Time limit for appealing the decision of the court of first instance in Arbitration
At the end of the decision it must be indicated that it can be appealed within a month from the date of its issuance. Time begins to expire from the next day after the date of drawing up the act in final form. You are not late with your appeal if you managed to submit it through the electronic service or sent it by mail before 24 hours of the last day.
Note! If the last day to file an appeal falls on a date that is not on the calendar, then the time period for appealing ends on the last day of that month. For example, when a court decision was made on January 30, and there are only 28 days in February, the deadline for appealing is February 28.
Other deadlines are established for appealing cases:
- on administrative liability - 10 days;
- to transfer the dispute to another arbitration - 10 days;
- on compulsion to convene a general meeting - 10 days;
- simplified production - 15 days.
After the appeal period has expired, the court decision comes into force.
Suppose a person missed the deadline for appealing the decision of the arbitration court of first instance. The applicant can then file a motion, which can be part of the appeal or an appendix thereto.
The paper will be accepted by the court, provided:
- The period does not exceed six months. For direct participants in the dispute, the period is counted from the day the verdict was drawn up, for others - from the moment they learned about the infringement of their interests.
- The reasons for absence were recognized as valid.
The court will consider them as such if:
- the face became seriously ill;
- the person was caring for a sick relative;
- the court did not comply with the deadlines for preparing the decision;
- the court late sent a copy of the verdict to a person who was not at the hearing.
Business travel, vacation of the applicant's representative, absence of a lawyer on staff and change of manager are not considered as significant reasons.
Refusal to satisfy the petition is an argument for appealing to the cassation authority.
Legal assistance in appealing to the Courts of Appeal
Consultation in the office and by phone
+7(495) 728-99-14
Help from a lawyer. 18 years of experience in appeals in the Courts of Appeal!
We are working during the quarantine period of 2021! Call.
Appeal in an administrative case
The appeal process in administrative cases is governed by the norms of Section 6 of the CAS of the Russian Federation.
As a general principle, you can appeal a district court decision that has not entered into legal force within a month from the date of its announcement.
However, the law also provides for other deadlines for appeal.
Decisions must be challenged within ten days:
- which relate to issues of deportation of foreign persons from the territory of Russia;
- which are associated with administrative supervision and forced hospitalization in medical institutions;
- which relate to the dissolution of the representative body of municipal government, the removal from office of the heads of the municipal organization.
Decisions regarding election and voting issues made by the district court can be challenged within 5 days. This clause also includes any violations that relate to a citizen’s voting rights.
If during the court hearing only the operative part of the decision was read (punishment, without justification), then the period for challenging is calculated from the moment the full text of the document is read.
Important: decisions made under the simplified procedure are subject to appeal within 15 days.
There are two ways to write an appeal against a court decision: by mail or by submitting it to the office (in person or through a legal representative).
The procedure for appealing the decision of the arbitration court of first instance (main stages)
To challenge the decision of the first court, the APC provides for several steps.
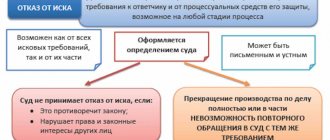
Appeal . The plaintiff, defendant or other interested person has the right to file a written objection to both the decision and the ruling of the court. It is not possible to raise new claims in the appellate court. If you want to add new documents to the case, you must have good reasons.
Cassation . Here they are more concerned with checking the legality of the decisions made. In order to overturn the original decision, gross errors in the application of legal norms must be discovered. In the court of cassation it is impossible to re-evaluate evidence if it was contradictory. The complaint is submitted directly to the cassation division.
Supervision . The complaint is sent to the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation. In this instance, the decisions of previous courts are reviewed for legality.
Payment of state duty
The legal requirement for payment of state duty is enshrined in Chapter 25.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The amount of the state fee depends on the status of the applicant and the type of appeal. Individuals pay 150 rubles, legal entities - 3000 rubles.
If the appeal is sent to the arbitration court, the state fee will be 3,000 rubles, regardless of the status of the applicant.
You should not ignore paying the state fee; without a receipt, the complaint will remain either without consideration or without progress.
You can get legal assistance regarding an appeal against a court decision on our website.
Nuances of an appeal against a decision of the arbitration court of first instance
Let's look at what nuances you need to know in order to avoid making common mistakes in the appeal.
Firstly, the unconditional grounds for canceling the judicial act of the first instance are not checked. Some lawyers set out the circumstances of the case in detail and justify their position. But they forget to find at least one clue, after which the court decision is sent for a new consideration on the merits.
Secondly, the important and unimportant errors of the trial court are simply listed, without making reference to specific materials on the arbitration case. It is advisable to indicate no more than five reasons for canceling a judicial act. Here it is necessary to explain how each of them led to false conclusions of the court, and which conclusions will be correct.
Thirdly, lawyers are not active. New materials cannot be presented to the appellate court unless it is proven that they could not have been submitted for objective reasons or the lower court rejected them. Even if it is difficult to come up with a valid reason, it is still worth presenting significant evidence. Most often, the courts attach them to the case.
How to appeal a decision of an arbitration court in an appellate instance
I propose to consider the procedure for appealing the decision of the arbitration court of first instance.
A prerequisite is the written form and the signature of the applicant. The complaint can be filed remotely through the “My Arbitrator” system, by mail or in person to the court office. The choice of the appellate instance is carried out on a territorial basis.
The complaint is filed through the court of first instance, which initially considered the arbitration case. Within a few days, it is forwarded to the appropriate appellate arbitration court.
The complaint, like other procedural documents, consists of 4 parts:
- Introductory - name of the court, contact details of the applicant, case number,
- Descriptive - circumstances of the case,
- Reasoning - the grounds on which the decision should be reversed,
- Resolute - the claims of the party.
The final part contains a list of attached documents, which include, for example, documents on state duty.
In general, the arbitration process is similar to proceedings in a lower court. But there are several fundamental differences. The Court of Appeal considers the case in a collegial composition, without the participation of arbitration assessors. It cannot put forward new demands, change the grounds of claim, etc. In addition, appeals against rulings to transfer a case to another arbitration or disputes in a simplified manner may be considered without summoning the parties.
Note! If the determination to return the claim is disputed, do not forget to submit a statement of claim and the proposed documents.
Consideration of the appeal lasts for two months from the date of receipt of the last one with a full set of documents. In exceptional cases, the period may be extended by the chairman of the arbitration court to 6 months.
Consultation on appeal to the Courts of Appeal
+7(495) 728-99-14
Preparation of complaints to the court. Assistance in the Court of Appeal. Appeal lawyer.
Judges make procedural errors
- It happens that judges try to refuse to accept brief complaints, but this is illegal, and the higher courts will side with you.
- Don’t expect that the decision will be given to you on time - Moscow courts are very busy. Most likely, you will receive it within a month, maybe a little faster. This is why you need to file a short appeal - it will buy you time.
- Refusal from supervisory authorities is also not a reason to give up. Continue filing complaints: We have seen cases where persistence has paid off.
Is it possible to file a cassation without an appeal against an arbitration ruling?
As a general rule, an appeal to the cassation authority is possible only after an appeal has been completed. Having skipped this stage, the court decision enters into legal force and is not subject to appeal.
The only exception is the case when the court refused to satisfy the petition to restore the period of appeal, indicating this in the ruling on the return of the appeal. In this case, payment of state duty is not provided.
This exception does not apply to cases of bringing to administrative liability if the amount of the fine does not exceed 100 thousand rubles. for organizations, 5 thousand rubles for individual entrepreneurs.
What to do if you lose your case in court again and again and again?
There is another force that has, albeit unofficial, tangible power. These are journalists. If nothing helps at all, and you have become a victim of blatant injustice, you can turn to them. The hype generated in the press guarantees attention from the authorities, and sometimes this method really works.
Through the media, people were able to draw attention to housing and financial problems, they were able to obtain treatment, and the provision of medications required by law. But you need to understand that journalists are primarily interested in “hot” news—those that will help increase their ratings. If your story is outrageous, you have become a victim of a clear and terrible lawlessness, and even professional lawyers cannot help you, you can turn to the “fourth estate.”
To avoid losing the case?
There is always a chance of losing, even if it seems that the matter is nonsense, and the decision will definitely be made in your favor. We talked about what to do next if you lost the trial, and now let's talk about how to protect yourself. That is, do everything possible to win.
- Get ready to be rude. Unfortunately, most judges don't have time to listen to the whole story. Unfortunately, in court no one will treat you with understanding. The court is in many ways a conveyor belt, except for very high-profile cases. You need to understand that you will not be treated kindly, and not allow disappointment to break your morale.
- Do not neglect the services of lawyers. The lawyer may not be present at the meeting, but it is better to consult with him on all issues: regarding documents, chances, possible difficulties, draw up complaints with his help and think through defense tactics. Jurisprudence is a difficult science and quite confusing for an unprepared person. It may seem to you that you have taken into account everything, and then it turns out that you still forgot about some important nuance.
- Record absolutely everything. Unethical behavior and procedural errors will help when filing an appeal, and all kinds of documents can be attached to the case. Try to take pictures of everything, keep receipts, take receipts.
- Take the trial court seriously. In most cases, he is the only place where you will be allowed to talk about your trouble in detail. In the appellate and cassation departments they listen less and not so carefully. If you lost the trial court, try to hire a lawyer for subsequent hearings.
- Get ready for bureaucracy and wasted time. Meetings rarely last long, but you will have to wait in queues. Few processes start on time. Try to get enough sleep before your trip, don’t plan any important things right after. Do not be nervous. And trust your lawyer.
In our experience, many trials that are lost in the first instance are won in subsequent cases.
- No qualified lawyer can guarantee that the court will side with you. The decision is not made by a lawyer, and to predict it in advance is a sign of incompetence and even fraud.
- When you hire a lawyer, you are not paying for victory, but for the lawyer to find and use all legal opportunities for legal assistance. And it is these efforts that pay off.
- Criminal lawyers work primarily not to acquit the client, but to achieve the maximum mitigation of the sentence for him. The percentage of acquittals in criminal cases in 2017 was only 0.3%: this is 2,900 out of 958,000 cases considered by the trial court.
Results of the appeal against the decisions of the arbitration court
Based on the results of the consideration of the complaint, the judge makes a decision, which immediately comes into force. Possible outcomes of the appeal:
- leave the decision of the lower court unchanged,
- cancel the judicial act and send the case for a new trial to the arbitration court of first instance,
- cancel the judicial act in whole or in part and make a decision independently.
An arbitration lawyer always puts the interests of the client at the forefront. Therefore, she tries with all her might to resolve the dispute out of court.
It happens that the principal delays until the last minute contacting lawyers who are professionally involved in representation in arbitration courts. In turn, lawyers working within the company do not have a sufficient level of competence to comply with all formalities.
If you need help in drawing up a complaint or representing your interests in court, you can contact the Kakhiev and Partners law office. We will provide detailed advice and ensure effective judicial protection, both in the appellate instance and in cassation and supervision.
Review of decisions based on new and newly discovered circumstances
In addition to appealing the decision of the arbitration court to the appellate, cassation or supervisory authority, they can be reviewed due to new or newly discovered circumstances. At the same time, there is a significant difference between new and newly discovered circumstances:
- the newly discovered circumstances already existed at the time the appealed court decision was made;
- New circumstances are recognized that arose after the court decision was made, but if they existed at that time, they would have been significant for the court’s decision.
Article 311 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation clearly sets out the list of circumstances that the legislator considers as new and newly discovered. Accordingly, those circumstances that are not listed in the article do not constitute grounds for reviewing a court decision in this manner. An application for review of a decision based on new or newly discovered circumstances may be submitted to the arbitration court no later than three months from the date of occurrence or discovery of these circumstances. An application for review is submitted to the arbitration court in writing, signed by the applicant or his representative. The application can be submitted in person, sent by mail or by filling out a form posted on the official website of the judicial authority. The application must indicate:
- name of the judicial authority;
- information about the applicant, as well as about other persons participating in the case;
- information about the judicial act that is subject to revision due to newly discovered or new circumstances - the name of the judicial authority, case number, date of the decision and the subject of the dispute;
- the requirements of the person - the applicant, provided for in Article 311 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation and which, in the opinion of the applicant, are the basis for raising the issue of reviewing the decision;
- a list of attached documents is written down - copies of the application for reconsideration of the case, copies of the judicial act for which the applicant is applying for review, copies of documents - confirmation of newly discovered or new circumstances, a power of attorney for a representative if necessary.
Based on the results of consideration of the application, the judicial authority may make a decision to satisfy the applicant’s requirements and cancel the previously adopted judicial act or refuse to satisfy the application.