To be able to carry out the necessary tasks, each country requires economic resources. One of them is property that is in state ownership (federal or municipal). How effectively it is managed determines how the country accomplishes its objectives. From the article we will learn what kind of state and federal property there are and the reasons for its emergence.
Concept
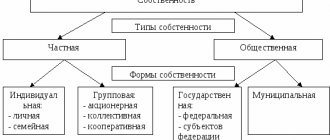
Previously, the state was the main form of ownership. But at present, the law enshrines the equality of participants in civil legal relations, which also extend to the state. Equality is ensured by the absence of some advantages, for example, the non-extension of the statute of limitations to a claim for the return of federal property from someone else's possession, carried out illegally. State property (federal and municipal) and private are considered as two components of economic relations, where the purpose of state property is the national appropriation of property, which is separate from the property of individual companies and citizens. The coincidence of national and state interests is based on Part 1 of Art. 3 of the main law of the country, according to which the people are the only source and bearer of power in the country.
Federal property includes property that belongs to the Russian Federation, regional property refers to property that belongs to individual subjects of the country. All this together constitutes state property. Possession, use and disposal of it is carried out in accordance with Articles 294 and 296 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Private
The Civil Code and the Constitution of the Russian Federation establish the concept of “inviolability of private property,” which protects the owners of such property from the illegal seizure of their valuables by other people.
Depending on the form of management, it is customary to distinguish two types of private property:
- individual,
- public
Moreover, each type has subcategories, which also have their own legal characteristics and legal justification. They are described in detail by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The individual form of private property is divided into:
- form of unity - all benefits are owned by a single citizen who can attract hired workers,
- partnership - an association of individuals to conduct business activities,
- cooperative - individuals form capital through the sale of free shares.
Public is divided into:
- collective form, in which management rights are shared among workers,
- state - the property belongs to the city or town,
- national - values that belong to all residents of the state (museums, memorial places, etc.),
- combined - formed when different forms of property are combined.
Joint and shared ownership play an important role in the life of an ordinary citizen, because each person is in one way or another involved in this form of property management.
Video: Concept and content of property rights
Joint
Joint property is property that simultaneously belongs to two or more citizens. At the same time, the values are not divided between individuals, that is, the partners own them on an equal basis. This happens between spouses after marriage. For example, an apartment purchased during marriage will not be divided into shares, but is considered common.
This point does not apply to values acquired before the conclusion of a legal union. That is, real estate purchased before marriage will not become common after signing the documents.
The legal characteristics characteristic of joint property are described in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Share
Shared ownership is property owned by two or more persons, which is divided into shares depending on the investments made or the territory purchased. With this form of ownership, the division of values can occur regardless of whether the citizens are relatives.
In order for ownership to be legal, the shares must be officially registered. After this procedure, the participant acquires the right to real estate.
You may be interested in: Sell real estate on Avito for free.
Types of state property
Objects classified as state property are established by law. They:
- They form the basis of Russia's national wealth.
- Necessary for the work of government bodies and solving problems on a national scale.
- Refers to defense production.
- Ensure the vital activity and development of the national economy.
- Refers to other objects.
Let's briefly consider each of them separately.
Objects for the functioning of government agencies and the management of government tasks
The objects that are needed for the work of government agencies and the management of national tasks include the following:
- The state treasury of the country.
- Property owned by the armed forces, police departments and other institutions, financed from the federal treasury.
- Universities, research institutes, enterprises and other facilities of the Russian Academy of Sciences, ministries, state research centers.
- Enterprises and other geological, geodetic, hydrometeorological and other services.
- Enterprises and institutions of sanitary and epidemiological and veterinary services.
- Patent service enterprises, metrological and machine testing stations.
- State reserves and reserves, enterprises that preserve them.
- Correctional institutions, medical and preventive enterprises.
Defense production
Defense production facilities include:
- Enterprises that produce weapons, explosives and toxic substances, radiation materials, rockets, space flight devices, equipment for the military; enterprises that service, launch and support spacecraft carry out research and development work in these areas.
- Premises of reserve points for the management of all government bodies and communication facilities, as well as infrastructure, which are intended for use at special times.
Objects for work and development of the national economy
Objects that ensure the work and development of the national economy:
- Enterprises related to the mining industry.
- Fuel and energy complex.
- Electrical energy.
- Railway, air, water, pipeline transport, gasification.
- Public roads and organizations that maintain them.
- Television, radio enterprises, communications.
- Breeding and equestrian state farms and factories, breeding centers, state inspections, laboratories for testing agricultural crops, fish production farms, serpentariums.
Subjects and objects
The entity that owns, uses and disposes of property is its owner. In relation to federal property in the Russian Federation, this is directly the state. The fact that the property belongs to the country is confirmed by the state register.
State property never belongs to private individuals. These are the state budget, communications, transport systems, financial organizations, etc. But certain federal property objects can be transferred to municipalities and regions. Some of them control budgetary organizations, while others belong to the state treasury.
Public
Public property is property owned and managed directly by society, represented by a collective entity.
There are three forms of public ownership:
- State - arises as a result of the internal activities of the country. This could be nationalization or construction at the expense of the federal budget.
- Collective - public organizations, churches or parties.
- Municipal - property owned by local authorities.
The current legislation ambiguously defines the concept of “public property.” In theory, everything that is not private is public, but in practice it works differently: even parks can be commercial.
Read also: Peasant farming - what is it?
What lands are federal property?
Let's look at them. State federal property includes the following plots of land:
- In accordance with paragraph 5 of Art. 1 of the Law “On Protected Natural Areas” No. 33-FZ.
- According to paragraph 10 of Art. 1 of the Law “On the Circulation of Medicines” No. 61-FZ and the Law “On the National Guard” No. 226-FZ, territories with military facilities and areas that are allocated for the needs of the army and the National Guard.
- Lands belonging to the forest fund, according to the LC RF.
- Territories of organizations and enterprises that belong to the state.
- Closed cities.
In addition, there is a federal reserve land fund.
Individual cases
According to the comments to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, individual cases of forms of ownership mean various public associations, for example, trade unions or political parties. They cannot be considered a private species, although officially they are legal entities, but it is also impossible to recognize them as a public organization.
Features of types of property for business in Russia:
Organizations
Due to gaps in the legislation, there are a number of organizations that are quite difficult to classify as one of the forms of property. This is due to the features of the structure and the functions performed.
"Special" organizations:
- unions,
- political parties,
- religious organizations.
Many experts believe that such companies belong to public property, but this cannot be legally confirmed.
Enterprises
For enterprises, the legislation distinguishes other forms of ownership, based on the characteristics of the organizational structure or on the shares of invested capital.
Other forms of property characteristic of the enterprise:
- mixed property - property based on a combination of different types of ownership,
- foreign - valuables owned by foreign persons,
- intellectual - the objects are the results of mental activity.
The rights of the last category of property are protected by special laws: on copyright and related rights, legal protection of programs for electronic computers, etc.
Real estate and residential premises
For residential and non-residential real estate, there is only one “other” form of property - general, which is divided into two categories depending on the management style.
Categories of general values:
- Joint - occurs between legal spouses. In this case, the real estate is not divided into shares, but belongs to the partners simultaneously.
- Shared - the property will be divided into equal shares. In this case, ownership and disposal of property occurs by consent of the owners.
A striking example of the second form is an apartment purchased under an equity participation agreement. A residential building is represented by private property - apartments, which are shares, and common property in the form of entrances, elevators and basements.
Demarcation
This procedure is the transfer of an allotment that previously belonged to part of an undelimited territory in the federal ownership of the Russian Federation. In the same way, lands that previously belonged to the regions are transferred.
The concept of demarcation arose in 2001. The adopted procedure was in effect until 2006, after which it was canceled due to the complexity of the process. From July 2006 to the present, delimitation is carried out on the basis of the Land Code.
Regional, municipal and federal property is determined in accordance with three main criteria, in particular:
- If there is a building on the site that belongs to one of the entities, it is this entity that has priority during the delimitation procedure.
- The land used by the organization can be transferred to the entity on whose territory it is located.
- If the law says so.
There is the following algorithm of actions, according to which the division of lands and their transfer to federal ownership is carried out:
- First, a law is developed in accordance with which this process is carried out.
- Cadastral services are working.
- The previously defined boundaries of the site are fixed. Then an individual number is set.
- An act is adopted according to which the corresponding site is recognized as federal property of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with certain circumstances, federal land plots can become the property of both regions and municipalities.
The main division of forms of property rights is the division of property into state, municipal and private. In turn, state property is divided into federal property, belonging to the Russian Federation, and property belonging to the constituent entities of the Federation.
Perhaps the special position of state property is due to its very nature, which ensures the existence of the state. The funds necessary for government expenditures can be acquired in different, but legally equally permissible ways. The two main systems are the following: the allocation of special state property from the entire national property, the income from which covers state costs; a requirement directly from citizens to allocate a certain part of their property in favor of the state. State property may consist of various types of profitable property, namely land property, industrial establishments and capital; the first two types of property can consist of property acquired according to the general rules of civil law, or of exclusive property, the right to which belongs only to the state, that is, of monopolies and regalia.
The legislation clearly defines state property belonging to the Russian Federation and property under the jurisdiction of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Objects that are exclusively federal property include:
· objects that form the basis of the country’s national wealth;
· facilities to ensure the functioning of federal authorities and management and solve all-Russian problems;
· defense production facilities;
· objects of industries that ensure the vital activity of the Russian national economy as a whole and the development of other sectors of the national economy;
· other objects: enterprises of the pharmaceutical industry, the industry of medical and biological preparations; enterprises and organizations producing alcohol and liquor products.
The law also defines objects related to federal property that can be transferred to the state ownership of constituent entities of the Russian Federation. This is for example:
· largest enterprises of the national economy;
· nuclear and power engineering enterprises;
· healthcare and public education institutions;
· research organizations;
· television and radio broadcasting enterprises and others.
State-owned property is assigned to state enterprises and institutions for possession, use and disposal in accordance with Art. 294-295 Civil Code.
Whatever type of state property we are talking about, in the civil sense it will be property. According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the concepts of “things” and “property” are used as synonyms. In this case, to define the term “property”, the formula is used: property is everything material that has value, as well as everything intangible that, being materialized, acquires value. The concept of property includes shares and property rights. The object of property rights can be precisely property, and one that has some economic value. Some objects of human activity can be regulated using property rights, but with a special legal regime, since they do not allow “full economic domination,” but only limited possibilities of use. In addition, there are categories that are generally not capable of acting as objects of property rights by their nature.
Meanwhile, the object of civil law and the object of property law are far from the same thing. As V. A. Dozortsev believes, not all property can be the object of ownership, but only material things limited in space[1]. Neither rights, nor securities, much less objects of intellectual property, in his opinion, are objects of property rights. He considers an enterprise as a property complex to be an exception to this rule, and even here, in a separate form, obligatory claims and other rights to objects that do not have a material nature cannot in any way be included in the list of objects of property rights. Therefore, one should quite clearly distinguish between property as a generic category and objects of property rights as one of its varieties. By the way, the concepts of state ownership and state property are used as synonyms in Russian regulations.
The need to classify the entire variety of property objects is obvious. A major division of state property can be carried out depending on their legal regime. It is known that even in ancient Rome there was a division into common property and public property. The common property is what belongs to everyone by natural law (air, running water, sea), and public and state property belongs to the Roman people (rivers and harbors). “The Roman jurists clearly distinguish between the public property of peoples... and the common property.” Public property has a very special regime, because its alienation requires the consent of the people.
Currently, in the West, so-called public property is distinguished within the framework of state ownership; it usually includes territorial and some other waters, seashores, the most valuable minerals, etc. These objects are the exclusive property of the state. It is believed that public property can only be used for the common good.
Among the objects of state property rights, the regulation of land rights deserves special attention.
As mentioned above, the right of state property means that the powers of ownership, use, and disposal belong to the state. The state, as a subject of state property rights, is represented not by one department, but by a number of different government bodies, between which property rights are distributed.
Taking into account the federal structure of Russia and the existence of two levels of state power, it is stipulated that the right of state property exists in the form of:
federal property and
· property of subjects of the Russian Federation (subject).
At each level, the powers of ownership, use and disposal are distributed between legislative bodies, relevant ministries and departments, as well as local governments, and are implemented through a system of state powers and management functions.
The object of state property rights are individually separated land plots that are not owned by citizens, legal entities and municipalities (Article 214 of the Civil Code). State land ownership has a leading place. State lands are the most extensive in area and have the most significant economic and environmental significance. The majority of industrial enterprises are located on state lands; the vast majority of environmental lands are in state ownership[2].
The development of state property rights is associated with the complex problem of distinguishing between federal and subject property rights. The problem is caused by the state’s insufficiently clearly expressed position on how to make the distinction. Two legally inconsistent approaches are used. On the one hand, it is envisaged to strictly delineate the right of state ownership physically, by object, and legally. On the other hand, the delimitation of state property rights is simultaneously provided for by delimiting the subjects of jurisdiction and powers to manage land legal relations between state and subject government bodies without physically delimiting the lands themselves and correspondingly consolidating the independent property rights of the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Political support for the first approach is expressed in the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to stabilize the socio-economic situation in the country, which provides for the delimitation of ownership of real estate, including land plots, between the Russian Federation, its constituent entities and local governments.
This approach was implemented in determining the legal regime of certain categories of land. Thus, the Water Code of the Russian Federation is based on the procedure for delimiting water bodies and, accordingly, lands of the water fund into federal and subject according to established criteria. Based on the Forest Code of the Russian Federation, the forest fund is declared federal property, subject to the transfer of part of the forest fund into the ownership of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with federal law.
At the same time, the Water[3] and Forestry[4] codes, regardless of the actual delimitation, establish a procedure for coordinated joint decision-making on issues of the legal regime of the respective lands. In the development of the Forest Code, not a single decision was made regarding the recognition of forest fund areas as subject property. Water bodies are partially demarcated, but the legitimacy of such delimitation is questionable, since on the basis of Art. 67 of the Constitution, internal waters and the territorial sea under no circumstances can be subject property, since they are not included in the territory of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Moreover, regardless of what actions are taken in this area, both Laws provide for the participation of government bodies of both levels in property management. The expediency of physically making a distinction in this case, as well as legal registration of the rights of two subjects, is called into question.
This contradictory situation gives rise to an interesting situation when, along with federal and subjective ownership of land, de facto, but outside the law, there is another type of state property right - the right of some “common” (not physically delimited) state property.
It is provided that the management of federal and subject property is carried out respectively by state authorities of the Russian Federation (Article 71 of the Constitution) and constituent entities of the Russian Federation, although in most cases the principle of separate management is not implemented.
Thus, we can conclude that the legal status of state-owned objects is contained in a number of regulations relating to various branches of law.
[1] Dozortsev V. Fundamental features of property rights in the Civil Code // Civil Code of Russia. Problems. Theory. Practice. Collection in memory of S. A. Khokhlov / Rep. ed. A..L. Makovsky.M., 1998. P. 205.
[2] Zvekov V. Participation of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities in relations regulated by civil legislation // Economy and Law. - 1998. - No. 5. — P.13-19.
[3] Water Code of the Russian Federation dated November 16, 1995 N 167-FZ (as amended and supplemented on December 30, 2001, December 24, 2002, June 30, December 23, 2003, August 22, 29 December 2004, May 9, 2005) // “Rossiyskaya Gazeta” dated November 23, 25, 1995.
[4] Forest Code of the Russian Federation dated January 29, 1997 N 22-FZ (as amended and supplemented on December 30, 2001, July 25, December 24, 2002, December 10, 23, 2003, August 22 , December 21, 29, 2004, May 9, July 21, 2005) // “Rossiyskaya Gazeta” dated February 4, 1997.
The emergence of federal property
There are certain rules. They determine the process of the emergence of federal ownership of land. This occurs through the use of the following methods:
- The state can initiate the process of confiscation of land that is owned by private owners. At the same time, Article 279 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right to withdraw the corresponding allotment in order to meet state needs through redemption.
- Another method is nationalization, which is referred to in Art. 235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to the provisions of this article, the conditions and procedure for the seizure of property are implemented through payment of compensation for the cost of the land plot, as well as other additional costs.
These two methods differ from each other, although in both cases financial losses are compensated.
Registration of ownership
Since 1998, the only place that can confirm ownership of property is the Unified State Register of Rights (USRP). To receive an extract, you need to order it from Rosreestr (GKN).
If the right of management has not yet been registered, then you need to apply to the nearest multifunctional center (MFC), attaching a package of documents.
List of required documentation:
- statement,
- passport,
- certificate of purchase of real estate,
- document on registered persons,
- cadastral passport,
- a receipt confirming payment of the state duty.
Depending on the specific circumstances, MFC employees have the right to request additional documents.
Seizure
This procedure is regulated by the Land Code. Redemption is one of the most popular legal instruments for such seizure. According to the law, the purchase of plots of land in order to meet state and municipal needs can only take place in exceptional cases. This principle protects the rights of citizens. The executive body issues a special order on this.
A decision can be made regarding federal property and the property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation by the relevant authorities. Local authorities do not have such powers. Therefore, for this they have to contact higher authorities. As legal practice shows, which is aimed at purchasing land for state needs, usually ownership is transferred to a third party.
Denationalization process
Denationalization is usually understood as the process of transferring property from the state into the hands of private individuals. The procedure includes several directions, the main one of which is reducing the share of public sector participation in the country’s economy.
Denationalization is a system of measures aimed at transforming state property to eliminate excessive state participation in the economy.
Among other things, the procedure means the almost complete removal of most economic management functions from the state, but this does not mean that the country’s leadership ceases to play a significant role in the market economy.
Main methods of denationalization:
- liberalization of markets - opening up new opportunities for the establishment of a market by new economic entities,
- commercialization - transfer of state organizations to commercial calculation,
- encouraging the creation of mixed enterprises,
- denationalization.
All four tools are used in combination, resulting in changes in the forms of management of the organization and improvement of the mechanism of the market economy.
Seizure procedure
The procedure and procedure for seizure, as well as transfer to federal ownership, are established by land legislation. According to Articles 279-281 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, this process consists of compliance with the following stages:
- After a decision is made to seize land for municipal or state needs, government agencies send a written notification to the owner no later than one year before the repurchase is carried out.
- At the same time, certain guarantees are provided to citizens, according to which the plot cannot be withdrawn without the corresponding will of the subject for any reason within a specified period.
- Then a bidding procedure is carried out, in which government agencies and the owner of the land plot purchase the territory of interest.
If, in the opinion of the owner, such a seizure is illegal, he has the right to go to court to protect his interests.
Reasons for withdrawal
The corresponding grounds for seizure are provided in Art. 49 of the Land Code, which provides an exhaustive list. It includes:
- Transfer of land for state needs, if the state is thereby able to solve problems in fulfilling its obligations.
- The transfer of land into state ownership from private is carried out when it is necessary to locate a state facility and other options are unsuitable for construction.
- After the occurrence of circumstances provided for in federal law, the territory can be purchased.
At the same time, there are cases in which there is no right to transfer lands into federal ownership. These include the following:
- The lands are located on the territory of the protected area, in accordance with Art. 93 Land Code.
- Forest lands belonging to the first group, according to Art. 101 Land Code.
These restrictions ensure that the interests of protecting protected areas, forests and agricultural areas are respected.
Subjects of the economic market
Subjects of the economic market are enterprises, households and the state, united in a single system of economic relationships and performing certain functions. Separate forms of management are provided for them.
It must be remembered that since 2015 there are no such management methods as CJSC and OJSC. They were replaced by public and non-public organizations.
OOO
A limited liability company (LLC) is a form of property management in which the capital of the organization is formed from the contributions of participants. They take an active part in the promotion and development of the enterprise.
Features of the LLC ownership form:
- the minimum amount of authorized capital is 10,000 rubles,
- all decisions are made at general meetings by voting,
- The founders who created the LLC do not bear financial liability for material damage resulting from their activities.
It is the last point that ensures the popularity of LLCs: citizens or organizations that are part of the company do not bear material risks in the event of bankruptcy of the company or its arrest. A striking example of an LLC in Russia is the Renault car assembly plant.
You may be interested in: Decoding LLC: what does this abbreviation mean?
Individual entrepreneurs
An individual entrepreneur (IP) is the simplest form of property that has proven itself for beginning businessmen. In modern realities, it is the most popular type of management.
Why you should open a sole proprietorship:
- there is no minimum amount of money to start an activity,
- relatively small amount of reporting,
- no territorial restrictions,
- Besides taxes, all earnings go directly to the entrepreneur.
The main feature of individual entrepreneurs is that the owners are fully responsible for material damage caused by the organization. That is, the entrepreneur will have to cover the debt from his property in the event of bankruptcy.
Video: What is IP
Partnership
A partnership is a voluntary association of two people who come together to conduct a joint business for the purpose of making a profit. Partnerships may differ in the degree of participation of partners in the company’s activities, but this will not change the essence of the organization.
Benefits of partnership:
- easy organization - just sign an agreement,
- large initial capital due to the combination of people,
- simplified company management due to the distribution of responsibilities between owners.
The main disadvantage of a partnership is equal rights in management. Sharing power can lead to conflicts of interest.