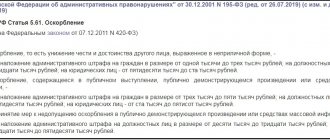
Errors in appeal
Lawyers typically make three basic mistakes in appellate court.
They do not check the unconditional grounds for canceling a decision
This is a strong argument for overturning the decision, but it is often overlooked. Lawyers are too keen on justifying their position and describing the circumstances, but forget to check whether there are unconditional procedural violations in the case.
If the appellant finds at least one such violation, the court will cancel the decision and reconsider the case according to the rules of the first instance, that is, it will reconsider the dispute on the merits. During such a review, it will be possible to submit petitions and statements, present evidence, if for some reason they did not do this in the first instance.
Most often in complaints, appellants refer to two violations - the court considered the case without a person participating in the case, who was not notified of the time and place of the hearing, or the court made a decision on the rights and obligations of persons who were not involved in the case.
If the judge in the case was illegally replaced or territorial jurisdiction was violated, you can refer to the consideration of the case in an illegal composition of the court.
Check if there is a court record in the case - higher courts often overturn decisions due to its absence. If there is no audio recording of the court hearing in the case, the courts can also overturn the decision on the same grounds.
The appeal will overturn the decision if there is no audio recording, but it contained information that served as the basis for the adoption of a judicial act. Therefore, indicate in your complaint what important information was on the audio recording. For example, interrogation of witnesses, experts, examination of evidence.
Lawyers are bad at building a defense
The lawyer cites in the appeal an endless list of court errors from serious to insignificant.
For example, when he points out that the judge incorrectly applied the rules and was not wearing a robe, the second argument clearly negates the seriousness of the first. The appellants usually formulate the violations themselves in general terms - without reference to specific evidence and case materials. Judges rarely take such complaints positively.
Recommendation - write no more than four to five clearly stated reasons for cancellation. In each argument, it is advisable to describe three points: the lower court's error, the incorrect conclusion it reached because of that error, and the conclusion the court should have reached.
Lawyers are passive during appeals
When the court has already considered the case on its merits, lawyers think that their task in the appeal is only to present arguments for and against the court’s decision. This is not entirely true. An appeal is the last opportunity to close evidentiary gaps in the positions of the parties in the case. Take advantage of this.
Try to present evidence essential to the case in the appeal, file motions. The appellate authority may accept additional evidence from a party and consider requests for new evidence, but only in two cases. The first case is if the party justifies that it could not present them to the first instance for valid reasons. The second is if the court of first instance rejected them. That is, in the appeal it is necessary to once again state all the petitions and evidence that were rejected by the first instance.
If you did not present evidence at the first instance, but it is essential to the case, still present it on appeal. If you cannot give good reasons or they are clearly “extracted,” the likelihood that the court will accept the evidence or satisfy the petition still remains: the court would rather accept new evidence than not accept it at the risk of canceling the judicial act.
For example, a company filed a claim against the company for unjust enrichment. Since the defendant did not provide evidence that he withheld the transferred money justifiably, the court granted the claim. To the appellate court, the defendant presented contracts and service acceptance certificates, which confirmed the existence of obligations between the plaintiff and the defendant and the basis for payments. The appeal added documents to the case and dismissed the claim. The higher courts agreed with the appellate court.
general information
Third parties also have the right to appeal when a decision affects their rights. It is possible to challenge the decision of both the world and district courts - only the decision of the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation is considered final. The appeal procedure is regulated by the Civil Procedure Code (Code of Civil Procedure), Chapters 39, 41, 41.1. You can challenge the decision in three ways:
- File an appeal. According to Article 320 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, this is how you can challenge the first court decision, which has not yet entered into force.
- Submit a cassation. According to Article 401.2 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, this method of challenging a court decision is suitable for a decision that has already entered into force.
- Make a supervisory complaint. According to Article 412.1 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, this is the last opportunity to appeal the court decision. It can be used when the above courts did not influence the course of the case.
It is worth noting that the mechanisms for appealing court decisions are quite effective. Today it is possible to challenge many decisions of the courts of first instance.
Errors in cassation
Lawyers make six common mistakes. The first three were discussed in the section on appeal. Three more errors are typical only for cassation.
The arguments of the complaint go beyond the scope of cassation consideration
In 99 percent of cases when cassation upholds decisions of lower courts, it indicates that the arguments of the complaint are aimed at reassessing the factual circumstances of the case and evidence. And this is not within the scope of consideration of the case in cassation. Cassation only checks whether the courts correctly applied the rules of substantive and procedural law.
The reason for this practice is that lawyers often copy the text of the appeal into the cassation complaint. For example, the complaint writes that “the conclusions of the courts do not correspond to the factual circumstances and the evidence presented in the case.”
If you want to present new evidence or perform procedural actions that are possible only in the first instance, look for unconditional grounds for reversing the decision.
In your cassation appeal, refer specifically to errors in the application of the rules - these are your main arguments. All arguments that are related to non-research or incorrect assessment of evidence are given only to confirm the court’s errors.
The arguments of the complaint do not correspond to the pleading purpose
The goal of the cassator is to achieve the reversal of judicial acts with which he does not agree. To do this, he can ask the cassation court, for example, to adopt a new judicial act in the case, to send the case for a new trial, or to leave in force one of the decisions or resolutions previously adopted in the case. Sometimes cassation officers ask to adopt a new act in the case - this is the most advantageous for the party, regardless of the circumstances of the case and the arguments that it brings.
The cassation court will not be able to adopt a new act, since to do this it will have to examine and evaluate the evidence, and the cassation court does not have the right to do this. Such a discrepancy between the request and the arguments reduces the credibility of the complaint and often raises questions and criticism in the court of cassation.
Study the case materials and select possible arguments for cassation. After this, decide how to formulate the pleading part of the cassation appeal.
Additional documents submitted too late
Lawyers often file position papers too late and draft them incorrectly. Courts usually accept documents directly at the hearing, but not cassation documents. If you submit a response to the complaint, additions, or written explanations directly to the hearing, the cassation office may reject them. For example, the court indicated that written explanations were received on the eve of the court hearing and refused to include them in the case materials.
Consider the peculiarities of the court. For example, the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District may not accept written explanations, since it considers them new evidence that the cassation cannot accept. Therefore, format additional explanations as the text of a speech - the courts usually accept it.
CALL +7 (495) 255-11-80, FREE CONSULTATION!
Supervisory complaint
Fyodor Stepanovich was not satisfied with the decision of the cassation court. The next and final step is filing a claim with the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. It has an impressive composition - 13 judges: the Chairman of the Supreme Court, his deputies and judges of the Supreme Court.
Article 391.3 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation regulates the requirements for the content of a complaint. The supervisory appeal is sent to the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation within 3 months. The authority does not consider all civil cases. The full list of cases is announced in Article 391.1 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. The review period is from 2 to 3 months. This decision cannot be appealed.
In what cases should you prepare to speak at a meeting?
The algorithm for resolving a dispute by the court of appeal depends on the method of proceedings by which the first instance made the final decision. In particular:
- In the case where the first instance resolved the dispute in a general manner, the appellate court is also authorized to schedule a general hearing. Each participant whose interests are affected by the verdict receives a summons to appear for consideration of the complaint.
- As practice shows, an appeal against a decision made in a simplified manner occurs at the request of the appellate judge. A meeting may be scheduled with the participation of all interested parties, but in most cases the complaint is considered without the presence of third parties.
- Preparing the writ is the responsibility of the federal court, but it may deny the applicant's request. In this case, the person has the right to appeal the refusal, but this happens without the announcement of the meeting, but in absentia.
Stage 1. Appeal
The appeal period is 1 month from the moment the court decision is made in final form. That is, within a month, the decision of the district court is considered not to have entered into legal force and does not carry with it any legal consequences. When a decision is made in his favor, the plaintiff cannot obtain a writ of execution from the court and transfer it to the bailiffs to initiate enforcement proceedings. The court decision is considered to have entered into legal force if within a month none of the parties filed an appeal. However, the decision can be appealed outside the period of one month, if the person who submitted the complaint can justify the valid reason for missing the deadline. The appeal is filed through the court that made the decision being appealed; it must be addressed to a higher court - if the decision was made by a magistrate, then the appeal will be considered by the district court, in another case - by the city, regional, regional, etc. The result of consideration of the case by the appellate instance is an appeal ruling, with the adoption of which the court decision comes into force. The following solutions may be considered for resolving a complaint:
- the court may leave the decision of the court of first instance unchanged and the appeal without satisfaction;
- the appellate instance may cancel or change the decision of the district court in whole or in a certain part, and make a new decision on the case;
- the decision of the court of first instance may be canceled in whole or in part and the proceedings in the case are terminated or the application is left without consideration in whole or in part;
- the complaint may be left without consideration on the merits if the document is filed after the expiration of the appeal period and the issue of restoring this period has not been resolved by the applicant.
If an appeal decision is made in favor of the plaintiff, he has the right to receive a writ of execution in the near future.
What is the period for appealing after receiving a copy of the order?
You can write an objection to the magistrate during a certain procedural period. For an order, this is ten days from the date of receipt of a photocopy of the documentation. Office workers hand it over to the parties personally or send it by registered mail.
Missing deadlines is grounds for refusal to accept the application. The exception is if you have a good reason. This includes:
- Late delivery of a photocopy of the order.
- Staying in a hospital for long-term treatment.
- Business trip to another location.
- Difficult family circumstances that prevented the timely filing of a complaint (death of a close relative).
To restore the deadline, you will need to submit a separate application to the court describing the extenuating circumstances. They are supported by written evidence - a document from the employer or a certificate from a medical institution about being in a hospital.
Complaint to the European Court of Human Rights
For citizens of any country there is such an opportunity as protecting their rights in the European Court of Human Rights. However, it is worth noting right away that this is not the most effective way - there are no clear criteria for the possibility of appeal, the appeal procedure itself is opaque and the court is highly politicized. With all this, when filing a complaint with the European Court of Human Rights, you must follow a few simple rules:
- the right that has been violated must be contained in the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms, and this right must have been violated by state authorities;
- a court decision and an appeal ruling must be made in the case;
- the deadline for filing a complaint is 6 months from the date of the appeal ruling; therefore, it is recommended to file a complaint to the European Court of Human Rights simultaneously with an appeal against the decision in the Russian cassation authorities;
- it is recommended to write a complaint in a certain form, the language of the document is English, French or the country of which the citizen is filing the complaint;
- the complaint must contain arguments understandable to European judges;
- There is no fee for filing a complaint with the European Court of Human Rights.
How to behave at a court hearing
It is necessary to initially understand that the procedure for considering a dispute and the decision-making algorithm of the appellate court are significantly different. The judge at the hearing does not reconsider the case in essence, but only confirms/annuls the legality and validity of the decision made.
Therefore, there is no need to re-prepare fiery speeches and start an argument with the defendant. The most important thing is to prove that the first instance made a significant mistake that affected the outcome of the paperwork. To annul a decision, it is sufficient to confirm only one violation, which is supported by evidence. The decision of the appellate judge will largely depend on the papers submitted by the complainant.
For its part, the defendant, that is, the party who is completely satisfied with the decision made, can bring counter arguments indicating that the decision was made correctly. You need to speak clearly and to the point, which is due to the small amount of time allotted for resolving the dispute.
Each participant will have up to 10 minutes of time for oral presentation and defense of personal opinion, so you need to briefly outline the essence of the claims and ways to confirm the violation.