legislative acts. Therefore, prices should be the same in different cities of the country. According to the law, you will have to pay 29 rubles for the procedure for accepting an inheritance. (1 BV – heirs of the first stage), 58 rubles. (2 BV - heirs of the second stage), 87 rubles. (3BV – heirs of the third stage).
Conclusion
There are many nuances in inheritance law that are difficult to take into account on your own. Problems arise when the transferred inheritance turns out to be collective property, when the heirs do not agree with the will, when common-law spouses do not receive property due to unregistered relations in the registry office.
If the situation with inheritance is non-standard, it is better to contact a lawyer and get competent advice from him.
Will forms
Compliance with the form of the will is one of the key factors. This document is considered invalid if it does not comply with the standards established by law. A will is drawn up in writing and must be certified by a notary. The Civil Code contains clarifications that in some cases, not only a notary can certify this document, in which case the will is equal in importance to a notarized will. The testator's signature must be present. If for good reason a person cannot sign on his own, another authorized person can do this, however, only in the presence of a notary. Also, in addition to the notary, witnesses must be present when drawing up a will. Two copies of the notarized inheritance are preserved: one is kept in the notary's office, the second is received by the testator.
The will may be closed, in which case the notary does not become familiar with the contents of the document, but simply certifies it. However, in this case, the will must be completely written by the testator and endorsed by his signature. Otherwise, the document will not be valid.
After leaving a closed will, the testator, in the presence of witnesses, passes the document to a notary for certification, the witnesses sign the closed envelope, the envelope is sealed by the notary in another envelope, on the outside of which information about the testator, the date of certification of the document and information about the witnesses are indicated. The testator has every right to change or cancel his will according to his decision, and it is also possible to make additions to the will.
Inheritance of real estate: legal platform in Belarus
In the legal field of Belarus, aspects of inheritance law are regulated by the norms of Section VI “Inheritance Law” (Articles 1031 – 1092) of the Civil Code of the Republic of Belarus.
All issues regarding the inheritance of real estate and other property located within the borders of the Republic of Belarus are resolved by notaries and courts of Belarus using these very rules.
In addition, the Republic of Belarus is a party to the “Convention on Legal Assistance and Legal Relations in Civil, Family and Criminal Matters,” which was signed on January 22, 1993 in the city. Minsk. According to the Convention, to which all CIS countries have become signatories, heirs can take possession of real estate and property belonging to a citizen of Belarus on the territory of any of the states that have signed it by contacting the competent authority of that state.
How to refuse an inheritance
A person specified in the testator's will, or a person who has the right to inherit an apartment by law, does not want to enter into an inheritance, has the right to refuse to enter into inheritance rights.
To do this, within six calendar months from the date of opening of the inheritance, you must contact a notary’s office, where you should write an application. It must indicate:
- information about what part of the inheritance the heir refuses;
- in whose favor the heir renounces a share or the entire amount of the inheritance.
When deciding to renounce the right to inheritance, you should remember that this procedure is irrevocable, therefore such a decision must be thoughtful and balanced.
If you want to buy an apartment on the secondary market or rent an apartment for long-term rent, the Hata.by real estate portal can help you with this. On our website there are a huge number of advertisements from owners, you can easily choose the right option.
Is it possible to inherit an apartment in a civil marriage?
Spouses who were in a civil marriage with the testator on the day of death cannot claim the status of first-line heir.
In such cases, testamentary inheritance applies. That is, a spouse can claim the right to inherit an apartment in the event of the death of the spouse only if the testator left a will in his favor.
If such an order was not registered by a notary before the date of opening of the inheritance, the person who was in a civil marriage with the testator can claim the right only to that share of the inheritance for which he can prove the investment of his own funds in monetary terms.
Documents and procedure for registering an inheritance for an apartment
Documents for inheritance under a will
Applications in the presence of a will are accepted by a notary from the moment the inheritance is opened. This is the day of death of the testator.
When submitting an application for inheritance of an apartment, the heir under the will must provide the notary with the following documents:
- Passport or other document confirming identity;
- Death certificate of the testator;
- Documents confirming the existence of family ties between the heir and the testator
*if the heir does not have any for objective reasons, the relationship is established in court before filing the application and the notary is provided with a Court Decision;
- Certificate from the RSC about the last place of residence of the testator.
Documents for inheritance by law
The procedure for inheriting an apartment is initiated by filing a claim with the Court before the expiration of six months from the date of death of the testator. During this period, the Court accepts applications from heirs of the 1st – 4th stages and identifies applicants for inheriting an apartment who have submitted their applications to other notary offices in Belarus.
With the statement of claim, persons claiming to inherit an apartment or a share in it must provide the Court with:
- Passport or other document confirming identity;
- Death certificate of the testator;
- An application for the Court to establish the degree of relationship or documents confirming it;
- Certificate from the RSC, establishing the last place of residence of the testator.
The statement of claim itself must contain the following information:
- details established by the Code of Civil Procedure
- complete information about the object being inherited;
- information about the testator and the person who actually accepted the inheritance;
- information about when the applicant actually accepted the inheritance and about documents confirming this fact.