Home / Real estate / Land / Ownership / Forms of ownership
Back
Published: 07/14/2017
Reading time: 12 min
0
382
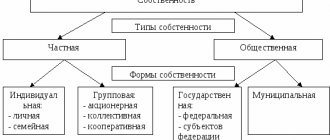
The presence in the civil legislation of the Russian Federation of several different forms of ownership in which property may be located provides the opportunity to own it to many different entities.
One of the basic rights of property is public, which applies to real estate owned by the state. Next, the concept of this type of right, the grounds for its occurrence, as well as the distinctive features will be examined in more detail using the example of this type of real estate such as a land plot.
- Concept and legislative regulation
- Reasons for occurrence
- What areas can be publicly owned?
- Rights and obligations of participants
- Differences from private property
Concept and legislative regulation
Along with legal entities and citizens, the state in the Russian Federation acts as a separate and completely independent subject of law. Therefore, a very large share of real estate (not only land, but also buildings and structures) is publicly owned.
The public form of ownership implies that the property belongs to the following public entities:
- the state as a whole;
- a specific subject of the Russian Federation (represented by its executive authorities);
- to a separate municipality.
Public property rights are divided into two groups:
- state;
- municipal.
For a long time (almost the entire last century), it was public property (specifically state property) that was the main and, in most cases, the only form of ownership of this type of real estate such as land.
And only a couple of decades ago, the process of privatization began, that is, the registration of private rights to state or municipal property by legal entities and individuals.
The main documents with the help of which legislative regulation of public ownership is carried out are the Land and Civil Codes of the Russian Federation. Also, all legislative acts and Decrees of the Government of the Russian Federation that affect this issue should be taken into account.
Description
To better understand the economic component of this concept, we highlight the following characteristics:
- The property in question carries out the tasks of realizing state interests by accumulating and redistributing part of the national income.
- Covers the market space that is uninteresting to private property entities due to: high costs, low profits, significant risks, where successful production is not ensured, where activities are accompanied by large losses (or there is a risk of such) and threats to the existence of the entire society.
- Due to public interest, management is structured taking into account the implementation of the main socio-economic interests.
- The dual nature of public property is revealed in its market and non-market nature. Therefore, assessing the success of the application of the relevant entities is based on socio-economic components, and not only on economic aspects.
Reasons for occurrence
The Land Code of the Russian Federation provides for a separate chapter 3, which regulates issues related to land ownership rights. In particular, this chapter provides articles with the grounds for their occurrence in various cases, among which it is worth highlighting:
- Art. 17 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, devoted to the grounds for the emergence of federal ownership of land (that is, belonging to the Russian Federation). This type of law covers the following areas:
- recognized as such in accordance with current federal laws;
- the right to which arose during the delimitation of state property;
- acquired on the grounds provided for in civil legislation.
In accordance with Art. 218 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the grounds for the emergence of property rights include:
- carrying out a legal transaction (purchase and sale, donation, exchange or other type of agreement for the alienation of property);
- obtaining a plot that does not have a legal owner (if the latter is unknown, voluntarily refused or was deprived of rights to it);
- creation of a new site (for example, by dividing or merging it).
Each of these grounds must necessarily be in accordance with the requirements of the law (mainly civil).
- Art. 18 of the RF Land Code provides for the same grounds for the emergence of property of subjects of the Russian Federation as in the previous case, as well as one more additional one:
- allocation free of charge from federal property.
Taken together, the property of the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the Russian Federation constitutes state property.
- Art. 19 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation contains the same grounds for the formation of municipal property that have already been listed.
It is obvious that these grounds are almost identical, only in some cases there are their own characteristics. It is worth considering that for certain types of land plots, the law allows only a public form of ownership; they cannot be private.
Such features will be discussed in more detail below.
Flaws
Speaking about municipal housing, one cannot fail to note the disadvantages. The apartments in question have two significant drawbacks. The first is the impossibility of selling, donating or inheriting housing, since the owner is the state. Thus, it is it that controls the future fate of the property. The second disadvantage is that there is a risk of deprivation of living space. If the tenant violates the law, he has the right to evict him without the possibility of providing other housing.
In case of forced eviction of conscientious citizens, they are provided with another living space. However, in the case of the owner, eviction cannot be carried out at all.
In order to gain full rights to an apartment, it must be privatized. But if the housing is in emergency condition, then there is no need to rush, since in this case nothing will be provided in its place.
What areas can be publicly owned?
First of all, the plot must comply with the general requirements that are put forward in the law to it as an object of ownership:
- presence of established boundaries;
- a specific location or exact address;
- registration with the state cadastral register.
Otherwise, state or municipal authorities can own land with virtually no restrictions. It is worth highlighting certain types of plots that can only be in state ownership:
- lands of forest and water funds (in the latter case, water bodies must be in federal ownership);
- specially protected areas that are of federal significance;
- lands of defense and security;
- reserve lands, subject to the placement of federal real estate on them;
- lands of settlements, transport, communications, industry, agricultural purposes, television and radio broadcasting, environmental and cultural significance, computer science, energy and space purposes;
- areas under the surface of which there are subsoil of federal significance.
This list is not exhaustive; therefore, federal and regional laws of the Russian Federation may define other additional grounds for land to be in state ownership only.
As for the municipal one, any types of plots belonging to both the state and private individuals can be transferred to it (for example, in the event of their death or voluntary abandonment of the land).
Advantages
The majority of people using public property on the basis of a lease seek to register it as their property as quickly as possible. However, you should not always rush to do this. Using the example of a municipal apartment, let's look at the advantages of housing owned by someone on the basis of a social tenancy agreement. These include the following:
- No real estate taxes. Owners are charged a fee of 0.3 to 2% of the cadastral value of housing.
- Possibility of improving living conditions. If the apartment does not meet the established standards, then in the future the residents will be able to get housing with a larger area.
- If the apartment is lost for reasons beyond the control of the tenant (for example, due to a fire or earthquake), then the state is obliged to provide other housing.
- It is simply not possible to transfer ownership of a state-owned apartment to another person. Therefore, scammers remain powerless in this case.
Ownership of public legal objects was especially common during the Soviet Union. But even today there are many residential buildings that belong to the state. As you can see, there are a number of advantages provided by housing provided under a social tenancy agreement.
Rights and obligations of participants
Public lands may, in some cases, be provided for use by citizens and legal entities (on the basis of lease, permanent perpetual use or ownership). Moreover, the specific set of rights and obligations of these persons will directly depend on the specific right on which he receives the property. General rights include:
- the ability to use the land at your own discretion (including growing various plants, raising animals, and engaging in other types of economic activities);
- the right to erect buildings on it;
- the opportunity to carry out entrepreneurial activities;
- the right to transfer land for use to third parties (but not always).
It is worth considering that all these rights are limited by the type of permitted use of the site, which the owners must take into account when operating it.
For example, if the land is intended for agriculture, but does not allow the construction of residential buildings, then it will not be possible to build them legally. Therefore, the main responsibility of each owner is to use the public land provided to him only for the intended purpose.
Other responsibilities may include:
- compliance with the law when operating the allotment;
- payment for it (if its provision was not free of charge);
- granting the right to limited use of land to other citizens (that is, easement) in cases established by law;
- ensuring the safety of individual objects located on the territory of the allotment (if they are subject to special protection);
- other duties established by current legislation.
When allocating a plot of land on a lease or free use basis, this transaction must be documented with the help of an appropriate agreement. It is in this document that the mutual rights and obligations of both parties will be officially established.
Drawing up an act of transfer of a land plot to a land donation agreement will help protect your rights. Large families can receive land on preferential terms. Read more about this in our article. To carry out land surveying, you will need to collect a package of certain documents. You will find the list here.
Documentation
In fact, the collection of documents for privatization occurs in two stages. Preparation, collection and execution of documents for submission to the local municipality. The second stage of registration in Rosreestr, delivery for cadastral registration. Let's move on to the first point. What documents need to be prepared?
- Application for privatization of real estate or land.
- Identity document
- Documents for the right to use. For example, a rental or social tenancy agreement.
- Documents for the provision of benefits (if any).
- Receipts of payment and absence of rent arrears.
- For a land plot - its plan and the act of approving boundaries.
When purchasing real estate through an auction, the following documents will be required:
- Application for participation in the auction.
- Report with the final results of the auction.
- Receipts for full payment of the purchased property (land).
Privatization is completed within 30 days. The deadlines are also valid for purchases through auction. If necessary, registration takes place simultaneously with privatization. The main thing is not to forget to fill out the documentation. After registration of all rights, an application is submitted to the cadastral service.
IMPORTANT! You can also submit documents through the multifunctional center (MFC). But it is worth considering that registration through the MFC takes 2 days longer. The cadastral service issues the final transfer of rights within 7 days.
Next, information about the new owner is entered into Rosreestr. It is at this moment that the final transition of state real estate to private ownership occurs.
The main difficulty in registering public property is strict control by the state because real estate and land are among the most valuable, and most importantly non-renewable, resources of our country.