The Family Code of the Russian Federation obliges both parents to support their minor children until they reach adulthood. If parents do not comply with this, then child support is collected from them in court. If parents do not pay alimony, then bailiffs will collect arrears of alimony from them by decrees.
What should a parent know from whom the bailiff is collecting or has already collected arrears of child support?
This will be discussed in this article.
Minimum amount of alimony in 2021
Russian legislation does not limit the minimum amount of alimony. The amount of payment is determined by the parents at the conclusion of the agreement or by the court. There are three options:
o as a percentage of the payer’s income (salaries, pensions, scholarships, unemployment benefits, etc.) minus personal income tax (13% in Russia). Assigned if the payer has a stable income.
o in a fixed amount of money (TDS). Appointed if the income of the alimony holder is unstable.
o in a mixed way - used when the alimony payer has several sources of income: stable and periodic.
The idea of establishing a minimum amount of alimony at the state level has been discussed for a long time. Similar bills have been submitted to the State Duma more than once. In such initiatives it was proposed to tie child support to a specific amount - usually to the children's regional monthly allowance. There is no movement on this issue yet. There is a possibility that in 2021 the authorities will return to this problem.
What amount can be assigned?
When filing a claim for alimony, you can specify a fixed amount for monthly payments or a share of your ex-spouse's income. But the court will not simply assign a fixed amount; reasons are needed for this, for example, if the ex-husband has no official income, irregular earnings, or he receives a salary in foreign currency or food rations.
The amount of payments depends on the usual level of expenses for children in the family and on the cost of living for minors in the region. The court will review the claims and decide how much alimony to award.
Alimony payments according to the law:
- for one child - 25% of the parent’s income;
- for two children - 33%;
- for three or more - 50%.
All children from different marriages are counted. If a father left his first family, leaving two children there, and then left his second wife with one child, then he will give no more than 50% of his income to the three children. This money will be divided equally between the children - each will get 16.6%. If he left five children, each will receive 10% of his father’s earnings.
The court may determine different amounts of alimony depending on the situation. For example, one of the ex-wives cannot fully provide the children with what they need, while the second can cope without the help of the child’s father. Then the court can set the amount of alimony for the first wife higher than for the second.
Parents must also share among themselves the costs of treating a child’s serious illness and paying for his care. And if the child does not have housing, then, taking into account the new amendments to the Family Code of the Russian Federation, you also need to take care of living conditions and additionally pay part of the rent for a rented apartment or mortgage payment. The amount of such payments is determined by the court.
Read on topic: Divorced mothers (or fathers) will receive additional alimony: how it works
If a parent is going to leave the country, then it is necessary to agree in advance on the amount of compensation and sign an agreement indicating how he will pay alimony: regularly, immediately allocate the amount for several months, or transfer his property to the children for alimony.
Payment of alimony stops when:
- the child is 18 years old or has acquired legal capacity before this age, for example, got a job, opened his own business, or got married;
- the child was adopted by another person who himself will fulfill the responsibilities for his maintenance;
- the paying parent has died.
If a parent’s financial situation has changed, then the amount of alimony can be changed through the court. This is possible if, for example, the alimony worker retired and his income decreased, he changed jobs and his salary became higher, or he had a child in another family and new expenses appeared.
Most often, the court considers issues of changing the method of calculating alimony: moving from a fixed amount to a share of earnings and vice versa.
The amount of income is determined in accordance with the list of income from which alimony is paid. It includes all income from the main place of work, part-time work and running a business.
When the alimony payer officially has a low salary, but has income “in an envelope,” proof is needed that he receives more. Provide evidence in court that your ex-spouse makes large purchases, expensive renovations, vacations abroad, and generally lives beyond his means.
2-NDFL certificates for past periods will help confirm that before alimony was assigned, the payer received a higher salary at the same place of work. You can request documents through the court.
If your ex-husband is on the labor exchange and is unemployed, file a claim to recover a share of the income. In this case, part of the unemployment benefit will be withheld from him.
If he does not receive unemployment benefits and does not officially work anywhere, then it makes sense to file a claim demanding payment of alimony in a fixed amount. The amount is determined by the plaintiff, but must be justified in court. In most cases, the amount of alimony is determined at the level of the subsistence minimum per child in the region. The final amount of child support is decided by a judge.
If your ex-husband is officially employed, file a claim to revise the amount of alimony due to a change in the financial situation of the payer.
Alimony from the state
There is hope that the long-awaited alimony from the state will be introduced in 2021. Bills on state alimony have also been repeatedly submitted to parliament for consideration. Finally, in September 2020, President Vladimir Putin instructed the Government to develop initiatives for targeted social assistance to children for whom parents do not pay child support.
Taking into account the results of the State Council meeting on September 28, 2020, the President compiled a list of instructions to the Government. Response proposals are expected until 08/01/2021, that is, a specific date has been announced. Perhaps they will be so well developed that alimony from the state will be introduced before the end of 2021. On the other hand, funds must be provided in the budget for the payment of state alimony, but they are not included in the Russian treasury for 2021.
What should needy families who are not receiving enough child support do now? You can try to apply for the following types of social assistance from the state:
— Child benefit for low-income people. If an unlucky parent does not pay child support, in many regions it is assigned in an increased amount by 50%. You can find out whether such an opportunity is provided in your region by contacting the social security authorities.
- Survivor's pension. If the defaulter is not announced at all, you can file a lawsuit to find him. A pension will be assigned if the enforcement search does not produce results within a year and the debtor is declared missing.
What laws govern child support payments?
The regulations for financial assistance for children are described by:
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the list of types of wages and other income from which alimony for minor children is withheld”;
- Family Code of the Russian Federation (Article 81-83);
- Methodological recommendations for fulfilling the requirements of writs of execution for the collection of alimony.
Bankiros.ru
Deposit “Valuable asset smart” Renaissance Life, Persons. No. 3354
to 10%
per annum
from 100 thousand
91 days
Make a contribution
Housing alimony
The main change of the previous year 2021 was the introduction of housing alimony.
“Housing support” is part of the additional expenses for children. According to Art. 86 of the RF IC, earlier to recover funds for additional. expenses may be incurred in connection with the following exceptional grounds:
• injury or serious illness of a child;
• payment for compulsory child care by strangers, and so on.
The law on “housing alimony” supplemented Art. 86 of the RF IC with the words “lack of residential premises suitable for permanent residence.” Thus, the list of grounds on which additional expenses for children can be recovered has expanded.
The parent with whom the child remains will be able to claim child support if the following conditions are met:
- The alimony payer himself must be able to work.
- Both the child and the parent should not have property for permanent residence. In this case, we are talking not only about the right of ownership as such, but also about the right to use. For example, if a mother and child are registered in the house or apartment of their grandparents, then housing support should not be collected.
- A mother (or father) applying for additional financial assistance must confirm that she is in a difficult life situation and cannot pay for housing.
Funds to pay for housing will be collected from the alimony payer in a fixed sum of money (TDS). The court will determine the amount of payments depending on the life situation of each of the interested parties.
We can agree
The payer may also have arrears of alimony due to non-payment for some time under a voluntary agreement.
Then the spouses need to sit down at the negotiating table and try to resolve this issue peacefully. One way out is to change the terms of the agreement (amount of alimony, terms of payment, etc.) so that the interests of the child are not harmed and the payer has money to live on.
With a spouse obligated to pay alimony by court decision, you can also try to resolve the issue peacefully.
The ability to reach an amicable agreement can save both parties from unnecessary problems and hassle. And this is even more in the interests of the payer, who, as a result of non-payment of alimony, risks losing parental rights, receiving a criminal record and an amount of debt that exceeds what has already accumulated. Therefore, the claimant has many arguments that can force a negligent father to pay alimony, which they previously agreed upon peacefully or which was awarded by the court.
How to bring your ex-husband to criminal liability for non-payment of alimony
As of December 2021, the Ministry of Justice is developing amendments to Art. 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Their task is to clarify the wording of the law so that defaulters cannot transfer incomplete amounts of alimony to children and thereby evade criminal liability. Nowadays, the alimony worker can pay rarely and little by little, about once a year, but he cannot be subject to the most severe punishment, since he cannot be called a malicious defaulter. The Ministry of Justice plans to ensure that child support providers regularly transfer the full amounts established by the court to children. I would like to hope that these amendments will be adopted in 2021.
Important update:
The Ministry of Justice is developing a draft law prohibiting the admission of alimony debtors to take the driver's license exam, the head of the SSP department said during the round table.
According to the head of the SSP, the draft law has already received approval from the Ministry of Internal Affairs, which proposed applying similar measures to other debtors.
In addition, the Federation Council proposed limiting the right of alimony debtors to obtain a foreign passport and register property rights. One of the senators made such a proposal on July 23.
Important update of judicial practice at the end of the article!
ATTENTION! In the near future, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation will establish the minimum permissible amount of alimony. Stay tuned to this site for updates.
There are four possible options
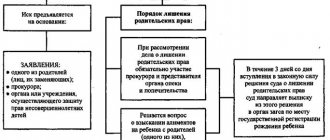
The first is to go to court with a claim for deprivation of parental rights (Articles 69 - 70 of the RF IC). Often such a step forces the debtor to pay the debt and start paying alimony. Even if this does not happen, it is better for the child that the parent is deprived of parental rights. This will avoid further claims from a disabled parent against an already adult child for the collection of alimony (Clause 1, Article 71 of the RF IC).
Let us note that deprivation of parental rights does not relieve parents from the obligation to support their child (Clause 2 of Article 71 of the RF IC).
The second is to hold the debtor accountable for late payment of alimony. So, if the debtor does not pay alimony under a notarial agreement, then he will bear responsibility in the manner provided for by this agreement (Clause 1 of Article 115 of the RF IC).
If the debtor does not pay alimony according to a court order, he will pay a penalty in the amount of one-half percent of the amount of unpaid alimony for each day of delay. The recipient of alimony also has the right to recover from the defaulter all losses caused by the delay in the part not covered by the penalty (Clause 2 of Article 115 of the RF IC).
These requirements must be formalized as a statement of claim and filed in court.
The third is to bring to administrative responsibility. Thus, if a parent, without good reason, in violation of a court decision or a notarized agreement, does not pay child support for two or more months from the date of initiation of enforcement proceedings, and if such actions do not contain a criminal offense, then such parent may be held administratively liable in the form of compulsory labor for a period of up to 150 hours, or administrative arrest for a period of 10 to 15 days, or an administrative fine in the amount of 20 thousand rubles. (Part 1 of Article 5.35.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Fourth - bring to criminal liability in the form of correctional or forced labor for a term of up to one year, or arrest for a term of up to three months, or imprisonment for a term of up to one year (Part 1 of Article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation; Part 6 of Article 102 Law N 229-FZ). It is possible to bring a parent to criminal liability if he has failed to pay child support without good reason repeatedly, has been brought to administrative responsibility for failure to pay child support and is considered subject to administrative punishment (clause 1 of the Note to Article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation; Part 1 of Article 4.5 of the Administrative Code RF). At the same time, under certain circumstances, the court may exempt from criminal liability (Article 76.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Don't despair if your husband doesn't pay alimony
Fortunately, the legislation of the Russian Federation obliges the ex-husband to pay monthly child support.
Therefore, they provide many different ways to force the father to fulfill his parental duty. Among other things, there is a possibility that you will encounter a bailiff who is not particularly conscientious or efficient, who, instead of helping in collecting alimony, will cause you even more problems. Therefore, knowledge of the law, its leverage over your ex-spouse and your rights can make life much easier for you and your children, as well as speed up the process.
Why doesn't the father pay child support?
Before you find out how to force your ex-husband to pay alimony, it is worth understanding why he does not do it. There can be many reasons for non-payment. For example: Out of a feeling of revenge on my ex-wife. Most often, women initiate divorce, and the husband tries to take it out on the children and does not pay alimony. Due to undeveloped parental instinct. The woman herself becomes the culprit for this, by protecting the father too much from all worries about the children during marriage. It is not surprising that even after the divorce the husband does not try to take care of the children and, even more so, will not pay alimony payments. Due to the ex-husband’s lack of a job or other type and source of income. It's worth figuring out why this happened. If he cannot get a job for objective reasons, then try to be understanding, but if the ex-spouse deliberately does not get a job so as not to pay money for maintenance, then he can be held accountable. Because of selfishness. If the husband does not have an innate sense of responsibility, then he can only be forced to pay alimony through the courts. First, try to solve the problem peacefully. Talk to your ex-husband and find out why he wants to pay alimony. Try to explain to your ex-husband that your money is not enough to support the child and the father’s financial help is vital. You can also contact your ex-husband’s parents so that they try to influence the negligent parent and force him to pay, or they themselves help you.
Regulatory framework
| Laws | Articles |
| Family code | Article 69 – grounds for annulment of a parent’s rights to a minor child. Article 70 – features of the judicial procedure during which a decision is made to annul the rights of a parent to a minor child. Article 114 – grounds and procedure for releasing the alimony holder from repaying alimony debts. Article 115 – forms of liability for alimony providers who approach the issue of alimony payment irresponsibly. |
| Code of Administrative Offenses | Article 5.35.1 describes what threatens alimony defaulters if an administrative case is opened against them. |
| Criminal Code | Article 157 describes what awaits alimony defaulters if a criminal case is opened against them. |
How to force my husband to pay alimony?
The easiest way to solve the problem of divorce is to enter into an agreement on the payment of alimony payments. The agreement must be secured by a notary so that the husband is required by law to pay maintenance money. This document must indicate the amount, as well as the procedure for exactly how the ex-husband will pay. If the ex-husband does not pay alimony, then the money for child support will have to be recovered through the court. Payment of alimony You need to contact the bailiffs and get from them a certificate about the amount of debt the child's father owes for alimony payments. Draw up a statement of claim addressed to the senior bailiff stating that the bailiff handling your case is not taking sufficient action to search for and collect alimony from your husband. For example, find out whether the bailiff made requests to the Pension Fund or the Tax Inspectorate. Ask to monitor his actions or inaction and notify you. Draw up an application addressed to the senior bailiff to initiate a criminal case against your ex-husband, since he does not pay alimony, as well as to issue a ban on leaving the territory of the Russian Federation so that he does not escape. Next, you need to submit a petition to the traffic police and the Office of the Federal Registration Service (UFRS) in order to verify the fact of your husband’s ownership of real estate and vehicles. Contact the court with a claim and a certificate of debt in order to charge a penalty for non-payment of alimony. Also file a complaint against the senior bailiff if he has not responded to your statements. Attach copies of all letters, petitions and other documents related to this case (they must indicate that the application was accepted). Send a copy of the court decision to collect maintenance money to the bailiffs along with the notice. After this, wait for the obligatory official response from this service.
How to apply for alimony
In addition to the main documents, the court must provide bank details for sending alimony. There are several ways to send papers. Documents are sent via mail and courier, printed and certified by a notary by registered mail. If you have an account with government services, you can submit an application through this service.
The claim document for alimony is accepted at multifunctional centers. To do this, make an appointment and visit the MFC with all the necessary documents.
You can send documents to the magistrate’s court through the website “GAS Justice” or on the official portal of the magistrate’s court. In response, they send a notice of acceptance of the claim.
Due to the spread of coronavirus, the reception of citizens is currently limited and submission of papers through the electronic portal is encouraged.
Where to go if your ex-husband does not pay child support?
So where should you go and what should you do if your father refuses to pay child support? To begin with, it is worth noting that a husband can pay alimony both during marriage and after its dissolution, and even if the marriage union has not been formalized. However, in the latter case, it is necessary that both parents are indicated on the children's birth certificate. If the father is not indicated, then you will have to carry out a procedure to establish paternity, including a DNA test, and only after that oblige him to pay child support. Going to court If your ex-husband does not pay alimony, then to go to court you will first need to draw up a claim in 3 copies. It must indicate: Passport details of the plaintiff indicating the place of residence; Children's data; Passport details of the alimony payer indicating the place of residence; As well as grounds for forced collection of alimony payments. The following list of documents must be attached to the claim: Photocopies of children’s birth certificates; A photocopy of the marriage or divorce certificate; An extract from the house register or another type of certificate from housing authorities confirming the child’s residence with the plaintiff; Document about the defendant's income level. For example, certificate 2-NDFL.
Cancellation of child support after challenging paternity
Is it possible to completely and legally not pay child support? Of course - after challenging paternity (as well as motherhood). However, this right is granted to a citizen only within the framework of judicial proceedings.
Important : the statute of limitations, calculated as a general rule of three years, does not apply in this case.
The exceptions are:
- A case when a child is conceived not naturally, but through medical intervention - artificial insemination, surrogacy, and the parents gave their written consent to medical manipulation.
- Recognition of paternity, if the citizen was reliably aware that he is not the biological father of the child.
So, if during the trial the fact of lack of relationship was established, the next step will be to contact the registry office - it is necessary to cancel the record of paternity (after the court decision has entered into legal force).
A judicial act satisfying the plaintiff’s demands to challenge paternity and cancel the payment of alimony will be a document that is presented to the bailiffs or the employer - after which the collection will be canceled.
Important : it is impossible to return previously paid alimony amounts, except in cases where they were assigned on the basis of knowingly false documents/information.
How to collect alimony
It is worth noting that the husband’s lack of work and other income does not exempt him from alimony obligations to the children. The court will oblige him to pay alimony in a fixed amount, the so-called hard cash. Where and how the spouse will take the money to pay it, he will decide for himself. However, if the ex-husband does not fulfill his alimony obligations, then bailiffs can seize his property and force him to sell it, and give the money received to the plaintiff for child support. If the ex-husband is disabled, then he should receive an appropriate pension, from which alimony may also be withheld. In a situation where the debtor works unofficially, then you need to contact the police or bailiffs to find out the real level of his income. By the way, for concealing this information the debtor faces administrative punishment. Also, depriving the child’s father of parental rights will not exempt him from paying child support.
What else do you need to know?
A claim for alimony can be filed at any time, but the maximum period for receiving alimony payments for the past period is 3 years. Even if your offspring is already 18 years old, the ex-husband will be obliged to pay the debt for the last three years plus a penalty for each of the overdue days in the amount of 0.5%. What you need to know Another unpleasant moment may be the fact that the father may begin to hide, not wanting to pay child support. In such cases, contacting bailiffs will help resolve the situation. The debtor will be added to the list and put on the wanted list, and a criminal case will be initiated. Even if the woman refuses the funds, the defaulter will still be required to pay all debts. If you know where your ex-husband works, but he does not pay money for maintenance, then you can reduce the time for court proceedings to collect alimony payments by sending the received writ of execution directly to his work or to the local branch of the Pension Fund of Russia, in the event if he receives a pension. It is important to know that if the father does not pay maintenance money for more than 4 months, then he becomes a willful defaulter and a criminal case can be initiated against him under Article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. After the court finds out exactly why the spouse does not pay alimony, in order to clarify the nature of the malice. To do this you need to: Send a notification to the bailiff service; Contact the internal affairs bodies or the prosecutor's office to draw up a statement under the above article. The maximum punishment under this article for a defaulting father is imprisonment for up to 3 years or correctional labor.
The needs of children today are quite great. A mother, after she has divorced the child’s father, cannot always support her son or daughter on her own. In principle, this is not necessary. Art. 80 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation states that each parent is responsible for making payments to their children. Or rather, this is how: one parent transfers money, and the second, with whom the child lives, spends part of his income in the interests of the minor. But not every dad wants to lose part of the money he earns; sometimes, he doesn’t even have any money. Therefore, the question of what to do if the ex-husband does not pay alimony is very relevant.
Will alimony be written off in bankruptcy?
Many citizens are sure that personal bankruptcy is a kind of indulgence. You went through the procedure, declared yourself bankrupt and you don’t have to worry anymore.
Old debts are written off - it's time to make new ones. However, there is a whole set of obligations that are not reset in bankruptcy. Among them are alimony payments.
But alimony can lead to bankruptcy.
According to Article 223.2 of the bankruptcy law, if we are talking about an out-of-court procedure (this is when debts do not exceed 500 thousand rubles and you need to apply for bankruptcy at the MFC), alimony must be included in the calculation of the obligations that the debtor indicates in his application.
That is, the amount that is subject to mandatory collection. But as mentioned above, bankruptcy will take place, and alimony debts will remain with the applicant. Therefore, it makes no sense to initiate this procedure in order to legally write off overdue alimony.
But if the amount of alimony debt is large enough, then other creditors may not get anything. The fact is that in case of judicial bankruptcy, alimony is compensated from the funds of the bankruptcy estate in the first place.
Creditors can, of course, try to challenge the payments, but it is unlikely that they will succeed. At the same time, if for some reason alimony does not fall into the bankruptcy estate, then its recipient will not lose anything except time. Sooner or later he will be paid alimony.
For violation of terms of payment of alimony, a penalty is charged. This is stated in Art. 115 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation. Since 2018, the amount of the penalty is 0.1% for each day of delay, but it can be higher if the parents agree on this.
Is it possible to release the debtor from paying alimony arrears?
In court practice, there are situations when the amount of debt is reduced or completely written off from the debtor. Of course, there must be serious reasons for this that prevent the payment of alimony.
Such circumstances include: serious illness, loss of employment, financial difficulties, the emergence of new dependents, and the like. There is no specific list of situations in the legislation. Mitigating circumstances are supported by documents or witness testimony at the hearing.
Thus, enforcement proceedings can be called the initial mechanism for collecting debt from the alimony provider. Sources of liquidation can be not only wages, but also the property of the debtor. In addition, the recipient may file a claim in court to recover a penalty.
The legislation establishes various methods of putting pressure on the defaulter, including imprisonment. In addition, the alimony provider has the opportunity to avoid debt payments. To prevent this, you can ask a lawyer by phone or online on our portal.
How is a penalty calculated and collected on debt obligations?
Not everyone knows that failure to repay a debt entails liability for late payments. Let's take a closer look at this issue.
Since the alimony payment responsibilities and arrears are not relieved from the alimony holder, he can be held financially responsible for the missed deadline for making payment amounts. This penalty is called a penalty. She leaves half a percent of the total debt amount daily until it is repaid. It turns out that the outstanding debt is not only being written off, it is increasing every day.
To collect the penalty, you need to contact the bailiffs to get a certificate about the current amount of the debt. Next, you need to contact the court with a statement of claim for the recovery of a penalty and attach a certificate. It is worth noting that a claim can be filed at any time, since the law does not limit this issue by statute of limitations. It is recommended to do this periodically, since huge amounts of debt and penalties will only delay the payment process.
In addition, family law prescribes payments not only for non-payment and alimony, but also compensation for losses that the alimony recipient suffered due to late payments. Unfortunately, the connection between losses and debt is difficult to establish.
Content
1. Mechanism of enforcement proceedings
2. From what sources are amounts of money collected to eliminate debts?
3. How is the penalty calculated and collected on debt obligations?
4. Mechanisms influencing the defaulter established by law
5. Deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of child support obligations
6. Criminal liability for non-payment of alimony
7. Is it possible to release the debtor from paying alimony arrears?
Responsibilities for paying child support are assigned to the parent living separately from the child. After the divorce process, the volume and procedure for payment of alimony obligations are established by a settlement agreement between the spouses or by the court (formation of a decision or order).
In situations where funds are not paid to the alimony recipient on time, arrears on alimony obligations are formed. There are situations when the debt becomes impressive and is not paid off by the alimony provider.
In this article we will look at what actions to take in this situation and what mechanisms exist for collecting alimony.