Renting specialized housing
Specialized housing is space owned by a city, municipal or private fund, intended for rent to citizens to solve certain tasks (official, maneuver and social).
Reference! Renting such residential premises is carried out by signing an agreement. Relations under such a document are regulated by the Housing Code, in particular Section IV.
Model agreement
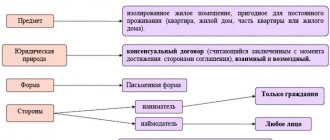
Special agreement rental is a bilateral agreement between the Landlord and the Tenant , on the basis of which the owner of the premises transfers it to the citizen for use and possession for temporary residence.
Such a document is drawn up in writing, according to the model approved by law. Each type of specialized hiring has its own approved template. All relations under such an agreement are regulated by Articles 100-102 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
An object
The subject of a standard agreement is isolated housing (a house, part of a house, apartment, part of an apartment or a room in a dormitory), classified as a specialized housing stock on the basis of the rules specified in the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 26, 2006 No. 42.
Parties
Special agreement The lease is bilateral and is concluded between the Landlord and the Tenant for a certain period. The person providing the accommodation may be:
- Russian Federation.
- The subject of the Russian Federation.
- Municipality, institution, enterprise.
- Legal entity (usually for official housing).
Important! The second party to the contract, that is, the Tenant, is always only a civilian.
Rights and obligations
Rights and obligations of the Landlord:
- demand full and timely payment for accommodation and utilities (you can find out the legal details of payment under a rental agreement here, and you can find the payment schedule and details of paying rent for an apartment here);
- transfer housing for use in proper condition, legally free from the rights and claims of third parties;
- ensure access to public utility services of adequate quality and quantity;
- carry out major repairs;
- be responsible for the maintenance and repair of common property.
Rights and obligations of the Tenant:
- move in and register family members and third parties at the place of residence;
- demand elimination of violations in relation to utilities and common property;
- maintain the allocated living space in a suitable condition for living;
- carry out routine repairs and preventive maintenance;
- pay for housing and utility services on time and in full;
- report the circumstances leading to the termination or modification of the tenancy agreement.
Terms of imprisonment
The contract for the provision of specialized housing is fixed-term. However, its termination is not associated with the onset of a specific date, but occurs due to a change in circumstances, for example:
- obtaining other housing;
- dismissal from work;
- completion of renovation work at the main place of residence.
Form and content
Government Decree No. 42 of January 26, 2006 regulates the standard type of contract for each type of specialized hiring, namely for:
- temporary settlement of internally displaced persons and persons recognized as refugees;
- maneuver fund;
- office premises;
- living space in a dormitory.
The content of all these contract options is different, but the form is the same. They all consist of the following points:
- Details of the Parties.
- Subject of the agreement.
- Rights and obligations of the Tenant and his family members.
- Rights and obligations of the Landlord.
- Termination and termination of contractual relations.
- Paying a fee.
- Other conditions.
- Signatures of the parties.
Pay
For each subject of the Russian Federation, individual maximum amounts are established for payment of 1 square meter of housing. In each region they vary depending on:
- territory of the municipality;
- consumer properties;
- level of improvement;
- sizes of residential premises.
Payment for specialized housing may include:
- communal payments;
- expenses for construction, maintenance and repair of housing;
- other expenses provided for by the housing legislation of the Russian Federation.
Rights and obligations of the parties to the rental agreement for specialized housing
Since the rental agreement for specialized residential premises is concluded between two participants in legal relations (the owner and the tenant), the rights and obligations are also assigned to all entities that sign the contract.
If we talk specifically about the landlord of an apartment from a specialized fund, then he is assigned the following list of obligations:
- the owner of the property must transfer the premises to the tenant within the period established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. At the same time, at the time of transfer, the real estate must be completely freed from any claims on the part of third parties, government encumbrances, etc.
- The owner of the property undertakes to provide the consumer with a full range of utilities that are necessary for comfortable living in the apartment. At the same time, the quality of such services must be at an acceptable level in accordance with the conditions of the area where the real estate is located.
- The lessor must be directly involved in the maintenance of the property. In addition, he bears the financial burden of paying contributions for major renovations of the premises.
As for the rights of the landlord, the subject of the agreement has the legal right to demand from the second party to the agreement to pay for housing and utilities within the period established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The obligations of the tenant under a social tenancy agreement, which are regulated by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, are no less broad. In particular, the person undertakes:
- use housing only in accordance with its intended purpose;
- maintain the proper condition of the premises, including taking part in ongoing repairs of housing;
- make financial transfers to the owner’s bank account as payment for the use of housing and utilities on time;
- not violate the legitimate interests and rights of neighbors who live on the territory of the same apartment building or dormitory.
As for the rights of the employer, they are as follows:
- third parties who are recognized as members of the applicant’s family can be moved into specialized housing;
- the tenant has the right to demand a reduction in payments for housing or utilities if the landlord does not fulfill his obligations;
- the right of use is retained by the tenant even in the temporary absence of allocated housing on the territory, but this period is not precisely defined by law;
- the tenant is given the opportunity to terminate the contract with the landlord at his own request, etc.
The legislator also provides for other obligations and rights on the part of the employer, which may be regulated by laws at the federal, regional or local level.
Reasons for refusing to complete a transaction
You can always refuse the government offer. housing authorities.
If the reason is that the premises do not meet sanitary, hygienic and technical standards and rules (for example, they are in an emergency condition, or there is no access to natural light), then the citizen has the right to demand a replacement, and, if necessary, file a claim in court.
In the case where the refusal of the proposed residential premises is not motivated by anything, dictated by subjective considerations (they don’t like the floor, neighbors, view from the window, etc.), the citizen cannot demand a replacement. If he refuses housing, he will not be provided with another one.
Features of the contract
A typical specialized rental agreement necessarily includes:
- Detailed information about the parties to the agreement, including the names and passport details of all members of the applicant’s family.
- Basis for obtaining the right of residence.
- Full characteristics of the transferred housing, its technical condition, availability of furniture and repairs.
- Rights and obligations of the parties regarding the maintenance and repair of housing.
- Procedure for terminating the contract
- Size and payment methods
- Other, individual conditions for each specific case
Important! The Landlord is responsible for major repairs, the quality of utilities and general technical condition, and the Tenant is responsible for maintaining the housing in proper condition and minor cosmetic work.
Dorm room
A contract for renting a room in a hostel is intended for the temporary accommodation of citizens, while two or more persons are allowed to occupy one room. The peculiarity of such dwellings is that they must be furnished and equipped with necessary household items. A dorm room must have at least 6 square meters. meters of living space per resident.
Official
A contract for the rental of a service apartment or other housing - the type and characteristics of such premises are directly related to the position and nature of the Employer’s labor relations. The official rental of an apartment or other housing is provided in connection with election or appointment to a position, as well as during business trips or service (read all about renting an apartment on a business trip here). The lease terminates at the same time as the employee's employment ends.
For orphans
Housing rental agreement for orphans - residential premises are provided for a period of up to 5 years, and then can be extended if circumstances are identified that indicate the need to assist orphans in overcoming a difficult life situation
Attention! Housing is not provided to foreign citizens and stateless persons.
Subject of the rental agreement
If we talk about what is the subject of a contract for the rental of social housing from the housing stock, then first of all we are talking about a building that has a single purpose - residence on its territory for a certain category of citizens.
It should be noted that any contract for the rental of property from the social housing stock, regardless of its type, must contain comprehensive information about the subject of the agreement.
In particular, within the framework of official documentation, the address of the location of the object, its living area, which must comply with the provision norm and accounting norm, are indicated.
In addition, it is a mandatory requirement to indicate in the contract the additional property that is provided to the tenant along with the residential premises itself, as well as its technical condition. This expands the subject of the rental agreement, but allows you to resolve all conflict situations in the event of litigation.
Termination
The rental agreement can be terminated at any time by agreement of the parties, or due to the occurrence of the following circumstances:
- end of employment relationship;
- completion of repair work at the citizen’s main place of residence;
- provision of other, permanent housing;
- use of residential premises for other purposes;
- non-use of housing for more than 6 months;
- change of ownership of housing, etc.
In case of termination of the contract, residents must vacate the occupied space. But there are categories of citizens who cannot be evicted without providing other housing:
- family members of a deceased or missing Tenant;
- pensioners;
- disabled people;
- orphans;
- low-income people registered as needing housing.
Important! A specialized rental agreement is automatically terminated in the event of the destruction of housing (Article 102 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) or the death of the Tenant.
Restrictions when a tenant uses residential premises of a specialized housing stock
A specialized rental agreement, in contrast to the usual social rental agreement, has legal restrictions that are imposed on the tenant during the operation of the allocated housing. This is stated in Art. 100 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
If we turn to this legal norm, we can come to the conclusion that the restrictions are that the employer cannot:
- exchange a residential building for another by agreement with another tenant;
- draw up a sublease agreement with a third party even in the temporary absence of the applicant himself from the premises.
Such restrictions arise due to the special legal regime for the use of specialized housing. If a violation of such restrictions is revealed, the contract will be terminated. It should be noted that termination of the contract in such situations occurs only forcibly by a court decision within the period specified by the legislator.
Thus, we can come to the conclusion that the rental agreement for specialized housing, although it has common features with the social rental contract, still provides for enormous differences that determine the unique legal status of such transactions.
Author of the article
Is it possible to rent?
Renting out official housing, be it an apartment or a dorm room, is illegal; this clause is stipulated in the contract. The homeowner has the right to terminate the tenancy agreement with the lawbreaker and evict him. However, when receiving specialized housing, for example, during a business trip, a citizen has the right to rent out an apartment or room in a hostel that is his property or to sublet housing that is on social rent.
A certificate of delivery of official housing confirms the lack of living space , which allows you to demand inclusion in the lists of those in need of residential premises and be provided with official residential premises for the period of service. To obtain this certificate, it is necessary to vacate the previously allocated residential premises in the prescribed manner, draw up an appropriate act and deregister.
Civil servants cannot rent out not only service apartments, but also apartments they own or rent, since such activity implies receiving additional income, which is prohibited by law.
- § 1. Lease agreement for specialized residential premises, its conclusion, termination and termination
- § 2. Purpose and specifics of providing certain types of residential premises
- Service living quarters
- Dorms
- Flexible fund houses
- Residential premises in houses of the social service system
- Funds for temporary settlement of internally displaced persons and persons recognized as refugees
Chapter 9
RESIDENTIAL PREMISES OF SPECIALIZED RESIDENTIAL FACILITY
§ 1. Lease agreement for specialized residential premises, its conclusion, termination and termination
In accordance with Art. 92 Housing Code of the Russian Federation specialized housing stock
is a set of residential premises of state and municipal housing funds intended for residence of certain categories of citizens.
To living quarters
specialized housing stock
includes
:
1) service residential premises;
2) living quarters in dormitories;
3) residential premises of the maneuverable fund;
4) residential premises in houses of the social service system;
5) residential premises of the fund for temporary settlement of internally displaced persons;
6) residential premises of the fund for temporary settlement of persons recognized as refugees;
7) residential premises for social protection of certain categories of citizens.
The use of residential premises as specialized residential premises is permitted only after such premises have been classified as a specialized housing stock. The inclusion of residential premises in a specialized housing stock with the assignment of such premises to a certain type of specialized residential premises and the exclusion of residential premises from the specified stock are carried out on the basis of decisions of the body that manages the state or municipal housing stock.
According to Art. 99 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, specialized residential premises are provided only to those citizens who are not provided with residential premises in the corresponding locality.
Specialized residential premises are not subject to alienation, transfer for rent, with the exception of the transfer of such premises under lease agreements provided for by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation - this provision is established by Art. 92 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
They are provided on the basis of decisions of the owners of such premises (authorized bodies of state power or authorized bodies of local self-government acting on their behalf) or persons authorized by them under contracts for the rental of specialized residential premises, with the exception of residential premises for the social protection of certain categories of citizens, which are provided under gratuitous contracts use (Article 99 of the RF Housing Code).
In accordance with the Housing Code of the Russian Federation:
1) determination of the procedure for providing residential premises of the municipal specialized housing stock is within the competence of local government bodies in the field of housing relations;
2) determination of the procedure for providing residential premises of a specialized housing stock of a subject is within the competence of the state authorities of the subject of the Russian Federation;
3) determination of the grounds for the provision of residential premises under lease agreements for specialized residential premises of state and municipal housing funds is within the competence of government bodies of the Russian Federation in the field of housing relations.
A rental agreement for specialized residential premises is a single document signed by two parties and drawn up in writing.
The parties to this agreement are
(according to Article 100 of the RF Housing Code):
1) on the one hand – the owner
specialized residential premises for rent. An authorized government body or a local government body vested with the necessary powers may act on his behalf, or these functions may be transferred to another person authorized by him, also acting as a lessor;
2) the other party to the contract is the employer
specialized residential premises - an individual.
Under the terms of the rental agreement for the specified category of housing, the housing stock is transferred by the lessor to the tenant for temporary possession and use for temporary residence. This agreement is a paid agreement - the transfer is carried out for a fee.
The exception is residential premises for the social protection of certain categories of citizens, which are provided under free use agreements.
The basis for signing a lease agreement and transfer of specialized residential premises is a decision made by the owner of the specified property being rented out. The right to act on his behalf belongs to an authorized government body, local government body, or these functions can be delegated to another authorized person.
A mandatory condition of the rental agreement for specialized residential premises is the agreement upon signing the subject of the agreement, the rights and obligations of the parties relating to the ownership and use of the specified premises.
These provisions must be specified in the contract when it is concluded.
The parties to the rental agreement for specialized residential premises are required to comply with the rules established by Art. 65, parts 3 and 4 art. 67 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
A mandatory condition of the rental agreement for specialized residential premises is the presence in it of a list of family members of the tenant (if any).
The rental agreement for specialized residential premises may be terminated on the grounds specified in Art. 101 LC RF, in the following cases:
1) at any time by agreement of the parties;
2) on the initiative of the tenant of specialized residential premises - at any time without indicating the grounds for termination and in a pre-trial manner;
3) at the request of the landlord in court if the tenant and his family members living with him fail to fulfill their obligations under the lease agreement for specialized residential premises. That is, the basis for the request for termination must be significant violations
terms of the contract on the part of the employer (Article 83 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). They can be expressed as follows:
• failure by the tenant to pay for housing and (or) utilities for more than six months;
• destruction or damage to residential premises by the tenant or other citizens for whose actions he is responsible;
• systematic violation of the rights and legitimate interests of neighbors, which makes it impossible to live together in the same residential premises;
• use of residential premises for purposes other than their intended purpose. The rental agreement for specialized residential premises is terminated upon the occurrence of the conditions established by Art. 102 Housing Code of the Russian Federation:
1) in connection with the loss (destruction) of such residential premises;
2) in the event of transfer of ownership of office residential premises or residential premises in a dormitory, as well as when transferring it to the economic management or operational management of another legal entity. The exception is situations when the new owner of such residential premises or the legal entity to which such residential premises have been transferred is a party to an employment contract with the employee who is the tenant of such residential premises.
The consequence of the termination or termination of a rental agreement for specialized residential premises is the obligation of tenants to vacate the residential premises that they occupied under these agreements (Article 103 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). In case of refusal to vacate such residential premises, these citizens are subject to eviction in court without the provision of other residential premises, except in cases where:
1) the landlord is a party to the employment contract with the employee who is the tenant of such residential premises;
2) also cannot be evicted from service residential premises and residential premises in dormitories without the provision of other residential premises who are not tenants of residential premises under social tenancy agreements or family members of the tenant of residential premises under a social tenancy agreement, or owners of residential premises or family members of the owner of residential premises and registered as needing residential premises:
a) family members of military personnel, officials, employees of internal affairs bodies, bodies of the Federal Security Service, customs bodies of the Russian Federation, bodies of the state fire service, bodies for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, institutions and bodies of the penal system, dead (deceased) ) or missing in action while performing military service or official duties;
b) old age pensioners;
c) family members of an employee who was provided with official living quarters or living quarters in a dormitory and who died;
d) disabled people of groups I or II, whose disability occurred as a result of a work injury due to the fault of the employer, disabled people of groups I or II, whose disability occurred as a result of an occupational disease in connection with the performance of work duties, disabled military personnel who became disabled of groups I or II due to injury , concussion or injury received during the performance of military service duties or as a result of an illness associated with the performance of military service duties.
That is, these citizens living in service residential premises and residential premises in dormitories can be evicted with the provision of other residential premises, provided that they are not simultaneously tenants under a separate social tenancy agreement.
These persons are provided with other residential premises, which must be located within the boundaries of the relevant populated area. The implementation of these actions is assigned by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation to the previous owner or the legal entity transferring the relevant residential premises.
This eviction procedure is subject to application in relation to another category of persons. According to Art. 13 of the Federal Law “On the entry into force of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation”, citizens who live in office residential premises and residential premises in dormitories provided to them before the entry into force of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation are registered as those in need of residential premises provided under social tenancy agreements, or have the right to be on this account, cannot be evicted from the specified residential premises without the provision of other residential premises, if their eviction was not permitted by law before the entry into force of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
§ 2. Purpose and specifics of providing certain types of residential premises
The RSFSR Housing Code did not provide for the provision of residential premises in a specialized housing stock; it spoke about its specific types - office residential premises, housing funds for temporary settlement and dormitories.
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation combined them into one concept - specialized housing stock - and supplemented it with a flexible stock, residential premises in houses of the social service system for the population and for the social protection of certain categories of citizens. It is necessary to dwell on each category.
Service living quarters
They are intended for the residence of certain categories of workers who, due to the specific nature of their labor relations, have the right to reside in them. These persons must be in an employment relationship with a government body, a local government body, a state unitary enterprise, a state or municipal institution, serve, be appointed to a public office of the Russian Federation or a public office of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, be elected to elective positions in government bodies or local governments.
Only the above-mentioned organizations have the opportunity to provide office living quarters for their employees.
Service residential premises are provided to citizens in the form of a separate apartment.
In accordance with Art. 104 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, the right to establish a list of categories of citizens who are provided with office residential premises belongs to:
1) to the government body of the Russian Federation. This structure has the right to regulate the provision of office space in the housing stock of the Russian Federation;
2) a government body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation. He was given the authority to provide office space in the housing stock of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
3) local government body. This body is responsible for the provision of office space in the municipal housing stock.
Service residential premises are intended for citizens to live in under a rental agreement for the period they have an employment relationship related to the government position they hold in the Russian Federation, a government position in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or an elected position.
In the event of termination of labor relations or tenure in the specified positions of the relevant bodies, as well as dismissal from service, the rental contract for office residential premises is terminated.
Dorms
Dormitory
is a residential premises specially built or converted for the purpose of being used for temporary residence of citizens during their work, service or training. It may occupy a building or house as a whole or part of it.
A mandatory requirement for these categories of residential premises is that they be equipped with furniture and other items necessary for citizens to live in.
The legislation provides for cases when certain groups of people are provided with dormitories without fail. In accordance with the order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation dated February 15, 2000 No. 80 “On the procedure for providing living quarters in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation” to military personnel who entered into a contract for military service before January 1, 1998 (with the exception of cadets of military educational institutions of vocational education ), and their family members living with them are provided with service living quarters or dormitories for the first five years of military service. If they continue military service beyond the specified periods, they are provided with living quarters on a general basis.
Resolution of the State Committee for Higher Education of the Russian Federation dated May 31, 1995 No. 4 approved the Standard Regulations on student dormitories of educational institutions of higher and secondary vocational education in the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Standard Regulations). The student dormitory (campus) of an educational institution of higher and secondary vocational education of the Russian Federation is intended to accommodate nonresident students, graduate students, doctoral students, interns, students of preparatory departments of institutes and faculties of advanced training and other forms of postgraduate and additional professional education for the period of study. In some cases, educational institutions have the right to decide to place students permanently residing in a given area in a dormitory. Residence in the student dormitory by unauthorized persons, placement of departments of the educational institution, as well as other organizations and institutions, except for the cases established by the Model Regulations, is not allowed. When all students in need are fully provided with places in the dormitory in accordance with established sanitary standards, isolated empty buildings, floors, blocks can, by decision of the administration and the students' trade union committee or other representative body authorized by students, be converted into dormitories for teachers and staff or rented out to third-party organizations.
Residential premises in dormitories are provided at the rate of at least six square meters of living space per person on the basis of Art. 105 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
The rental agreement for residential premises in a dormitory is concluded for the period of employment, service or training. That is, the basis for concluding this agreement is the existence of an employment relationship between the employer and the lessor, completion of service or training. Termination of employment, study, as well as dismissal from service are grounds for termination of the tenancy agreement for residential premises in a dormitory.
Article 7 of the Federal Law “On the entry into force of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation” provides that relations for the use of residential premises that were located in residential buildings owned by state or municipal enterprises or state or municipal institutions and used as hostels, and transferred to the jurisdiction of local authorities self-government, the norms of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation on social tenancy agreements are applied.
Flexible fund houses
Flexible housing stock
- a type of specialized housing stock. It has a strictly intended purpose and is used in accordance with Art. 95 and 106 Housing Code of the Russian Federation.
Residential premises of flexible housing stock are provided to citizens temporarily, in accordance with Art. 95 Housing Code of the Russian Federation cases. These include:
1) the period of major repairs (reconstruction) of the house in which there are residential premises occupied by citizens under social tenancy agreements. According to Art. 88 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, when carrying out major repairs or reconstruction of a house, if such repairs or reconstruction cannot be carried out without eviction of the tenant, the landlord is obliged to provide the tenant and his family members with another residential premises for the duration of the major repairs or reconstruction without terminating the social tenancy agreement premises located in the specified house. Relocation of the tenant and his family members to the residential premises of the mobile fund and back is carried out at the expense of the landlord;
2) if, as a result of foreclosure on residential premises (which were acquired through a loan from a bank, other credit organization, funds from a targeted loan provided by a legal entity for the purchase of residential premises, and then pledged to secure repayment of the loan or targeted loan), the citizen lost the specified residential property premises, while it was his only place of residence;
3) if there is a need for urgent resettlement of citizens from residential premises declared unsuitable for living as a result of emergency circumstances (from dilapidated houses, houses threatening to collapse, in cases of natural disasters and other emergency circumstances that pose a threat to the health and life of people).
The above list is not exhaustive. The Housing Code of the Russian Federation leaves the opportunity to provide residential premises for flexible housing stock in other cases provided for by law.
Residential premises of the flexible stock are provided at the rate of no less than six square meters of living space per person (Article 106 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
The rental agreement for residential premises of the maneuverable fund is concluded for the period:
1) until the completion of major repairs or reconstruction of a house with citizens in connection with major repairs or reconstruction of a house in which there are residential premises occupied by them under social tenancy agreements;
2) until the completion of settlements with citizens who have lost residential premises as a result of foreclosure on these residential premises, which were acquired through a loan from a bank or other credit organization or funds from a targeted loan provided by a legal entity for the purchase of residential premises, and pledged to secure the repayment of the loan or a targeted loan, if at the time of foreclosure such residential premises are the only ones for them;
3) until settlements are completed with citizens whose only residential premises have become uninhabitable as a result of emergency circumstances;
4) established by law when concluding such an agreement.
This type of contract is fixed-term, therefore the expiration of the period for which it was concluded is grounds for termination of this contract
.
Residential premises in houses of the social service system
Social Services
– these are enterprises and institutions, regardless of their form of ownership, providing social services, as well as citizens engaged in entrepreneurial activities in social services for the population without forming a legal entity.
The social services system includes:
1) state system of social services - a system consisting of state enterprises and social service institutions that are the property of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and are under the jurisdiction of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
2) enterprises and institutions of other forms of ownership, as well as citizens engaged in entrepreneurial activities in social services for the population without forming a legal entity.
Residential premises in houses of the social service system are intended for the residence of a certain category of the population, which includes citizens in need of special social protection. The specified residential premises should provide a range of medical and social services.
According to Art. 11 of the Federal Law of December 10, 1995 No. 195-FZ “On the Basics of Social Services for the Population in the Russian Federation” temporary shelter is provided in a specialized social service institution:
1) orphans left without parental care, neglected minors, children who find themselves in a difficult life situation (a situation that objectively disrupts the life of a citizen, for example disability, illness, orphanhood, poverty, lack of a specific place of residence, conflicts and abuse in the family, loneliness, etc., which he cannot overcome on his own);
2) citizens without a fixed place of residence and certain occupations, victims of physical or mental violence, natural disasters, as a result of armed and interethnic conflicts;
3) other social service clients in need of temporary shelter.
The activities of social assistance institutions (night houses, social shelters, social hotels, social adaptation centers, etc.) created in the system of social protection bodies to provide social assistance to persons without a fixed place of residence and occupation are regulated by the Model Regulations on the Institution of Social Assistance for Persons without a definite place of residence and occupation, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 8, 1996 No. 670. The main objectives of the institution are: providing a temporary place of stay or overnight accommodation for persons who find themselves without a definite place of residence and occupation, primarily the elderly and disabled; providing assistance in the implementation of measures for the social adaptation of persons who have lost socially useful connections (primarily persons released from prison) to living conditions in society.
Issues regarding the procedure and conditions for the provision of residential premises in houses of the social service system to citizens should be regulated by federal legislation, as well as the legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Funds for temporary settlement of internally displaced persons and persons recognized as refugees
Residential premises for temporary settlement, in accordance with housing legislation, are classified as specialized residential premises.
Forced migrants
Specialized residential premises are provided to families of forced migrants in the following cases:
• in the absence of the possibility of independently determining your new place of residence on the territory of the Russian Federation;
• if none of the family members has residential premises provided under a rental agreement;
• if none of the family members owns the residential premises.
In accordance with Art. 7 of the Law of the Russian Federation of February 19, 1993 No. 4530-I “On Forced Migrants” (hereinafter referred to as the Law of the Russian Federation “On Forced Migrants”), the territorial bodies of the migration service, in the manner determined by the Government of the Russian Federation, provide the forced migrant and members of his family with including those living in temporary accommodation centers for internally displaced persons, residential premises from the housing stock for the temporary settlement of internally displaced persons.
The Regulations on the Housing Arrangement of Forced Migrants in the Russian Federation, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 8, 2000 No. 845 (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations on the Housing Arrangement of Forced Migrants in the Russian Federation), determines the procedure for the housing arrangement on the territory of the Russian Federation of citizens recognized as forced migrants. A forced migrant has the right to independently choose a place of residence on the territory of the Russian Federation, to live in the established manner with relatives or other persons, subject to their consent, regardless of the size of the living space occupied by relatives or other persons.
Residential premises for temporary settlement are provided to a forced migrant with his consent (clause 27 of the Regulations on the housing arrangement of forced migrants in the Russian Federation).
Based on clause 28 of the said Regulations, with the consent of a forced migrant to move into the proposed residential premises, an agreement is concluded for renting residential premises from the housing stock for the temporary settlement of forced migrants. The rental agreement is concluded for a period not exceeding the period of validity of the forced migrant status.
In accordance with clause 5 of the Regulations on the housing arrangement of forced migrants in the Russian Federation, the housing stock for temporary settlement of forced migrants is a set of residential premises (residential houses, apartments, dormitories and other residential premises) intended for temporary residence on the territory of the Russian Federation of persons recognized in accordance with the established procedure as forced migrants, during the period of validity of the forced migrant status.
According to the Law of the Russian Federation “On Forced Migrants”, the status of a forced migrant is granted for five years. And if there are circumstances that prevent a forced migrant from settling in a new place of residence, the validity of his status is extended by the territorial migration service authority for each subsequent year at the request of the forced migrant.
According to clause 12 of the Regulations on the housing arrangement of forced migrants in the Russian Federation , persons living in residential premises for temporary settlement do not have the right:
• privatize these residential premises;
• exchange and book residential premises;
• rent out residential premises for rent, lease or sublease;
• divide the occupied living space;
• move in temporary residents without permission from the territorial body of the Ministry of Federation Affairs, Nationality and Migration Policy of the Russian Federation.
Upon expiration of the rental agreement, persons living in the residential premises are obliged to vacate it within a month and hand it over according to the act.
If they refuse to voluntarily vacate the premises, they are subject to judicial eviction. Refugees
In accordance with the Federal Law of February 19, 1993 No. 4528-I “On Refugees” (hereinafter referred to as the Federal Law “On Refugees”), a refugee is recognized as a person who is not a citizen of the Russian Federation and who, due to well-founded fears of becoming a victim of persecution based on race, religion, nationality, nationality, membership of a particular social group or political opinion is outside the country of his nationality and is unable or owing to such fear to be unwilling to avail himself of the protection of that country; or, being of no nationality and being outside the country of his former habitual residence as a result of such events, is unable or unwilling to return to it owing to such fear.
Housing fund
for temporary settlement of persons recognized as refugees - this is a set of residential premises provided to persons recognized as refugees and members of their families.
The formation of the housing stock is carried out taking into account the General Scheme of Resettlement on the Territory of the Russian Federation and other urban planning documentation approved in accordance with the established procedure, as well as the need to regulate migration flows by determining a quota for the distribution of persons recognized as refugees by region.
The formation of the housing stock is carried out through the acquisition, construction or rental of residential premises.
Residential premises from the housing stock, with the exception of rented ones, are federal property and are under the operational management of the relevant territorial body for migration issues.
According to Art. 11 of the Federal Law “On Refugees”, the housing fund for temporary settlement is intended for the residence of persons recognized as refugees and members of their families who do not have housing on the territory of the Russian Federation, during the period of recognition of them as refugees.
That is, residential premises from the housing stock are provided to persons recognized as refugees if they or members of their families do not have residential premises provided to them under a rental agreement or owned by them on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The housing stock for temporary settlement includes houses, apartments, dormitories, and other residential premises.
The use of residential premises leased by a territorial body of the federal executive body for the migration service for the temporary settlement of persons recognized as refugees and members of their families is carried out on the basis of a lease agreement with the owner of the residential premises.
Residential premises from the housing stock for temporary settlement are provided in the order of priority established by the territorial body of the federal executive body for the migration service.
Residential premises from the housing stock for temporary settlement are not subject to privatization, exchange, reservation, or subletting. A person living in the specified residential premises is not allowed to divide the space he occupies and move in temporary residents without permission from the territorial body of the federal executive body for the migration service.
The conditions for granting foreign citizens and stateless persons, as well as members of their families who arrived with them, in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation “On Refugees”, the possibility of temporary stay on the territory of the Russian Federation are regulated by the Procedure for granting temporary asylum on the territory of the Russian Federation, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 9 2001 No. 274. Temporary asylum is provided for a period of up to one year. The period for granting temporary asylum may be extended for each subsequent year by a decision of the territorial body on migration issues with which the person is registered, based on a written application from the person to extend the period for granting temporary asylum and in the presence of circumstances that served as the basis for granting the person temporary asylum.
A person who has received temporary asylum and members of his family who arrived with him:
1) have the right to use residential premises on terms of rent (sublease), receive assistance in traveling outside the Russian Federation, and can also enjoy other rights provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, international treaties of the Russian Federation and the legislation of constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
2) are obliged:
a) report within seven days to the territorial body on migration issues at the place of your registration information about changes in last name, first name, family composition, marital status, about acquiring citizenship of the Russian Federation or citizenship of another state, or about obtaining a permit for permanent residence in the territory of the Russian Federation ;
b) deregister with the territorial body on migration issues when changing the place of stay and, within seven days from the date of arrival at the new place of stay, register with the territorial body on migration issues.
The rental agreement is terminated early:
1) at the request of the employer;
2) in case of loss or deprivation of refugee status; obtaining (purchase or rental) other housing or completing the construction of individual housing; absence (non-use of the provided residential premises) without good reason for more than six months; identification of information in the submitted documents that does not correspond to reality, which served as the basis for the provision of housing;
3) by court decision in the event of a dispute.
Upon expiration of the rental agreement or upon its early termination, persons living in the residential premises are obliged to vacate it within a month and hand it over to the landlord according to the act.
In case of refusal of voluntary release, these persons are subject to judicial eviction without the provision of other living quarters. Funds for social protection of certain categories of citizens
The housing legislation of the Russian Federation classifies certain categories of citizens as needing social protection. Article 109 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation provides for the provision of residential premises for their social protection.
The provision of residential premises for the social protection of certain categories of citizens under gratuitous use agreements is carried out in the manner and on the conditions established by federal legislation and the legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
As an example, we can cite the provisions of Art. 14 Federal Law of January 12, 1995 No. 5-FZ “On Veterans”. In accordance with it, war disabled people are provided with specific measures of social support, in particular, the federal budget provides housing for war disabled people in need of improved housing conditions who were registered before January 1, 2005, which is carried out in accordance with the provisions of Art. 23.2 of the Federal Law “On Veterans”.
The Russian Federation transfers to the government bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation the authority to provide social support measures for payment of housing and communal services and to provide housing for categories of citizens in need of improved housing conditions, from among war disabled people registered before January 1, 2005.
Funds for the implementation of transferred powers are provided as part of the Federal Compensation Fund, formed in the federal budget, in the form of subventions.
The amount of funds provided for in the Federal Compensation Fund for the Budgets of the Subjects of the Russian Federation is determined by providing housing for citizens based on the number of persons entitled to the specified social support measures; total housing area 18 sq. m and the average market value of 1 sq. m of total housing area in a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, established by the federal executive body authorized by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Table of contents
Transfer to social status
A service apartment cannot belong to a tenant, however, although it is quite difficult to change the status of housing, it is possible due to circumstances that allow you to submit an application to local governments with a request to transfer the rental of an apartment or dorm room to social rent:
- living in service housing for more than 10 years;
- retirement or disability at the company that provided housing;
- the Tenant's family is officially recognized as low-income and is registered.
There are other types of rental housing, which have their own subtleties. If you are wondering how to rent an apartment without being scammed, pay attention to the nuances of concluding contracts and the necessary documents for:
- commercial hiring;
- short-term hiring.
In conclusion, it must be said that a special legal regime has been established for a specialized fund, strictly for its intended purpose. Such premises cannot be sold, donated or mortgaged, even if the Landlord has given his consent to this. Subsequently, such transactions will be declared invalid by the court.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Concept and types of specialized residential premises
Currently, the Housing Code of the Russian Federation uses the concept of “specialized housing stock”. Residential premises of such a fund are provided for a period of time under a rental agreement to certain categories of citizens, subject to special conditions.
Residential premises of state and municipal housing funds are used as specialized residential premises. The use of residential premises as specialized residential premises is permitted only after such premises have been classified as a specialized housing stock.
According to Art. 92 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, residential premises are classified as specialized:
- official;
- in dormitories;
- maneuver fund;
- in the homes of the social service system;
- fund for temporary settlement of internally displaced persons;
- fund for temporary settlement of persons recognized as refugees;
- for social protection of certain categories of citizens;
- for orphans and children left without parental care, persons from among orphans and children left without parental care.
Service residential premises (Article 93 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) are intended for the residence of citizens in connection with the nature of their labor relations with a government body, a local government body, a state or municipal unitary enterprise, a state or municipal institution, in connection with their service, in connection with appointment to a public position of the Russian Federation or a public position of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or in connection with election to elective positions in government bodies or local self-government bodies.
The obligation to provide office space, the specifics of their provision and release are provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts.
So, paragraph 1 of Art. 15 of Federal Law No. 76-FZ of May 27, 1998 “On the status of military personnel” provides that military citizens serving under contract and members of their families living with them are provided with service documents no later than three months from the date of arrival at the new place of military service Living spaces.
Dormitories (Article 94 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) are intended for temporary residence of citizens during the period of their work, service or training.
Residential premises of the maneuverable fund in accordance with Art. 95 Housing Codes of the Russian Federation are provided under a rental agreement for temporary residence:
- citizens in connection with major repairs or reconstruction of a house in which there are residential premises occupied by them under social tenancy agreements;
- who have lost residential premises as a result of foreclosure on these residential premises, which were acquired using a loan from a bank or other credit organization or funds from a targeted loan provided by a legal entity for the purchase of residential premises, and pledged to ensure repayment of the loan or targeted loan, if at the time of application such residential premises are the only ones for them;
- whose only living quarters became uninhabitable as a result of emergency circumstances;
- in cases provided for by law. (In paragraph 3 of Article 15 of the Federal Law of May 27, 1998 No. 76-FZ “On the status of military personnel” it is established that military personnel undergoing military service under a contract and members of their families who arrived at a new place of military service, before receiving residential premises service living quarters suitable for temporary residence, flexible living quarters or dormitories are provided).
According to Art. 96 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, residential premises in houses of the social service system are intended for the residence of citizens who, in accordance with the law, are classified as citizens in need of special social protection with the provision of medical and social services.
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 15 of Federal Law No. 442-FZ of December 28, 2013 “On the basics of social services for citizens in the Russian Federation,” a citizen is recognized as in need of social services if the following circumstances exist that worsen or may worsen his living conditions:
- complete or partial loss of the ability or ability to provide self-care, move independently, or provide basic life needs due to illness, injury, age or disability;
- the presence of a disabled person or disabled people in the family, including a disabled child or disabled children who need constant outside care;
- the presence of a child or children (including those under guardianship or guardianship) experiencing difficulties in social adaptation;
- lack of opportunity to provide care (including temporary care) for a disabled person, child, children, as well as lack of care for them;
- the presence of intra-family conflict, including with persons with drug or alcohol addiction, persons addicted to gambling, persons suffering from mental disorders, the presence of domestic violence;
- lack of a specific place of residence, including for a person who has not reached the age of twenty-three and has completed his stay in an organization for orphans and children without parental care;
- lack of work and livelihood;
- the presence of other circumstances that are recognized by the regulatory legal acts of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation as worsening or capable of worsening the living conditions of citizens.
Clause 3 of Art. 19 of this law stipulates that recipients of social services in a stationary form are provided with residential premises.
Social services in a stationary form are provided to their recipients during permanent, temporary (for a period determined by an individual program) or five-day (per week) round-the-clock residence in a social service organization.
In accordance with Art. 97 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, residential premises of funds for the temporary settlement of forced migrants and persons recognized as refugees are intended for the temporary residence of citizens recognized as forced migrants and refugees in the manner provided, respectively, by the Law of the Russian Federation of February 19, 1993 No. 4530-1 “On forced migrants” and Federal Law of February 19, 1993 No. 4528-1 “On Refugees”.
Residential premises for social protection of certain categories of citizens (Article 98 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) are intended for the residence of citizens who, in accordance with the law, are classified as citizens in need of special social protection. Such legislation includes, in particular, federal laws dated June 24, 1999 No. 120-FZ “On the fundamentals of the system for preventing neglect and juvenile delinquency”, dated December 21, 1996 No. 159-FZ “On additional guarantees for social support for orphans and children left without parental care”3, etc. The last of the laws mentioned in paragraph 1 of Art. 8 establishes that orphans and children left without parental care, persons from among orphans and children left without parental care who are not tenants of residential premises under social tenancy agreements, family members of such a tenant or owners of residential premises, and also who are tenants of residential premises under social tenancy agreements or family members of such a tenant or owners of residential premises, if their residence in previously occupied residential premises is recognized as impossible by the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation on whose territory the place of residence of these persons is located, in the manner established by the legislation of this subject of the Russian Federation, comfortable residential premises of a specialized housing stock are provided one-time under contracts for the rental of specialized residential premises.