Nuances of allocating premises for registration of a lease agreement
Share on social networks:
The owner of real estate has the right to carry out a division or allocation of premises, which will result in the creation of new real estate objects.
During the implementation of the division, the original object will cease to exist not only “de facto”, but also “de jure”, and all information regarding it will be deleted from the Unified State Register. Carrying out an allocation presupposes the preservation of the original object; only its characteristics change. Moreover, all changes that in one way or another relate to its characteristics must be made to Rosreestr.
Premises section
Partitioning a room is an operation during which it becomes possible to create two or more new rooms, each of which will be assigned its own parameters. The newly created premises must have the necessary signs of isolation and isolation. The absence of the last two signs is recognized as a legal basis for suspending and/or prohibiting actions related to registration (clause 34, part 1, article 26 of the Federal Law No. 218-FZ).
The procedure for dividing a room has several important features:
- the decision to carry out a division can only be made by the owner, and if there are several rights holders, it is impossible to do without obtaining the consent of each of them;
- the division is carried out during construction work that falls under the concept of redevelopment or reconstruction;
- redevelopment and reconstruction is impossible without prior approval - its implementation is possible only on the basis of project documentation. If the question of reconstruction arises, you will need to obtain a permit for reconstruction. We wrote in detail about how to issue a notification and obtain permission for construction or reconstruction here;
- the results are approved in the construction work report. After approval, the results are recorded in a technical plan, drawn up by a cadastral engineer (he begins this task only after he personally inspects the newly created premises).
The emergence of new premises implies mandatory recording of their characteristics and mandatory entry of information into the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
In what case will a redevelopment project be needed?
Redevelopment of a room is its structural change, which is characterized by a change in its dimensions. According to the project, the technical parameters of the room may change: integration of several rooms into one, change in their area. It is possible to change the quality parameters: covering the room with sound, heat or waterproofing materials, installing or replacing internal vaults. The redevelopment project for non-residential premises in the housing stock includes information about the replacement or relocation of utilities: sanitary facilities, electrical wiring, radiators and batteries.
How is the technical plan for the division of the premises drawn up?
- The cadastral engineer requests USRN information regarding the building, original premises and adjacent objects;
- A survey of newly created objects is carried out in situ (if the engineer establishes deviations from the design documentation, he is obliged to reflect these facts in his conclusion);
- The cadastral engineer records the location of new premises on the floor plan of the building, as well as their boundaries;
- The characteristics and parameters of each new room are described in text and graphic form, and diagrams and drawings are included in the technical plan.
Thus, based on the results of the section, technical plans are drawn up for each new premises, as well as for the building itself, since its characteristics have changed as a result of construction work.
Are there storage rooms in the basements, but they don’t give you space?
In new housing stock, basements are often immediately equipped in such a way that residents can store their personal belongings in separate rooms. But here you may encounter another difficulty: often new residents do not get a storage room, because “everything has long been distributed among those who moved in earlier.” This is a violation of your rights! All residents have an equal right to use the common property. And if the composition of the residents has changed, the rules by which meters in the basement are distributed may also change.
To achieve justice, it is necessary to initiate a general meeting of residents, and at it to review the conditions for the use of common property. If those previously living in the house contributed their own funds to furnishing the basement, newcomers may be asked to contribute certain amounts.
If an amicable agreement cannot be reached, you can file a complaint with the management company.
Cost and terms of division of premises
Cadastral registration of a property in Rosreestr takes 10-14 days. The state fee for registering rights to each newly formed premises in 2021 is 2,000 rubles for individuals and 22,000 rubles for legal entities. The details for paying the state duty will be different for each region - they can be clarified through the Rosreestr website.
The cost of the work of designers and cadastral engineer is determined based on the volume and urgency of the order. To prepare documents for division, many approvals are required, and any mistake will lead to suspension or refusal to register rights to newly created real estate.
The Central Cadastral Bureau will help you go through all stages of approval and registration the first time. We will draw up design documentation for the division of premises, carry out the necessary cadastral work, prepare technical plans for newly created real estate, register them in the cadastral register and register ownership.
Reason for popularity
You may be interested in: Jordanian dinar: description, exchange rate to other currencies
Non-residential premises are in great commercial demand. Entrepreneurs often buy apartments on the ground floor with the aim of converting them into non-residential buildings. Such measures make it possible to organize a hairdresser, shop or workshop in a busy area with guaranteed high traffic, without resorting to the construction of a separate structure.
Allocation of premises
The main difference between an allocation of premises and a partition is the preservation of the existence of the original premises. But its characteristics are undergoing significant changes (primarily they will affect the total area). As a result of the allocation of premises, one or more new premises are formed, and each of the newly formed ones will have its own characteristics.
Allocation is carried out only when allocating a share in kind, i.e. This option is only possible for objects with shared ownership.
Both temporary and permanent allocation of premises is possible. At the same time, registration of a new property seems possible only if there are signs of isolation and/or isolation. The allocation can be temporary - a conditional object is considered as an independent unit of accounting, but only for a specified period, for example, temporary cadastral registration is carried out when part of the premises is allocated for rent.
The allocation of premises becomes possible only if the following requirements are met:
- preservation of the original cadastral number when the characteristics of the original object change;
- all changes and adjustments made during the allocation of premises can only occur during redevelopment or reconstruction and are subject to mandatory approval;
- the selected object must be isolated and separate, then it will be put on permanent cadastral registration. Otherwise, we can only talk about temporary cadastral registration.
In order to allocate premises, the owner must order a project, obtain a technical opinion and draw up a technical plan from a cadastral engineer. The procedure is the same as for dividing premises.
The difference is that when divided, the original premises cease to exist in kind, but when allocated, they are preserved in a modified form.
If there is a temporary allocation of premises, there is no need to order and approve design documentation.
About commercial objects in an apartment building
On May 29, 2021, changes to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation regarding the placement of commercial properties in residential buildings came into force in Russia. The law allows you to organize a business in specially equipped non-residential premises of an apartment building and even use your own apartment for professional and entrepreneurial purposes. Experts from the Federal Cadastral Chamber of Rosreestr explained what types of commercial activities can be carried out in a multi-storey residential building.
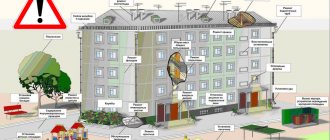
An apartment building is a building, most of which is reserved for residential premises. In many old buildings, apartments on the first floors have long been transferred by the owners to the category of non-residential, refurbished and function as retail outlets and service enterprises. In modern new buildings, the first floors are initially designed by developers as non-residential - to accommodate various commercial objects. The premises are equipped with separate entrances, display cases, and connected to utility systems. The law allows citizens to change the purpose of a premises from residential to non-residential and vice versa and establishes certain standards for the operation of the premises depending on the chosen purpose.
LIVING SPACES
Russian legislation allows the use of residential premises not only for their intended purpose - for living, but also for doing business.
Thus, according to Article 17 of the Housing Code, professional or individual entrepreneurial activities in residential premises can be carried out by citizens legally residing in it, provided that the rights of other residents are respected, as well as the requirements that the residential premises must meet. In other words, the work of an entrepreneur should not cause inconvenience to other residents of the apartment, as well as neighbors in the house, lead to violation of sanitary standards and safety regulations during the operation of residential premises, or cause damage to engineering equipment or the structure of the building. Individuals registered as individual entrepreneurs or self-employed have the right to conduct business at home. Tutors, translators, lawyers, accountants, programmers, web designers, tailors, etc. often combine home and work in this way. In addition, in some apartments of residential buildings there are still small accommodation facilities: mini-hotels and hostels.
The ability to provide hotel services in residential premises of apartment buildings will cease from the moment the amendment to the Housing Code comes into force, according to which “residential premises in an apartment building cannot be used to provide hotel services.” Thus, from October 1, mini-enterprises of the hotel business can only be organized in non-residential buildings.
The current legislation also does not prevent the organization of small private production in an apartment, for example, making cakes, packaging and packing goods, and soap making. But you won’t be able to count on large production volumes: the Housing Code prohibits placing industrial production in residential premises. Thus, the possibility of using devices or machines that violate permissible noise or vibration levels and consume large amounts of electricity is automatically excluded.
Another prohibition of the Housing Code applies to conducting missionary activities in residential premises, with the exception of cases provided for in Article 16 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ “On Freedom of Conscience and Religious Associations.”
If you want to scale your business, organize a full-fledged office, bureau, atelier, shop, cafe-confectionery in an apartment building - with a sign, a separate entrance and staff - the entrepreneur will have to move from the apartment to a premises with a “non-residential” purpose.
NON-RESIDENTIAL PREMISES
Non-residential premises in an apartment building are intended only for commercial, administrative, public and other activities and cannot be used for temporary or permanent residence of citizens. As a rule, they house shops, pharmacies, beauty salons, offices, medical institutions, kindergartens, utility companies, etc.
Activities in non-residential premises are strictly limited by fire, sanitary and urban planning standards and should not lead to air pollution and residential areas, exceed the permissible noise level, or pose a threat to the life or health of the residents of the house. In particular, the law prohibits the placement in residential buildings of stores selling chemicals, explosive substances and materials, synthetic carpets, auto parts, tires, and motor oils.
The ban also includes establishments operating after 11 p.m., institutions and funeral service stores, warehouses for any purpose, specialized fish stores, baths and saunas, laundries and dry cleaners, and public toilets.
In apartment buildings, non-residential premises are often located on the first and ground floors. It is not prohibited to place them higher, but in this case, the real estate directly below them must also be non-residential. By law, each non-residential property must be equipped with a separate entrance, so owners of apartments on floors above the first rarely exercise the right to change the purpose of the premises to non-residential: practice shows that the attendance of a commercial facility largely depends on its accessibility.
In most cases, residents of the first floors in standard high-rise buildings, the designs of which did not include the construction of special premises for doing business, transfer their apartments to non-residential buildings. However, recently this procedure has become much more complicated. According to Federal Law No. 116-FZ “On Amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation”, before applying to the authorized body with an application to transfer residential premises to non-residential premises, the owner must obtain the written consent of each owner of the premises adjacent to his apartment, as well as a majority vote owners of residential and non-residential premises located in the house and entrance.
The law does not have retroactive effect, but gives residents the right to decide whether another commercial premises will be opened in their building. The innovations are, first of all, aimed at protecting those owners who actually bought apartments adjacent to the “residential” first floors, but after a while were faced with the potential opportunity to be adjacent to an office.
INFORMATION PROVIDED BY THE KHABAROVSK REGION BRANCH OF FSBI "FKP ROSRESTRA"
Source of publication: information monthly “The Right Decision” issue No. 09 (203) release date of 09/23/2019.
The article was posted on the basis of an agreement dated October 20, 2016, concluded with the founder and publisher of the information monthly “Vernoe Reshenie” LLC “.
What happens if you run a prohibited business at home?
Neighbors usually write complaints about business in an apartment. And here an entrepreneur can be pecked by several government agencies at once.
The Housing Inspectorate fines for using apartments not for housing under Art. 7.21. Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Fines for citizens from 1000 to 1500 rubles, for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles. But if you're lucky, the inspectors will limit themselves to a warning.
Rospotrebnadzor fines for violation of sanitary regulations in an apartment building under Art. 6.4 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. For individuals, the fine is from 500 to 1000 rubles. For individual entrepreneurs - from 1000 to 2000 rubles or suspension of activities for up to three months. For legal entities - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles or suspension of activities for up to three months.
The Ministry of Emergency Situations will fine for violating fire safety rules under Art. 20.4 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Individuals face from 2000 to 3000 ₽, individual entrepreneurs - from 20,000 to 30,000 ₽, legal entities - from 150,000 to 200,000 ₽.
And most importantly, neighbors or the prosecutor’s office can, through the court, prohibit conducting business activities in the apartment.