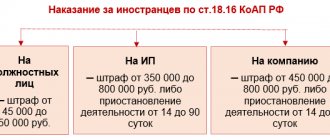
Responsibility for an administrative illegal action refers to a special measure of punishment, expressed in the recovery of money from the offender as income to the state. This punishment is used to prevent repeated illegal actions by the same offender or to prevent other citizens from committing offenses. Administrative liability includes penalties for non-compliance with the norms of labor, housing, family, land, customs, antimonopoly, tax legislation, legislative norms on consumer rights and other branches of law.
Responsibility for administrative illegal actions is regulated by the Code of the Russian Federation No. 195-FZ of December 30, 2001 (as amended on November 28, 2018). An administrative penalty for an offense is imposed in accordance with Article 3.5. Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation Law No. 116-FZ of June 22, 2007.
What is an administrative fine?
An administrative fine is a financial penalty for committing an illegal offense.
According to many lawyers, collection of funds for an administrative violation is the most effective way to punish a violator. Any illegal action has three characteristics:
- Illegality, manifested in violation of established legal norms.
- Guilt, implying the presence of a fault in the action (the fault can be planned or executed through negligence).
- Punishability of an illegal act, that is, the imposition of an administrative penalty.
Illegal actions of an administrative nature can be divided into types in various areas:
- As part of the protection of the borders of the Russian Federation.
- In the agricultural production sector.
- In the field of property protection.
- In the field of natural protective measures in the environment.
- In the area of information and communication.
- In the field of military registration of persons.
- Within the framework of protecting public rules and state security.
Illegal offenses can cause harm to the health of individuals, encroach on property, sanitary conditions, morality, etc. Any illegal action must be accompanied by administrative punishment.
Types of administrative punishment:
- Warning.
- Confiscation of the instrument with which the offense was committed.
- Detention.
- Narrowing of the rights of an individual.
- Disqualification.
- Expulsion from the Russian Federation of a foreigner or individual without citizenship.
- Suspension of professional functioning.
- Administrative financial penalty.
What sanctions are provided for repeated offenses?
The statute of limitations for administrative offenses is 2 years if the resolution has not entered into force. In other cases, non-payment is evasion, and a violation committed a second time in a year is repeated.
Art. 4.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses considers this as an aggravating circumstance. The defendant faces a penalty equal to twice the previous fine.
The legislation establishes administrative violations, the minimum and maximum limits of monetary liability. Payers can deposit funds in several ways and arrange a deferment.
Article 4.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation “The period during which a person is considered subject to administrative punishment”
Deadline for payment of an administrative fine
Regulatory acts of the Russian Federation allow 60 days to pay off an administrative penalty. In this case, after the announcement of the verdict, 10 days are given to appeal it. Thus, the violator has a total of 70 days to pay off the financial fine. If the debt repayment period is overdue, the bailiffs will be inactive for the first month. However, they will then take the following actions against the borrower:
- First, the debtor will be awarded another fine, usually in the same amount.
- The materials on the debtor will be re-sent to the judicial structure.
- Thus, a debt not paid on time may double in size already in the first overdue month.
- Repeated failure to repay the financial penalty may result in the offender being arrested for 15 days.
Important information on debts
Late implementation of sanctions entails additional problems with law enforcement officials. One of them is the imposition of an additional penalty on the amount of the debt. Therefore, it is important to promptly identify its presence and close it.
From 2021, the minimum amount of financial responsibility is 500 rubles, and the payment period is limited - 60 days from the date of entry into force of the resolution.
These conditions apply in most situations, but not always.
| An exception to the generally accepted rules | Mechanism of action |
| Payment of fines by stateless persons or foreigners who are at risk of forced displacement outside the state | The entire amount must be paid the next day after receiving instructions from the authorities |
| Payment for administrative violations on the roadway | 50% of the fine must be transferred within the first 20 days, the rest - over the next 60 days |
Methods of paying an administrative fine
Any person who is imposed an administrative penalty must pay it off on time, otherwise he faces additional punishment in a more severe form.
The most common type of administrative punishment is a traffic police fine for non-compliance with traffic rules. This penalty is applied to prevent similar actions by the motorist in the future. In case of such a violation, the traffic police inspector draws up a protocol in which the violator must sign.
The protocol should display the following information:
- Date and place of execution of the document.
- FULL NAME. and the position of traffic police inspector.
- FULL NAME. and contact information of the driver who committed the offense.
- FULL NAME. and contact information for witnesses and victims (if any).
After a court order is issued to impose a penalty, the violator has the right to appeal the court decision within 10 days.
Judicial structures have 3 months at their disposal to force the violator to pay the fine, otherwise more severe penalties will be applied to him, including arrest.
How to pay such a fine in order to prevent further troubles?
It should be noted that today there are many ways to pay off debts to government agencies, using various online resources that provide services for transferring debts on fines without leaving home. To do this, you need to have a computer or mobile application and an Internet connection.
Among the most common ways to pay off administrative fines are the following:
- Service "Government Services".
- Sberbank Online.
- A number of payment systems, for example, Yandex money, QIWI.
Service "Government Services"
This service belongs to the official government resource called electronic government.
The resource provides a search for outstanding fines and their payment. The advantage of this resource is that no commission is charged when transferring funds.
To use the Gosuslugi portal, you must first register on it. After registration, opening the site, you need to find the required tab, fill in the driver's document number and car number.
The user will see a page displaying information about outstanding penalties, indicating the order number, date and location of the traffic violation.
To make a transfer to pay off a fine, you need to click on the “Pay” button located next to the name of the resolution.
Sberbank Online
This resource provides payment of administrative penalties online. Sberbank clients registered on the website have a personal account where they can make payments from a plastic card via the Internet.
To transfer money to pay off a debt, you need to select the “traffic police fines” tab in the “payments” section. Then you need to fill out information about transport and details of the punishment order. You can make another payment online in the same way.
Payment of administrative penalties is carried out by debiting funds from the client’s Sberbank account. Therefore, users are required to have the required amount in their account. The transfer is completed within 24 hours; no commission is charged when paying a fine.
Yandex money
To pay penalties using the Yandex resource, the user is required to register an account in the system.
First, you need to use the search mode to check for any outstanding debt. To do this, enter the driver's document number or vehicle registration certificate in the form that opens. The user will see a page with outstanding debts.
To pay off the debt, you need to click on the “pay” column. Money is debited from the payment system account or from an attached bank plastic card. The money transfer operation is carried out within a few minutes, the transfer fee is 1%.
Wallet – QIWI
The procedure for paying off fines in this resource is similar to the resource on Yandex. There is also a function to check for fines and transfers.
A traffic violation violator will need to fill out a form with the number of the resolution, the amount of the fine and the date of the violation.
Among the named fine payment services, Qiwi is the least popular payment system, since the transfer fee is 3%. To close the debt, you can use a bank plastic card, a Qiwi wallet account, or Web Money.
( Video : “The amount of fines for administrative offenses may be reduced”)
How to check?
There are several ways to detect the decision and the fact of payment of an administrative fine on the subject:
- Register on the State Services website, go to the information section, click “Get a service.” Most often, the presence of a fine in the traffic police is checked by name or STS number.
- View on the traffic police website. You will need the registration number and STS of the car. You will need to go to the “Check fines” section and enter the data.
- On the FSSP website. You need to log in to the “Base of Enforcement Proceedings” service. There you can find out the debts and the amount of current payment by full name, date of birth and region.
Ways to check a fine
Important! The FSSP website will provide information if enforcement proceedings have been initiated against the debtor.
Amounts of administrative fines in 2021
The amount of the administrative penalty imposed depends on the type of violation and the consequences. When determining the amount of the penalty, the following points are considered:
- The nature of the actions and the resulting consequences as a result of the offense.
- Carrying out a repeated illegal action if the individual has been punished for such actions.
- The subject who committed the offense. The measure of punishment and the penalty imposed depends on the subject (individual, official or legal entity). Various penalties are imposed here.
Note. Punishment for an offense can be imposed not only as a separate penalty, but also in combination with other sanctions. For example, when driving while intoxicated, the driver may not only be fined, but also have his driver’s license confiscated. Or, for example, if an institution fails to comply with environmental standards and safety regulations, a fine may be issued to the enterprise with a simultaneous suspension of work.
A fine imposed on an individual goes to the state. The amount of the penalty depends on the following points:
- The minimum wage (without taking into account regional coefficients), established by law on the date of completion of the offense or on the date of its detection.
- Assessment of the subject on the date of completion of the offense or on the date of its suppression.
- The amount of tax debt intended for payment on the date of completion of illegal actions or on the date of suppression, or the size of a currency transaction carried out in violation of the law.
Note. The amount of an administrative fine cannot be less than 1/10 of the minimum wage. This norm is used both for Muscovites and for other individuals (including foreign citizens) located or living in the Russian Federation.
Misconduct at work
We often hear that for some kind of misconduct at work, the Director fined the employee a certain amount. However, the management of enterprises and organizations is not included in the circle of persons who have the right to impose fines, and the Labor Code clearly defines the range of possible forms of punishment for employees for offenses committed.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 192. Disciplinary sanctions
For committing a disciplinary offense, that is, failure or improper performance by an employee through his fault of the labor duties assigned to him, the employer has the right to apply the following disciplinary sanctions: 1) reprimand; 2) reprimand; 3) dismissal for appropriate reasons. Federal laws, charters and regulations on discipline (part five of Article 189 of this Code) may also provide for other disciplinary sanctions for certain categories of employees. Disciplinary sanctions, in particular, include the dismissal of an employee on the grounds provided for in paragraphs 5, 6, 9 or 10 of part one of Article 81, paragraph 1 of Article 336 or Article 348.11 of this Code, as well as paragraph 7, 7.1 or 8 of part one of Article 81 of this Code Code in cases where guilty actions giving grounds for loss of confidence, or, accordingly, an immoral offense were committed by an employee at the place of work and in connection with the performance of his job duties.
As you can see, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a single mention of fines as a measure of disciplinary action.
However, a number of employers understand that by collecting a fine from an employee, they are breaking the law. And they came up with a loophole for this case. The fine is not collected from wages, but is deducted from the amount of the bonus at the end of the period. So, when concluding an employment contract, you need to make sure that the salary amounts are clearly specified. Bonuses “based on results” are a subject of risk.
Maximum fine for an administrative offense in 2021
When carrying out more serious illegal actions, for example, in the foreign exchange sector, smuggling or other areas, the minimum threshold for penalties increases:
- For individuals, the amount of penalties increases to 200 minimum wages.
- For legal entities – up to 5000 minimum wage.
Note. When carrying out illegal actions in the field of taxation, the amount of the fine can reach the total amount of taxes not transferred to the Federal Tax Service.
What happens if you don’t pay an administrative fine?
Delay in repayment of financial debt is equivalent to an offense that entails repeated punishment, but with an increase in the amount of the fine.
Therefore, it is in the interests of the offender to pay off debts as quickly as possible. For failure to pay a fine, the following measures may be taken:
- Seizure of property.
- Prohibition of traveling abroad until the debt is paid.
- Seizure of bank accounts.
- Arrest of the debtor for 15 days.
Repayment of fines may be delayed if the offender lacks funds. The maximum deferment period cannot be more than 5 years, however, traffic violations can only defer payment for 3 months.
To receive an installment plan, you must write an application with appropriate argumentation. If the arguments are considered valid, the deferment will be approved.
Note. Deferment of repayment of the fine does not exempt from collection for late repayment of debt. That is, if the violator is late in any payment, then the amount of the penalty doubles. Therefore, one must use the delay very carefully.
Thus, the best solution is to pay the fine in a timely manner to prevent the severity of the punishment from increasing.
Photos and videos in the cinema
Usually, before the start of the show, viewers are asked to turn off their mobile phones and not take photos or videos of the film being shown. But suddenly, for some reason, you decided to capture some particularly spectacular shot or scene from the film. And this caught the eye of the cinema staff.
They begin to persistently demand a fine from you for this violation. Is this legal?
The fact is that the cinema has the right to prohibit photo and video shooting in the hall. But this organization has no right to fine anyone for violating this ban. I repeat: it can be banned, but not fined.
When you tell the administration this, especially advanced cinema employees begin to appeal to Art. 1252 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, explaining that you have violated copyright.
But, in this case, they should be reminded that the cinema is not the copyright holder of these films, and therefore the requirement to pay for copyright infringement on the part of the cinema is illegal.