In practice, there are often cases when disabled people who are registered as needing improved housing conditions are excluded from the lists for free housing provided by the state in the absence of legal grounds.
If you have been removed from the queue for housing, you are encouraged to study this information and, if there are doubts about the legality of the decision made by the official to remove those in need of housing from the register, file a claim with the court to declare such a decision unlawful. At the same time, you should not delay filing a complaint, since Article 219 of the Code of Administrative Proceedings of the Russian Federation provides for a three-month period for filing an administrative claim from the moment you became aware of the controversial decision.
An alternative way to protect your rights may be to contact the prosecutor's office. However, there are risks of formal consideration of the application, and by the time the inspection is completed, the deadline for filing an administrative claim may have expired. Missing the deadline for going to court without a good reason is grounds for refusing to satisfy such an application.
Reasons for deregistration of those in need of housing
The Housing Code provides for a number of reasons that may affect the deregistration of a citizen. These grounds are considered:
- the citizen submits an application for deregistration;
- the citizen has lost the grounds on which he was registered as in need of living space;
- moving to another entity at the municipal level, excluding situations where this occurs within the boundaries of settlements of federal significance;
- receiving financial assistance from the budget from government agencies for the purchase of living space: houses, apartments;
- the procedure for providing government bodies or local administration with a plot of land for the purpose of building a house;
- detection of unreliable information in the documentation submitted by a citizen for registration of living space, as well as identification of illegal actions of employees of the authorized body who registered citizens in need of housing.
Does it happen that it was removed legally and is there a chance in this case?
In my practice, there have been cases when removal from the housing queue was legal. For example:
- Change of place of residence - if you have moved permanently to another city or region;
- Purchasing housing, receiving housing by gift or inheritance, if as a result of this, the persons in line became provided with housing according to the provision rate;
- When transferring subsidies for the purchase of housing in the prescribed manner.
In these cases, it is unlikely that you will be able to restore the housing queue, but it is better to consult with an experienced lawyer or lawyer. On your own, you may not be able to understand the issue of legality/illegality of removal from the housing queue.
Deregistration at the initiative of the applicant
The procedure for registering as those in need of housing is regulated by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation. Having collected the necessary package of documents, the citizen has the right to register accordingly. For people in need of housing or increasing living space, the algorithm of action is simple. An individual independently decides for himself whether to register for living space or not. This is his right, but not his obligation. If the need for social housing has ceased for some reason, the citizen has the right to write an application to remove him from the register of those in need of housing.
The application must reflect his desire to be deregistered as a living space. The Housing Code of the Russian Federation does not provide a strict form for the application for deregistration of residential space. It is compiled in any form. The citizen addresses the application to the authority in which he is registered as in need of improved housing conditions. The application is signed by the citizen in order to identify himself. Like the application for registration, the request for deregistration is also considered by the authorized body.
The Housing Code of the Russian Federation (norm 52) states that citizens with a lack of legal capacity in this case can act through their representative, who on their behalf writes a statement regarding the residence of the incapacitated person on the premises. But the Housing Code of the Russian Federation does not prescribe a procedure for withdrawing an application from persons incompetent to deregister them.
Persons who are legally incompetent can be registered through a representative, but a proxy has no right to be deregistered. The way out of this situation is the volitional action of the authorized body, which carries out registration of those in need of living space.
But deregistration of citizens in need of housing without incapacity occurs by the authorized body only if there are no grounds for obtaining residential premises.
The procedure for registering those in need of residential premises means that low-income categories recognized by law can apply for housing under social rent. It is possible to register if several prerequisites are met: but in order to do this, first of all, you need to obtain low-income status. If a citizen has lost his status as a low-income person, he will be denied housing. Grounds for loss of status may include:
- an increase in the price of property owned by a married couple with children recognized as poor;
- increasing family income per each of its members, etc.
Appealing the municipality's decision.
By law, any action of an authorized body or an official acting on its behalf can be appealed in court.
Let's consider the questions of how to get back on the waiting list for housing: where to go, procedure, list of documents, deadlines and cost.
Svetlana
Real estate expert
The final authority in cases of protecting the rights of citizens is the court. Claims challenging decisions of state and municipal bodies are subject to consideration by district or city courts. Accordingly, appeals against decisions of courts of first instance are carried out in regional and regional courts, and in exceptional cases, the Supreme Court becomes the final authority.
The applicant's procedure will follow the following algorithm:
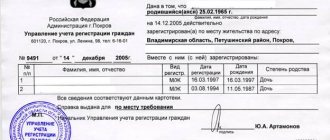
- Receive written notification of deregistration. This document is especially important, as it must contain the reason and basis for the citizen’s exclusion from the waiting list.
- Request for clarification. This step is optional, but advisable if the notification does not contain comprehensive information. An application to the municipality is submitted in the form of an appeal, the response to which, in accordance with Federal Law No. 59-FZ, is sent to the applicant within 30 days.
- Drawing up an application. An approximate example of a claim for reinstatement in the queue for improving housing conditions can be found on the Internet, however, due to the fact that in each specific case the contents of the document will be different, it is more advisable to seek help from a lawyer.
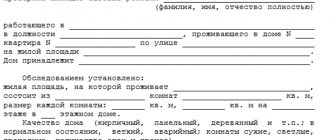
- Collection of application documents. The latter will also vary depending on the circumstances of the case, but a general list may include:
- a copy of the notarized power of attorney, if the applicant has a representative;
- receipt of payment of the duty;
- a copy of the applicant's passport;
- an extract from the house register;
- documents for the existing living space;
- a copy of the notice and response to the plaintiff’s appeal;
- documents confirming the right to receive free housing;
- other documents.
- Participation in the process. According to the rules of the Code of Civil Procedure, an administrative claim is considered within 10 days, however, this period may increase due to the need to schedule a second meeting.
- Getting a solution.
- Submitting a copy of the decision and application for reinstatement in the queue to the authorized body.
The cost of challenging an administration decision consists of the state fee for filing a non-property administrative claim (300 rubles) and the costs associated with obtaining application documents. A separate line includes the costs of paying a lawyer.
In terms of timing, you need to know the following: after receiving a notice of deregistration, a citizen has only 3 months to file a claim. If the deadline is missed, the possibility of its restoration is determined by the court.
It might be interesting!
How to get free housing.
Deregistration when changing place of residence
The condition that is necessary in order to register those in need of residential premises is that the person lives in the municipality of a certain locality. The departure of citizens outside its borders entails their removal from the register of those in need of housing.
In order to deregister citizens who need improved living conditions, the order of a person’s place of residence is determined on a formal basis. Otherwise, the issue related to proving the place of actual residence of citizens on a permanent basis will require a considerable amount of time and the number of documents required to be submitted to the authorized body will increase. In addition, errors will arise due to illegal deregistration. Based on this, in practice, when a citizen changes his place of residence, if he has not fulfilled the obligation to notify state authorities about his new place of residence, this does not entail deregistration. The main evidence for government agencies is the place of its registration.
Is there any point in filing a lawsuit?
Judicial practice: review, examples, is not able to give a clear answer to this question. Much will depend on the validity of the complaint and the completeness of the evidence presented.
So, for example, if the person on the waiting list and his family actually improve their living conditions or lose the status of a low-income family, you should not count on satisfaction of the requirements. Loss of status, that is, the grounds for registration, will lead to similar consequences.
At the same time, there is a high probability that the claim will be satisfied if the authorized body refers to the person on the waiting list’s refusal to inherit or to the fact that he has a garden house.
A notable example from court practice is when a plaintiff, living in a room in a communal apartment and on the waiting list for housing since 1980, was removed from the register due to the fact that her daughter grew up and married a man registered with her parents in a three-room apartment.
The Supreme Court, which reviewed the case, pointed out that neither the daughter nor her husband became members of another family, but retained the right to use the residential premises in which they were registered. As a result, the court came to the conclusion that the living conditions of the waiter had not changed, overturned the decisions of the courts of previous instances, and satisfied the plaintiff’s demands.
Natural deregistration of those in need of residential premises
This basis is associated with the death of a registered citizen. This is a circumstance that, according to Art. 17 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, determines the end of the individual’s legal personality. In the event of his death, family members of the deceased remain registered. It is logical that the basis for the natural removal of a deceased person cannot in any way affect the desire of the remaining family members to obtain an apartment.
The government agency decides whether to deregister a citizen no later than thirty days from the discovery of circumstances that are grounds for this action. Decisions in finished form on deregistration are sent or given no later than three days from the date of creation.
Citizens have the right to disagree with the decisions of authorized bodies. It can be appealed to a judicial authority.
If 3 months are missed, what should I do?
They removed me from the queue without notifying me of this, neither in writing nor verbally. I found out about this after much more than 3 months.
Alexei.
It is necessary to go to court in the manner of claim proceedings, which is provided for by the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. The limitation period is 3 years.
Remember yourself and advise your friends who are in line for housing
At least once a year, find out how your queue is moving there, to see if there are any unpleasant surprises!
Subsidies for improving housing conditions
The “Housing” program, adopted for the period 2015-2020, is focused on state assistance in housing. In particular, it states that it is focused on providing support to citizens who need improved housing conditions. The state provides assistance to provide citizens with housing. In particular, the state is acting with the task of improving living conditions in premises for the category of young families.
This program is aimed at creating conditions for creating a segment of the budget, affordable housing market, increasing the volume of developments, and improving the construction sector as part of measures to support the construction of residential premises in the regions. All this is done in order to improve the living conditions of citizens.
One of the types of government support for citizens in order to improve their living conditions is subsidies. There are certain rules that prescribe the procedure for providing these payments to the population to improve housing conditions. The rules are fixed in the resolution of the highest body belonging to the executive branch of government dated 2009 (No. 63). The subsidy can be used in the purchase and sale of residential premises and is aimed at improving the living conditions of civil servants. The subsidy is also used as a share contribution, but on the condition that the citizen is a member of housing or housing construction cooperatives.
Author of the article
Why are they removed from the queue?
According to Article 56 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, an applicant may be removed from the queue for improvement of housing conditions if the following occurs:
- Moving to another region or country.
- If a person himself has submitted an application to be removed from the queue.
- The family no longer has grounds on which it can be recognized as needy. For example, an apartment was received as a gift or inheritance, which is quite suitable for the whole family to live in, without violating housing and sanitary requirements.
- The applicant has received a housing certificate - in this case, he is removed from the queue to receive an apartment, since instead he received money to purchase it.
- A plot of land was provided for individual housing construction. But such a replacement does not give the right to exclude a large family from the queue.
- False information was provided - the applicant provided false information in order to obtain unlawful benefits.
In some cases, an applicant is removed from the queue for housing if he was registered with the company and was fired.
It is also not uncommon for a family to deliberately worsen their living conditions in order to be given an apartment. For example, they had good real estate, which they sold and, citing the fact that they had nowhere else to live, became registered.
Important: refusal to be placed on the queue or removal from there is not always legal. Therefore, if you find yourself in this situation, seek advice from a lawyer - in most cases you can find a way to appeal such a decision. You can get a free consultation on our website.
Mortgage specialist
Online magazine about mortgages and real estate in Russia
Who is getting a mortgage in 2021? Check your chances online
Online magazine about mortgages and real estate in Russia
Reference to legislation
In accordance with current legislation, military subsidies are a specialized program to support army personnel, through which they can quickly resolve their housing issues.
The amount received can subsequently be spent on:
- purchasing your own real estate;
- repayment of an already issued mortgage;
- construction of your own home.
Payment of the required amount is carried out only once, that is, the person is immediately transferred the required amount in one transaction. To do this, it is mandatory to open an individual personal bank account.
The key provisions that govern the receipt of this state assistance are set out in the following regulations:
- Article 15 of the Federal Law “On the Status of Military Personnel”;
- Article 51 of the Housing Code;
- Order of the Ministry of Defense, which was published in 2014 and regulates the procedure on the basis of which housing subsidies are issued to persons serving in the army;
- Government resolutions on the basis of which the subsidy for the purchase of residential real estate for military personnel is calculated;
- Presidential Decree.
In accordance with current legislation, after submitting a complete package of necessary documents, civil servants are given no more than 30 days to check them and make a final decision. After the final decision is made, it must be sent to the specialized financial support department of the Ministry of Defense within the next three days.
We will tell you below what documents to submit to expand your living space.
- purchasing your own real estate;
- repayment of an already issued mortgage;
- construction of your own home.
In what cases is a military personnel compensated for the cost of renting an apartment?
If a serviceman was not provided with official housing within 3 months from the date of arrival at the place of service, he has the right to compensation for rent.
Payment of monetary compensation for the rental of residential premises to military personnel and members of their families is carried out monthly through the accounting department of the military unit where he is serving, on the basis of an order from the commander of the military unit (head of the organization).
- copies of passports, birth certificates of the child
- copies of marriage certificates (divorce)
- extracts from house books, copies of financial personal accounts from the places of residence of military personnel and members of their families for the last five years before filing the application
- copies of documents on the right to provide additional social guarantees in terms of housing provision in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation
- information on the availability (absence) of residential premises occupied under social tenancy agreements and (or) owned by the military personnel and members of his family
Basic moments.
There are several categories of citizens who can count on receiving assistance from the state when solving the housing issue. The right to support is given to persons with a special preferential status. This group includes WWII participants, combat veterans, and legal officers killed in action. A similar opportunity is provided to low-income and large families, orphans, disabled people and victims of emergency situations.
To receive housing from the state or a subsidy for the purchase of real estate, a citizen must receive the status of a person in need. Depending on its availability and the circumstances of the case, a person may be included in the priority, extraordinary or general queue.
The following conditions are mandatory for participation in a social project:
- Having Russian citizenship and living in the region for a long time;
- Lack of real estate ownership in excess of the established norm per person;
- Receiving income below the approved legal minimum;
- Absence in the past of receiving assistance to solve a housing problem;
- Confirmation of eligibility using official documents and certificates.
Extraordinary provision of housing may be associated with the appearance of persons injured as a result of accidents or natural disasters. Orphans, internally displaced persons and a number of other categories of citizens have this right.
Who has the right to buy out the last room in a communal apartment?
Sometimes neighbors who want to purchase the last room face opposition from the municipality - the owner of the property, since according to the norms of housing legislation, the priority right to move into this property belongs to numerous categories of beneficiaries. These are low-income groups or families on the waiting list for improved living conditions. Also, municipalities have waiting lists for inexpensive housing, and if neighbors do not belong to any of the preferential categories, then their chances of acquiring this share are minimal.