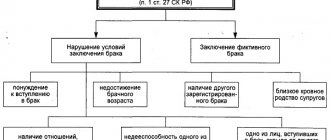
Fictitious “donation” of property acquired during marriage by one of the spouses
Imagine the situation. Married spouses purchased an apartment or house, then the relationship between them deteriorated and they decided to divorce. And during this period, one of the parties to whom the property is registered withdraws the disputed object from the jointly acquired property. To do this, the owner registered in the Unified State Register “donates” an apartment or house to a third party (an acquaintance or relative). Formally, after registering the transaction, real estate leaves the joint property. Such an agreement can only be declared invalid in court. As a rule, the applicant’s arguments in this case are standard: the transaction is invalid because the property was acquired during the marriage, and the defendant did not receive the plaintiff’s notarial consent to donate the property (Decision of the Izobilnensky District Court in case No. 2-745/2017 of 10/12/2017 ).
Cancellation of donation
The provisions of Art. 578 of the Civil Code establishes one of the most pronounced features of a gift agreement - the donor’s right to cancel the transaction . The specified law is applicable to them, regardless of whether the contract was concluded through the transfer of a gift or was executed after the promise of its transfer, the main thing is that their application is possible only after the actual execution of the transaction . The donor's right to cancel the gift is due to the fact that when enriching another person at his own expense, the donor can well count on loyalty on his part. The grounds for cancellation precisely exclude such loyalty.
For your information
The institution of cancellation of donation cannot be identified with the norms of termination and dissolution of the contract, as well as declaring it invalid. The cancellation of a donation, in contrast to the termination of legal relations under a contract, is aimed at the annulment of the donee’s property rights and does not initially contain defects in the transaction as grounds for invalidity.
The first reason for canceling the donation, according to paragraph 1 of Art. 578 of the Civil Code, it should be considered the infliction of bodily harm by the donee or an attempt on the life of the donor and his relatives . Such unworthy behavior of the donee, in order for it to become the basis for cancellation, must be deliberate and confirmed by official documents - certificates, extracts from the criminal case, etc.
In addition, the donation may be canceled due to dishonest use of the gift , which has a large non-property value for the donor, which may result in its irretrievable loss (clause 2 of Article 582 of the Civil Code). In court, the donor will have to prove the fact of such use by the donee of the thing transferred to him.
Cancellation of a donation is also possible if the donor outlives the donee , provided that such a right of the donor is enshrined in the gift agreement (clause 4 of Article 578). Based on this, the donor will definitely be deprived of this right if he makes the gift agreement orally.
Since the general grounds for cancellation are not applicable to a separate form of gift - donation, according to paragraph 5 of Art. 582 of the Civil Code, it can be canceled on a special basis - the use of a donation for other purposes or a change in such purpose in violation of the procedure established for this.
According to paragraph 5 of Art. 578 of the Civil Code, the consequence of the cancellation of the donation should be considered restitution - the obligation to return the gift that has been preserved in kind to the donor, and if it is lost, compensation for its value in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 1105 Civil Code. Since the consequences are of a legal obligation nature, the cancellation of a gift, in case of refusal to voluntarily return the gift, can only be carried out in court.
An agreement that violates the requirements of the law or other legal act
Sometimes there are situations when a gift agreement violates the law. For example, a woman received maternity capital and invested it in buying an apartment. By law, she is obliged to register her children, spouse and register common property. However, she does things differently. The mother arranges micro-shares for the children, and “gifts” 2/3 to a friend from whom she once borrowed money. Such a transaction is clearly contrary to the law and rules for the disposal of maternal capital. In this case, the court always recognizes the gift agreement as invalid (Decision of the Kurgan City Court of the Kurgan Region in case No. 2-9093/2017 of October 11, 2017). To achieve the desired result, the lawyer in this situation relied on the provisions of the law on the payment of maternity capital, an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, as well as documents confirming the receipt of maternity capital.
Invalidation of deed of gift: consequences
The consequences of declaring a gift agreement invalid are prescribed in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 167, 169 and 179). They entail:
- cancellation of the transaction and return to the original conditions;
- unilateral sanctions - return to the donor of property transferred into the hands of an unscrupulous recipient;
- compensation for losses - the recipient pays for damage caused to the donor’s property as a result of imaginary transaction;
- recognition of the transaction as void on both sides and transfer of property into state ownership.
In case of non-fulfillment or violation of current legislation, these consequences can be applied to any gift agreement. The consequences are established by the decision of the judicial authority and do not depend on the demands made by the plaintiff.
A void transaction entails the sham of a gift agreement and changes the property rights of its participants.
Author of the article
Dmitry Leonov
Work experience 15 years, specialization - housing, family, inheritance, land, criminal cases.
Author's rating
721
Articles written
712
about the author
Useful information on inheritance disputes
- Gift deed or will - which is better?
- Deed of gift with the right of lifelong residence
- Cancellation of deed of gift
- Challenging the deed of gift
- Gift agreement between close relatives
- Cost of deed of gift
- Documents for deed of gift
- Registration of a gift agreement
- Deed of gift with deferred rights of entry into property
- Registration of a gift agreement
- The difference between a will and a deed of gift
- Agreement for the determination and donation of shares
- Gift tax
- Invalidity of the gift agreement
- Donation of funds between individuals
- Is it possible to issue a deed of gift for a minor child?
- Agreement of gift or sale
- Share gift agreement between individuals
- Gift deed for an apartment
- Certification of the gift agreement by a notary
- Gift deed after the death of the donor
- Gift deed for garage
- Gift between spouses
- House donation agreement
- Deed of gift for a plot of land between close relatives
- Registration of real estate donation agreement
- How to draw up a deed of gift for a share in an apartment
- Transfer deed to the apartment donation agreement
- Gift agreement: pros and cons
- Gift deed for a relative's car
- Husband's consent to donate an apartment
- Is it possible to terminate a gift agreement?
Imaginary deed of gift
In this case, the gift agreement covers another transaction. Most often, a contract for the sale, rental or exchange of real estate. In reality, the parties transfer money to each other on a receipt, keys to a house (apartment), actually exchange real estate or enter into an agreement on lifelong maintenance with a dependent. However, on paper they sign an agreement on the donation of housing and send these documents to Rosreestr for inclusion in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. Subsequently, the counterparty, dissatisfied with the agreement (having not received money, services or property), files an application with the court and demands that the agreement be declared invalid. And if his arguments are supported by evidence (receipt, acceptance certificate, real contract, receipts for payment of taxes and utilities, and so on), then the court recognizes the donation as invalid (Decision of the Sovetsky District Court of the city of Ufa of the Republic of Bashkortostan in case No. 2-307/ 2016 dated 04/11/2016).
Arbitrage practice
More details about the grounds and methods for canceling a deed of gift are described in the article on how you can challenge a deed of gift. At the moment, we are more interested in the topic of invalidating deeds of gift and judicial practice in such cases. The examples are not tied to a specific location of the participants in the process, and the court and number of the claim will not be named. But the examples are taken from life and more detailed information on them can be obtained by downloading files with court decisions for free.
Example 1
The citizen, succumbing to her son’s persuasion, signed the only housing as a gift to him. In return, the son promised to take care of her and provide financially. The citizen admits that she was deceived by her own son because she confused the concepts of gift agreement and annuity. On these grounds, she asks the court to cancel the deed of gift and the record of registration of real estate in Rosreestr. The claim was denied.
Example 2
The citizen inherited the house from her husband. Then she gave it to her own son. Initially, they agreed that the son and his family would move into this house permanently only after the death of the plaintiff. The plaintiff is demanding that the deed of gift be cancelled, since the defendant does not live in the house and does not pay for utilities. And the house requires urgent repairs, as it is in a state close to destruction. During the court hearing, it was found out that the defendant does not visit this house because he had a quarrel with the plaintiff and due to the fact that she once already tried to cancel the deed of gift, accusing the defendant of assault (the plaintiff’s claim was not satisfied). The examination showed that the house is in good condition and only needs cosmetic repairs. In addition, the defendant filed a motion to apply the statute of limitations. The result is that the claims were denied.
Example 3
The plaintiff asks to cancel the deed of gift, setting out the events as follows:
- the apartment in which he lives with his wife and his wife’s minor son was taken out on credit (his wife is the guarantor);
- My wife and son had a room in a dorm; in order to sell it, the guardianship and trusteeship authorities required that the child have another place to live;
- in this regard, the plaintiff registered his apartment in his wife’s name through a gift agreement;
- the wife sold her own room and spent the money on personal needs;
- due to the fact that the relationship with his wife is not working out, he demands that the deed of gift be declared invalid (an imaginary transaction) and that the apartment be returned to him as his personal property.
The plaintiff insists that the gift agreement was concluded for one purpose - to give her an apartment. The room in the communal apartment was sold much later than the deed of gift was issued and one event was completely unrelated to the other. The requirement of the guardianship and trusteeship authorities, in order to obtain permission to sell a room in a communal apartment, was the division of the money received between the defendant and her son. That’s what was done - the money is in a bank account in the name of her son. The rest of the money was spent on family needs, including repairs to the disputed housing.
As a result of a careful study of all the circumstances of the case, the court decided to reject the claim.
Example 4
The plaintiff is the mother. She asks to cancel the deed of gift, since her son died and she survived him. The daughter of the deceased is claiming the inheritance, whom the plaintiff does not consider to be his son’s daughter (and his granddaughter), since the girl was not born out of wedlock. There are two heirs - the mother of the deceased and his daughter. The plaintiff justifies the cancellation of the deed of gift by the fact that after the death of the donee, the property should go back to the donor. The claim was rejected both in the court of first instance and in the appellate proceedings. At the court hearing, it was found out that when drawing up the deed of gift, the clause stating that the apartment would return to the donor after the death of the recipient was not included in the agreement. Everything related to inheritance and establishment of paternity should be considered in another court hearing if the parties wish to make counterclaims.
Example 5
The plaintiff asks to cancel the donation agreement in favor of the defendant. She insists that the defendant inflicted minor bodily injuries on her, which she has evidence of (certificates from the hospital and court records, since legal proceedings were initiated on the fact of causing intentional harm to health). The court of first instance, as well as after considering the appeal, made a decision in favor of the plaintiff.
Deed of gift made under the influence of delusion
This is perhaps the most numerous category of cases. The parties are mistaken regarding the subject, nature or circumstances of the transaction. Moreover, both the donor and the recipient can be mistaken. Most often this concerns an apartment donation agreement for pensioners and single people. The donor transfers real estate to a third party, thinking that he is signing an annuity contract, and the contractor will take care of him until his death. However, as a result, it turns out that the donee simply took advantage of the counterparty’s illiteracy and misled him.
But it also happens that the donee himself does not fully understand the meaning of the contract and what the donor requires of him. But here it turns out that you have to pay utility bills for the apartment, and maintaining the donor is a very expensive business. By the way, in this case, a second basis for recognizing the agreement as invalid appears - its imaginary nature. After all, in fact, donation simply covers rent. No more.
In such cases, the dispute ends up in court, which terminates the contract (Decision of the Verkh-Isetsky District Court of Yekaterinburg in case No. 2-6545/2017 of October 12, 2017).
The concept of an imaginary contract
According to paragraph 1 of Art. to create the appearance of its conclusion should be considered as an imaginary contract , without being aimed at the emergence, change and termination of rights and obligations typical for a transaction of this type. Such an agreement, due to its fictitiousness, is required by the legislator to be considered void - invalid from the moment of its conclusion and not entailing any consequences (Article 167 of the Civil Code).
For your information
The invalidity of an imaginary contract occurs even when the external design of the transaction and the conditions for its conclusion fully meet regulatory requirements. Such an agreement, despite its external legality, will violate one of the conditions for the validity of a civil transaction - it will not correspond to the true will of the parties who entered into it.
The definition of an imaginary transaction, enshrined in paragraph 1 of Art. 170 of the Civil Code does not contain a specific purpose for which such an agreement is concluded. In fact, an imaginary transaction is carried out by the parties to create specific legal consequences for one of its parties, and in relation to third parties - the appearance of a really non-existent legal relationship .
In addition to this purpose, to determine sham, the court must establish the direction of the actions of one of the parties to obtain a specific advantage, circumvent any prohibitions and restrictions , or other illegal consequences of creating an appearance in relation to third parties.
These unlawful consequences must directly violate the rights of third parties for whom the appearance of concluding a particular transaction was created. If, despite the absence of legal consequences of concluding an imaginary transaction, the rights of third parties are not violated, the transaction should still be considered imaginary, but its conclusion, as well as the recognition of imaginaryness, loses all meaning .
Let us recall that despite their insignificance, most of these agreements require thorough and convincing proof of their imaginary nature. Therefore, without defining the specific purposes of carrying out an imaginary transaction, it will be impossible to prove its such nature, and therefore, it is impossible to demand the application of the consequences of invalidity, defined in paragraph 2 of Art. 167 Civil Code.
Cancellation of the contract
Its cancellation should be distinguished from declaring an agreement invalid. As a rule, a contract that is pure from a legal point of view is cancelled. An exception is a transaction concluded by a legal entity or individual entrepreneur on the eve of bankruptcy, when the future bankrupt transfers assets to a third party.
In other cases, the reason for cancellation is an attempt on the life or health of the donor, or even his murder, as well as careless handling of the donated item. Let's be honest, the death of the donor at the hands of the donee is extremely rare. It is mainly present in detective novels and films. But beating the donor sometimes occurs in real life. For example, a mother gave her daughter an apartment, and a few years later she began beating her mother and leading an antisocial lifestyle. If these facts are confirmed by certificates from the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the court may cancel the contract and generally discharge the former donee from the premises (Decision of the Golovinsky District Court of Moscow in case No. 2-524/2013 of 02/08/2013).
Is it possible to invalidate a deed of gift as a concealment of property?
As mentioned earlier, on the basis of clause 3 of Art. 578 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a DD may be declared invalid if it is drawn up less than six months before the donor applies to the arbitration court to declare himself bankrupt. This is relevant if the donor is an individual entrepreneur (hereinafter referred to as an individual entrepreneur) or is part of the founders of a legal entity, and the donation was made at the expense of the property of the enterprise.
Individual entrepreneurs bear personal liability for transactions and business and are liable with their own property. If an organization is involved in bankruptcy, only things belonging to it are included in the bankruptcy estate. The founders do not bear personal liability. An exception is bankruptcy due to the fault of the owners: in this case, according to clause 3 of Art. 3 Federal Law No. 14-FZ dated 02/08/1998, subsidiary liability arises for the obligations of a legal entity.
Note! Creditors have the right to go to court at any time to bring the debtor to subsidiary liability if the property of the enterprise is not enough to repay the debts. If the application is granted, the founders and other responsible persons will have to part with personal money and valuables. Real estate transactions completed six months before the start of bankruptcy proceedings may also be challenged.
How to invalidate a gift agreement: step-by-step instructions
To challenge the DD, the plaintiff must collect a complete list of evidence and apply to the district court to find the property transferred by gift (Article 30 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The whole process looks like this step by step:
- Preparation of documents.
- Drawing up a statement of claim.
- Submitting a claim and documents to the court.
- Participation in the consideration of the case.
- Announcement of the decision.
- Waiting for the decision to enter into legal force.
- Re-registration of ownership.
Let's look at everything in detail.
Step 1: collecting documents
For legal proceedings you will need:
| Document's name | Where to get |
| Statement of claim | To be completed by the plaintiff independently or with the help of lawyers |
| Passport | Department of Internal Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs |
| Receipt for payment of state duty | Bank or online service through which the payment was made |
| Contested DD | Done by a notary or independently by the parties |
| Documents for donated property (if available) | Rosreestr or other government agency depending on the type of property |
| Extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate, if the real estate DD is disputed | Rosreestr, MFC |
| Information about assault | Medical institution |
| Court verdict to hold the donee accountable for a crime committed against the health of the donor and resulting in his death | The court that passed the sentence |
| Birth certificate of a child under 14 years of age, if he was the donor | MARRIAGE REGISTRY |
| Power of attorney for a lawyer | Notary |
| Notification of delivery of the claim and other documents to the participants in the process | Post office |
| Decision to declare the donor incompetent | Court |
You should also obtain witness testimony and, if possible, provide video and audio recordings. The burden of proving his case lies entirely with the plaintiff.
Step 2: filing a claim
The plaintiff can draw up a statement on his own or seek help from lawyers. In the first case, you need to take into account the provisions of Art. 131 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, according to which it must contain comprehensive data:
- Full name, registration address, passport details of the plaintiff;
- name and address of the court;
- Full name, address of the defendant;
- address, location of real estate transferred under the DD;
- date of preparation, number of the contested deed of gift;
- grounds for cancellation of the transaction;
- date of filing the claim;
- requirements: recognize the DD as invalid, apply the consequences of invalidity of the transaction;
- applicant's signature.
Sample statement of claim to invalidate a gift agreement:
Note! From October 1, 2019, plaintiffs, having completed applications and collected documents, must independently send them to all parties to the proceedings, incl. and the defendants. Evidence of mailing (receipt receipt) is provided to the court.
Step 3: going to court
Having sent the claims to the participants, you need to submit an application with attached documents regarding the case to the court. Within 5 days, the judge will review them and make a decision on acceptance for proceedings.
In case of refusal, an appropriate determination is issued indicating the reasons. They can be eliminated and appealed to the judicial authority again.
Step 4: Litigation
The parties are notified of the upcoming meeting in advance. The defendant or plaintiff has the right to request consideration without their participation.
During the proceedings, the circumstances of the case are clarified and the opinions of the parties are heard. The review period is 2 months.
Step 5: Making a decision
At the end of the trial, the judge makes a decision alone in the deliberation room, then announces it in the courtroom (Article 194 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Step 6: entry into force of the decision
The decision takes legal force 1 month after it is made. This time is given to the parties to appeal the appeal.
You can file an appeal through the court that made the contested decision. Subsequently, it is transferred to a higher authority.
Step 7: registering a new owner
If the decision has entered into force, a certified copy is sent to the registration authority to return ownership to the plaintiff. This is true for real estate deeds.
A copy is also provided to the donor; he must submit it himself in order to re-register the documents in his name.
State duty
When an individual goes to court to challenge a deed of gift, a state fee of 300 rubles is paid.
For organizations, the fee is 6,000 rubles. (Article 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Statute of limitations
To determine the statute of limitations, the basis for challenging the DD is important - voidability or a void transaction. Voidable ones are canceled within 1 year from the moment when the person became aware of the violation of his rights. Void ones are canceled within 3 years.
Important! If the deadline for going to court is missed, it can be restored if there are good reasons. For example, the impossibility of applying due to illness, stay in another city or other circumstances that occurred during the last 6 months of the specified period.
If the donation is declared invalid.
When a court decision is entered into declaring the gift invalid, the donee is obliged to return everything received under the contract (Article 167 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 of Article 578 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Data on registered rights to an apartment, return of ownership to the donor, are entered into the Rosreestr when a judicial act is provided. The keys are returned.
Based on this information, regarding the situation with the donated apartment, we explain the following:
- The court can invalidate the gift agreement at the request of the grandmother only if one of the above grounds is present: threat to life, damage to the apartment, etc.
- Heirs with a mandatory share in the event of the grandmother’s death can claim rights to the apartment. The statute of limitations for this claim expires after 2 years.
- When the contract is certified by a notary, the legal capacity of the citizen who is the donor of the property is checked (the notary must request from the donor certificates from the IPA and ND dispensaries). Cancellation of the transaction on the basis of Articles 176, 178, 179 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is excluded. Notarization is an additional guarantee of protecting the contract from being challenged in court.
Who has the right to file a claim to declare a transaction invalid?
Any individual or legal entity has the right to submit an application to the court to declare the DD invalid if the above grounds exist or the interests of the plaintiff are violated.
The case is being considered as a claim proceeding. Legal advice: simultaneously with the recognition of the DD as invalid, make a demand for the application of the consequences of the invalidity of the transaction. By decision of the court, the deed of gift and information about the owner (done) are canceled, and the donated property is returned to the donor, and upon the appeal of the heirs, it is included in the inheritance mass if the application is satisfied.
Donor
The donor has the right to go to court to challenge the deed of gift on any of the grounds.
You must provide the maximum list of evidence:
- medical certificates;
- police documents;
- expert opinions on damage to property of non-property interest;
- audio and video recordings.
It is recommended that witnesses be brought to testify. The request to summon them can be reflected immediately in the statement of claim.
Heirs of donors
The donor's heirs have the right to submit an application to cancel the DD and include previously donated property in the inheritance estate if he died due to the fault of the donee, and this fault is proven.
You will need a court verdict that has entered into force and other evidence confirming intentional guilty actions.
Third party
Third parties mean creditors of the donor participating in the bankruptcy procedure as a debtor.
Legal representatives and guardians of the citizen who donated the property, being partially or completely incapacitated, can also apply for a challenge.
How to donate property
In order to find out on the basis of what circumstances it is possible to terminate a transaction, you need to know how the donation is made.
Donation of property, things and real estate can be expressed in the form of:
- gratuitous transfer;
- promise to deliver by a certain date;
- exemption from the obligation to fulfill any requirement (for example, forgiveness of a debt for an apartment).
Donors can be:
- citizens, including close relatives;
- organizations.
For real estate donation transactions, compliance with the conditions is required (clause 3 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- written contract;
- registration of transfer of rights in Rosreestr.
The main requirement for making a gift is that the donor has ownership of the property.