In the modern world, the birth of a child in an officially unregistered marriage is not considered uncommon. Such a marriage has no legal force and the spouses can only be called cohabitants.
Popularly, such a union is known as a civil marriage. Since this is a fairly common phenomenon, the question remains relevant whether it is possible to register a child in the father’s surname if the marriage is not registered.
After all, the fate of the child and his material well-being may depend on this. Parental relationships work out differently and fathers are not always conscientious about fulfilling their responsibilities towards their children.
From the moment of his birth, any child acquires the right to a surname, first name and patronymic; it is enshrined in both international and Russian legislation.
The child receives a name by agreement of the parents or one of them . If it does not comply with the law, the registry office may refuse.
If a child has a father, he receives a middle name in accordance with his name; it cannot be chosen by the parents. The surname also cannot be assigned to any name; it is determined by the details of the spouses.
General procedure
The question of what the child’s surname will be if the parents have different surnames most often arises when the relationship between mother and father is not officially registered. In this case, you should act in accordance with the requirements of legislative acts.
The surname is given to the child when registering his birth at the registry office. After this, a birth certificate is issued containing this information.
If the legislation of the subject does not provide for a different procedure for obtaining a surname, then the baby is given the surname of either the mother or the father.
Before the changes were made, a child could receive a double surname only if one of the parents had it.
In the case of using a double surname, it is prohibited to use a different order of accession when forming the surname of siblings.
Sometimes it happens that the father and mother cannot independently reach agreement on the child’s first and last name. Then the dispute is resolved by the guardianship authorities. In their decision, they must be guided by the interests of the minor and take into account various factors, including the euphony of these data. If a newborn is left without parents, his last name and first name are given to him by his legal representatives in accordance with the general procedure.
When a baby is born in a marriage, it is automatically registered in the name of both parents: the spouse’s initials are written in the “father” column, and the spouse’s in the “mother” column.
However, if a child is born out of wedlock, complications arise. In this case, instead of an entry in the paternity column, a dash is placed, which is why the blood father is not considered such in the eyes of the state.
Some citizens believe that this problem can be solved by initiating an adoption procedure.
However, such a judgment is fundamentally incorrect. The citizen from whom the child was born is his blood parent.
Reference! According to the law, the blood father does not have the right to adopt his own son.
If the baby was born in cohabitation, a different procedure is required. In this case, the institution of adoption does not apply. It is necessary to establish the paternity of the baby.
To do this, it is enough for citizens to mutually apply to the registry office or, in case of difficulties, to the court. But the blood father cannot adopt his own child.
Alimony for illegitimate offspring
Despite the fact that the spouses were in a civil marriage, their offspring have the same rights to alimony as children born in a common marriage. The problem can only arise if the biological father was not included in the birth certificate of the minor citizen. In this case, it will be possible to collect alimony only after paternity has been established.
When filing a claim for alimony, they submit standard documents, only without a marriage certificate. Instead, you need a certificate of an examination to identify the father.
If the former common-law spouse renounces paternity and does not want to pay alimony, then in order to collect it you will need, in addition to evidence of consanguinity, to prove that the common-law spouse lived with you, which means you have the right to alimony payments. Evidence may include:
- witness statements;
- DNA examination certificate;
- joint photographs;
- correspondence via SMS or email;
- applications, questionnaires or other written documents;
- blog or social media profile where he acknowledged his paternity.
In conclusion, I would like to say that many people prefer a good civil marriage to a bad official one. But we must not forget that such a union can bring a whole host of legal and formal problems, and, of course, psychological ones, such as the uncertainty of the new family member in the strength and stability of their social unit.
The procedure for assigning a surname to a child if the parents did not register their relationship
In the modern world, people are in no hurry to officially register their relationships and often give birth to children in such a union. In this case, the question inevitably arises: is it possible to give the child the father’s surname if we are not registered. The legislation, which is also in force in 2021, allows us to solve this problem.
If at the time of the baby’s birth, mom and dad did not register their relationship, the child can be given the surname of one of them. To make a record of the father, paternity must be officially recognized. To do this, the father must write a corresponding statement. If the relationship is not registered, the parent is not required to go through the adoption procedure.
It is more difficult when the father is not listed in the documents at all. In this case, the surname is written in accordance with the full name of the baby’s natural mother. The patronymic name is set whatever the woman wishes.
Establishing the baby's initials is one of the many problems that arise when he is born in a civil marriage. Another difficulty is establishing paternity, especially if the blood parent does not recognize his child.
If a man does not want to acknowledge his paternity, an entry about the father can be made by a court decision. Thus, the child can be given the father's surname if the marriage is not registered.
In the event that paternity has not been established at the time of issuing the birth certificate, the baby will receive the mother's surname. Once paternity is established in court, it can be changed. When a child is born out of wedlock, it is important to take into account that if the parent recognizes the child as his own, his presence when receiving the birth certificate is mandatory.
When a child is born out of wedlock, it is important to take into account that if the parent recognizes the child as his own, his presence when receiving the birth certificate is mandatory. Because he must write a paternity statement. Otherwise, the fact that the child has a father will not be confirmed and the child will receive the mother’s surname.
✅ 3. The rights and responsibilities of parents towards their children are the same both within and outside of marriage
Both parents have the right:
- participate in the child's upbringing;
- receive leave to care for him;
- organize the child’s communication with his relatives;
- go to the hospital with your child;
- choose an educational institution (in agreement with the second parent) and so on.
And in the same way, they equally bear responsibilities: for the material support of the child, his upbringing and development, protecting the child from harmful influences, ensuring that he receives an education, etc.
Marriage in this situation is not of fundamental importance: the basis for the emergence of the rights and responsibilities of a parent is the entry in the child’s birth certificate.
✅ Outside of marriage, you will not lose the right to receive alimony for the maintenance of a joint child
If suddenly your union breaks up or creditors encroach on the property of the child’s second parent, the parent with whom the child lives has the right to demand that the other pay child support.
If you want to officially formalize the amount and procedure for paying alimony, there are two ways: concluding a notarial agreement on the payment of alimony and going to court. They are also available to everyone, regardless of whether they registered their marriage.
When resolving a dispute in court, the parties also have the right to enter into a settlement agreement or proceed to mediation at any time before the judge retires to the deliberation room.
✅ 4. Outside of marriage, you can also acquire property as community property
A couple can register any property, including real estate (house, apartment, land, etc.), purchased at the expense of the common budget, into common shared ownership.
In this case, the termination of the relationship or the death of one of the partners allows each of the partners to remain with their own. To recognize rights to a share in property, you do not have to go to court.
The difference from an official marriage is that there is no presumption of community of property acquired during cohabitation.
In marriage, you can move away from this “pre-established” option and enter into a prenuptial agreement or an agreement on the division of jointly acquired property.
Outside of marriage, on the contrary, it will be necessary to provide for the division of each individual object or several objects, or to enter into some kind of “framework” agreement for future acquisitions (for example, a simple partnership agreement).
✅ 5. Even without the consent of your partner outside of marriage, you can receive a share in the common property or return the money spent on it. But you will have to try for this
Often, in a couple that has not registered a marriage, property is purchased with common money and, for convenience, one of the partners registers it in his or her own name. If a dispute arises about the ownership of property or if the partner who is the official owner dies, the second partner can go to court.
There are three options:
1) File a claim for the award of a share in property rights.
This is a rather complex method of protection: positive decisions are made by the courts in cases where it is possible to prove the existence of an agreement between partners to acquire the disputed property as shared ownership.
2) File a claim to recover funds invested in the purchase as unjust enrichment, if there was no agreement on the joint acquisition of property.
It will not be possible to use this method if the court finds that from money transfers or correspondence between the parties it follows that the money was gifted or transferred to the second partner specifically for some purpose.
3) File a claim to recover the transferred funds under the loan agreement.
Don’t be confused by the word “agreement”: to file this claim, it will be enough to confirm the transfer of funds to the second party and (if there are objections from the opponent) to confirm the absence of intention to donate them. The absence of a written agreement or receipt only deprives the parties of the right to refer to the testimony of witnesses, but the rest of the evidence is correspondence, recordings of negotiations, bank statements, etc. - can be used. If you did not agree on a time frame for the return of funds, simply send a request for a return of funds to the other party. After thirty days (unless a different period is agreed upon in the contract), you can go to court.
Please note the statute of limitations: for each claim it is three years:
- for a claim for the award of a share in the right: from the moment when the share in the right should have passed to the plaintiff (and did not);
- for a claim for recovery of unjust enrichment: from the moment the defendant receives funds or other property;
- for a claim for debt collection under a loan agreement: from the moment when the debt should have been repaid under the terms of the agreement, and if the period is not agreed upon in the agreement - from the thirty-first day from the date of sending the demand for the return of funds (not counting the day the demand was sent).
✅ For comparison, a claim for the division of property acquired jointly during marriage can be filed at any time during the marriage and within three years after its dissolution.
✅ 6. Outside of marriage, you decide for yourself what debts your partner owes
An official marriage allows creditors to foreclose on jointly acquired property, demand its sale and, most importantly, demand payment of the debt assumed by your spouse. However, the debt will be presumed to be personal unless the creditor proves that the debt arose in connection with the needs of the family and with the consent of the second spouse.
In the case of unregistered relationships, there is a presumption that all debts of each partner are their own. Otherwise, it must be expressly provided for by the agreement of the parties (for example, you can agree and become co-borrowers on a loan or accept guarantee for the debts of your other half).
The rights to inherit and receive maintenance in an informal union are quite limited
An official marriage presupposes that if one of the spouses is incapacitated, the second, able-bodied spouse, assumes the obligation to take care of him. In the event of a dispute, the disabled spouse may demand the establishment of alimony: the main thing is that the incapacity for work occurred during the marriage and not through his own fault.
He also has the right to an obligatory share in the inheritance (it is half of what would be due to him by law). This rule cannot be circumvented either with the help of a will or with the help of an inheritance agreement (by the way, we wrote about it in one of our recent posts).
In an unofficial couple, all these guarantees are absent. To inherit, there must be a will of the second partner; there are no rights of the first-priority heir, and in case of inheritance without a will, there is no right to accept the inheritance. There is also no right to demand alimony (including for the maintenance of the mother of a joint child during pregnancy and for three years after the birth of the child - in official marriages this obligation of the spouse, including the former, exists).
✅ 8. You can get a tax deduction for a common child, regardless of whether you are married
To register, you must provide the child's birth certificate. The deduction is applied to personal income tax paid during the year and amounts to:
- 1,400 rubles - for the first child annually;
- 1,400 rubles - for the second child annually;
- 3,000 rubles - annually for the third and each subsequent child annually;
- 12,000 rubles - annually for each disabled child, full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student under the age of 24, if he is a disabled person of group I or II.
If one of the partners dies outside of marriage, the other will not be able to receive funeral benefits.
The vast majority of readers will involuntarily wince when reading this title. Of course, we prefer not to think about bad things and drive away thoughts of death.
Unfortunately, pills for immortality have not yet been invented. A funeral benefit does not compensate for the pain of loss, but in some cases it allows you to avoid aggravating the mental pain by urgently seeking a loan for the funeral of your partner and subsequent payments on it. Many take out loans from microfinance organizations out of desperation and time constraints, and are then forced to pay off debts for years.
For 2021, the funeral benefit in Moscow is 5,946 rubles. 47 kopecks for employed widowers and 16,946 rubles. 47 kopecks for unemployed and disabled citizens. Also in Moscow there is an additional payment from a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, it amounts to 11,000 rubles.
How to register a child in the name of the father if he was born out of wedlock
If the citizen who is the father of the child is known, to register him it is necessary to go through the procedure of establishing paternity. It is different from adoption. Citizens, if there is mutual agreement, can take one of the following paths:
- After the minor is born, both his parents must appear at the registry office . An application regarding the recognition of the baby is submitted to this institution. After all the nuances have been settled, the relevant data will be entered into the birth certificate.
- You can apply before birth. In this case, both citizens must simultaneously appear at the registration authority and draw up the appropriate document.
Important! If a citizen dies during birth or is declared legally incompetent, the father must contact the guardianship authority.
When contacting the guardianship authority, you will need to provide substantial evidence of the relationship and submit a request to include initials in official documents for the child. If an employee of this institution takes into account the citizen’s arguments, he will be recognized as the father of the baby.
Another way to register a minor as a father is to officially register the relationship. In this case, a marriage union is established between the spouses and the issue of paternity of the baby is resolved.
Filing a claim initiated by a man
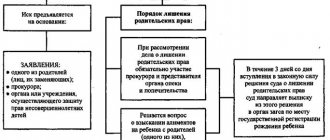
In a situation where a child is born in a civil marriage, only the mother is indicated as the parent. And if she dies, then officially the biological father remains a nobody for his offspring. For such cases, the law provides for the option of filing a claim on the part of the man to establish paternity. The biological father can file it in the following situations:
- the mother of a minor child died;
- the woman is officially declared incompetent;
- mother declared missing;
- the common-law wife does not live with the baby for more than 6 months;
- a woman has been deprived of parental rights by a court.
It must be remembered that such an application is submitted only with the consent of the guardianship and trusteeship authority, providing a package of documents certifying the basis for registering the child in this way.
This may be a death certificate of a common-law wife, a court order depriving her of maternity, a medical report recognizing the spouse’s incompetence, a certificate from law enforcement agencies declaring the woman missing, or another document depending on the specific situation.
Even if the guardianship authorities refuse to establish paternity to the biological father, the claim can be immediately submitted to the courts.
What surname will the child get if the father is absent?
When a child is born out of wedlock, the father's surname is assigned only with his consent and recognition of paternity. If a parent does not want to admit the fact of relationship with the baby, this can be done during the trial.
Formation of a family relationship leads to the emergence of certain rights and obligations. In a situation where the father of a newborn dies or the parents are divorced, the child can receive the father's surname if no more than 300 days have passed since the date of death or divorce.
During this time, paternity is recognized automatically and can only be revoked by a court. The surname may change if paternity is disputed in court and the plaintiff's claims are satisfied. A single mother has the right to give her child her last name. The child also receives a first and patronymic at the discretion of the mother.
Rights of children born in a civil marriage
Children who were born in an unregistered marriage have the same rights as children born in an official marriage:
- the right to live in a family with both parents;
- for a decent upbringing and provision of everything necessary;
- for protection;
- to express his own opinion when decisions are made regarding his future;
- for first name, patronymic and last name;
- to inherit property from parents.
Among the rights there is also the right to receive financial assistance in the form of alimony. However, one difficulty arises: first you need to officially prove paternity.
As for registration, the mother or father, if they live separately, can register the child in their living space.
Inheritance from paternal grandparents is also available to the child only with proof of paternity. Without him, he only has one set of grandparents - on his mother's side. And even if the father’s parents want to leave their property to their grandson or granddaughter, they will have to pay a special fee if paternity is not officially recognized.
If one of the parents does not want to carry out the paternity procedure
It is not always possible to solve a problem peacefully. The question arises: if a child was born out of wedlock, how can he be registered with the father when the latter refuses to recognize consanguinity? In this case, the mother must file a lawsuit to establish paternity. You should contact the magistrate.
Attention! The blood parent can also file a claim to be recognized as the child’s father.
In rare cases, the mother of the baby does not want to admit the fact of paternity . Such situations arise due to various circumstances, such as enmity, hatred between citizens, reluctance in the future to contact the blood father of a minor.
However, these subjective factors cannot become an obstacle to protecting the rights of the child. Therefore, a citizen can file a lawsuit with a corresponding demand. But in this case, a biological examination may be required.
How to file a claim against the mother of a baby?
There are situations when the biological father of a child born in a civil marriage refuses to acknowledge his paternity. In this case, the baby’s mother can file a claim with a court organization so that paternity is established, which means the child can claim his rights, including receiving alimony.
To conduct an examination to establish paternity, or more precisely, genetic fingerprinting, you need to independently find an institution that will conduct it. And in the lawsuit filed in court, you will need to indicate a request to entrust the procedure to this particular institution.
If the biological father and your former common-law spouse begin to evade the procedure to establish paternity and interfere with it in every possible way, then the court may recognize the relationship with the child without it.
Possible problems if mother and child have different surnames
If the child and mother have different last names, difficulties may arise after divorce or the death of the father. First of all, the problems will be related to the obviousness of the family connection.
To avoid this, you need to enter information about the newborn in the mother’s passport in the “children” column. This can be done at the passport office by presenting the child’s birth certificate. Difficulties may arise when contacting various authorities. Therefore, you should have with you a complete package of documents that confirms the change of surname by the mother and the fact of the relationship with the child. The following documents are required as confirmation:
- Child's birth document.
- Divorce document with a note about the mother's change of surname.
- Marriage document if the mother got married again and changed her data.
- A marriage certificate received from the registry office, which confirms the existence of a marriage relationship in the past.
In the case of different surnames of the mother and child, there may be problems when traveling abroad with a minor. In such a situation, you should also carry documents with you that confirm the existence of a relationship.
To avoid additional difficulties, you need to have an official translation of the child’s birth certificate. This can be done at the consulate of the country you plan to visit. Thus, if parents have different surnames, then the child can receive the surname of either mom or dad.
If at the time of the birth of the child the mother and father are not in an officially registered marriage, then the newborn can be given the father’s surname. To do this, the father must write a statement of paternity, on the basis of which information about him will be included in the child’s birth document. If a parent does not recognize his paternity, this can be done in court, in which case the child can also receive the father's surname.
What documents confirm registration?
- Exchange card received during the consultation process and filled out in the maternity hospital.
- Or a document issued by any other medical institution that performed the birth. If the birth was carried out by a doctor in private practice , then a certificate issued by him will also be suitable.
- An application to the registry office on behalf of someone present at the birth that took place outside a medical institution is also suitable Suitable for both written and oral delivery. If this person does not have the opportunity to appear in person at the registry office, his signature is also suitable, and it can be sent by any convenient means of communication.
- Documents that confirm the identity of the parent, for example a passport .
- If the marriage is still registered, you will need a marriage certificate.
Reference! There are situations when there is none of the above, in which case, only go to court.
Bastardy
Children were always born. And often outside of official relations. Society did not welcome this. Therefore, they tried not to make it public. The opening of the Iron Curtain led to the fact that a child born before the legalization of life together was no longer condemned by society. But the lack of official confirmation that he has a father gives rise to certain difficulties. Single mothers receive government support, monthly payments and benefits.
In the modern world, the concept of civil marriage is widespread. This status is assigned to families who live without official registration, but have joint property and a household. Previously, such relationships between a man and a woman were called cohabitation. Civil marriage has many supporters who are fighting to give it legal status. But so far, legal norms for such relationships do not exist, and accordingly, such partners cannot defend their rights, and if they do not sign, the resulting child will also be deprived of the privileges that a child whose parents have signed has.
Legal aspect
Article 58 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation establishes the child’s right to receive a surname, patronymic and first name. They are given to the child at birth, or more precisely, within three months after his birth. Subsequently, the data may be changed if there are sufficient documentary grounds.
A child born out of wedlock may be registered:
- In the mother's surname, indicating the real father's middle name or other data.
- For the biological father's last name.
- For the surname of a person who is not related to the newborn, but who wished to register it in his name.
The simplest and most common case is when a woman in labor registers the baby in her own name, giving him a middle name based on biological kinship. To assign a patronymic, no justification is needed; only an expressed desire is sufficient. It is somewhat more difficult to formalize a surname; here the situation is different.
Important!
A woman, upon her own application, has the right to give her newborn only her last name. To do this, she will need to bring a certificate from the maternity hospital and provide her own passport.