Current repairs of the premises - what is this according to the law?
What applies to current repairs? Current apartment repairs - what is this according to the law?
What is repair? Any property must be maintained by its owners (owners) in proper condition.
The provisions of the Civil and Housing Codes indicate that the owners of premises bear the burden of its maintenance. Therefore, if necessary, they must carry out the required repair work on them.
In addition, they participate in the costs of maintaining common property in a multi-storey building (hereinafter - MKD).
These include fees for routine scheduled repairs performed by service organizations. Persons occupying premises under lease agreements are given the obligation to carry out ongoing repairs.
More serious capital work is carried out by the owner. In this regard, the distinction between these activities is of great importance.
When assigning responsibilities for repairing premises, it is important to determine which actions belong to which type of repair. Civil and housing legislation does not answer this question.
The relevant information can be gleaned from the regulatory documents of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation:
- Resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 N 170 “On approval of the Rules and Standards for the technical operation of the housing stock.”
- Methodological manual on the maintenance and repair of housing stock MDK 2-04.2004.
RUE "Belstroytsentr"
Organizations of various forms of ownership and industry affiliation, when carrying out their economic activities, operate buildings and structures for various purposes: industrial, residential and public. Of course, organizations are engaged in their operation, maintenance, and in some cases, technical re-equipment.
In this regard, an important issue is the competent operation of buildings and structures, the adoption of timely measures to maintain facilities in good condition, which require, among other things, the performance of various construction works, as well as their correct qualification and documentation of business transactions.
In the practical activities of communication organizations, this often raises questions about classifying construction and installation work performed as a specific type: major and current repairs, reconstruction (modernization).
Obviously, this issue must be resolved by organizations at the initial stages of work, since there are differences in the formation of both the permitting package of documents, design and estimate documentation, and in cost accounting, taxation and the composition of primary operational and accounting reporting.
Non-compliance and violation of the requirements of regulatory legal acts when determining the type of construction work to be performed can lead to the application of liability measures to organizations, in particular, the imposition of significant penalties.
In order to correctly apply legal requirements and prevent adverse financial consequences from violations when determining the type of work performed and their reflection according to accounting data, an analysis of typical situations on this issue is presented for consideration.
Conditions taken into account when classifying completed work as a specific type
Issues of classifying construction work as a specific type are regulated by a number of regulatory documents.
Thus, the definition of the concepts of “repair”, “reconstruction”, “modernization” is contained in the documents of the technical regulation and standardization system of the Republic of Belarus, in particular, in the technical code of established practice “System of technical regulation and standardization of the Republic of Belarus. National complex of technical regulatory legal acts in the field of architecture and construction. Basic provisions" (TKP 45-1.01-4-2005), approved by order of the Ministry of Architecture and Construction dated July 18, 2005 No. 172.
Different operating conditions of both buildings as a whole and their structural elements determine different conditions for their maintenance and maintenance, requirements for the characteristics of the structural, technical, aesthetic qualities of the object and different frequency of preventive and repair work.
To correctly determine the type of work to be performed, organizations should take into account a number of factors that determine the purpose of the facility, the reasons and need for repair work, the service life of buildings (their structural elements) and the formation of a set of work to be performed.
These issues are defined by the technical code of established practice “Technical operation of residential and public buildings and structures. Procedure" (TKP 45-1.04-14-2005), approved by order of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture dated 10.10.2005 No. 262 (hereinafter - TKP 45-1.04-14-2005), and the technical code of established practice "Technical operation of industrial buildings and structures. Procedure" (TKP 45-1.04-78-2007), approved by order of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture dated September 17, 2007 No. 286 (hereinafter referred to as TKP 45-1.04-78-2007).
In addition, the order of the Ministry of Construction and Architecture dated July 15, 2010 No. 267 approved the technical code of established practice “Repair, reconstruction and restoration of residential and public buildings and structures. Basic design requirements" (TKP 45-1.04-206-2010 (02250)) (hereinafter - TKP 45-1.04-206-2010). The document defines the List of main types of work performed during current and major repairs, modernization of buildings and structures and restoration of tangible immovable historical and cultural assets, which is given in Appendices A-G TCP 45-1.04-206-2010.
Also, clause 4.7 of this TCP stipulates that the classification of work not specified in the appendices as types of repair or modernization must be carried out by the customer together with the design organization in accordance with section 3 of TCP 45-1.01-4-2005 and this technical code.
For industrial buildings, when deciding on the type of work performed, one should be guided by the List of main types of work performed during current and major repairs of buildings and structures, given in the Appendix to TKP 45-1.04-78-2007, and for reconstruction (modernization) work - in section 3 TKP 45-1.01-4-2005.
Let's consider the application of the above provisions in specific practical situations.
Situation 1
As a result of the inspection of the building, individual defects and damage to the structural elements of the building were identified. The action plan plans to eliminate them for various periods, taking into account the characteristics of the damage, the possibility of normal functioning of the building and the availability of funds. In addition, new technological equipment was installed in this building.
The following work was performed at various periods: replacing floor coverings, painting walls and ceilings, replacing door and window blocks, installing suspended ceilings, roofing repairs and others.
In practice, organizations often have a question: how should the costs of this work be taken into account (in general or based on their classification into different types: repair and modernization)?
Recommendations for resolving the issue
When analyzing the situation described above, it should be noted that the main criteria when making a decision are the reason for performing this work, the types of work and the changes that occurred after the completion of the work.
Thus, if the main reason for the work was the installation of new technological equipment, dismantling and other work was carried out, which led to a change in the number and area of premises, capacity, throughput, direction and (or) location of engineering and transport communications (replacement of their sections) and structures on them, then these works as a whole should be classified as reconstruction.
If the work was carried out to restore qualities lost during operation in the absence of the above conditions, then based on the type of work they can be analyzed separately.
Thus, when performing work on suspended ceilings in an administrative building, it should be taken into account that, depending on the fact of their presence and the actual work being performed:
— current repairs include “A.10 restoration of ceilings, including suspended ceilings in certain places” (clause 1 of section appendix A of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010);
— major repairs include “replacement of suspended ceilings” (clause 25 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010);
— modernization includes “installation of new suspended ceilings” (clause 14 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010).
When performing roofing work, their qualification must be carried out taking into account the following conditions.
Current repairs in residential and public buildings include “repair (partial replacement, no more than 50% inclusive) of individual sections of roofs or roof coverings, including junctions with vertical surfaces” (clause 5 of section A.4 of appendix A of TKP 45-1.04-206 -2010).
Current repairs in industrial buildings include “repair (partial replacement) of sections of roofs, roof coverings, including junctions with vertical surfaces (up to 10% of the area)” (clause 4 of section 6 of appendix to TKP 45-1.04-78-2007).
Major repairs in residential and public buildings include “the complete replacement of the roof or roof covering, as well as the replacement of more than 40% of the roof area of the building, including the use of new materials” (clause 14 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010) ;
Major repairs in industrial buildings include partial (more than 10% of the total area) or complete replacement of the roof (clause 2 of section 6 of the appendix to TKP 45-1.04-78-2007).
A similar analysis of the quantitative (percentage of area, percentage of total quantity) and qualitative (percentage of wear) characteristics of structural elements should be carried out for other work performed.
In addition, organizations should pay attention to the fact that, in accordance with the provisions of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010, work that is separately attributable to routine repairs, but accompanying other types of work, generally relates to this other type of work (major repairs). - clause 35 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010, for modernization - clause 35 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010).
Situation 2
In accordance with the defect report, during an inspection of the facility, it was established that the walls of the building’s facade have an uneven surface and require plastering and painting. The organization’s commission proposed to reduce the plastering of the wall area by using thermal insulation boards with an additional reinforcing layer to a height of up to 2.5 m.
The subject of the construction contract for the work performed in June–July 2010 was “external wall insulation using the thermal fur coat method of the bakery shop.” In accordance with the above agreement, work was carried out on one of the walls of the building.
According to the technical passport of this building, it is one-story and includes both production and institutional space. The building has been in operation since 1944 and during the period of its operation no work was carried out to insulate the walls of this building.
Recommendations for resolving the issue
Assessing the work performed at the site, it should be noted that the “thermal fur coat” system refers to a lightweight insulation system, is used for thermal insulation of walls of various designs and provides:
— standard values of heat transfer resistance of the enclosing structure;
— standard values of resistance to vapor permeation of the enclosing structure;
— protection of the enclosing structure from atmospheric influences;
— improving the aesthetic perception of facades.
In accordance with paragraph 4, section 2 “Walls and Columns” of Appendix K TKP 45-1.04-78-2007, major repairs of elements of industrial buildings only include “protection from noise and vibration, elimination of dampness, increased air permeability and insulation of freezing sections of walls in individual rooms ", that is, all larger-scale works relate to reconstruction or modernization.
In accordance with paragraph 8 of Appendix B of TKP 45-1.04-206-2010, the modernization of elements of residential and public buildings includes “bringing all building elements to modern regulatory requirements for thermal resistance (thermal modernization).”
Thus, in the general case, carrying out work using the “thermal fur coat” method involves thermal insulation and external insulation of walls and, provided that work is carried out on the entire structural element (wall) and the thermal parameters are improved, it should be qualified as “modernization”.
At the same time, in accordance with the defective act, the use of this method was not intended to insulate the walls, but was used “to reduce the plastering of the wall area.”
In this situation, making the right decision on the qualification of the type of work performed is possible only if there are thermal engineering calculations of the resistance to heat transfer, vapor permeability and air permeation of enclosing structures using the Termoshuba system before and after the work, which will indicate a change (non-change) in the thermal insulation parameters of the building and their compliance regulatory requirements.
Thus, if there is a justification (calculation) that the thermal insulation parameters of the building have not changed and their compliance with regulatory requirements, and before the work is carried out, the construction work performed at the site can be classified as repair, otherwise - as modernization.
Liability measures for violation of the law when determining the type of work performed
Incorrect determination of the type of work performed can lead to the lack of necessary permits, design estimates and other construction documentation, as well as violations in the pricing of construction work.
Thus, in accordance with Article 21.3 of the Code of Administrative Violations (hereinafter referred to as the Administrative Violations Code), sanctions may be applied to business entities and their officials for violating the requirements of technical regulatory legal acts in the field of architectural, urban planning and construction activities (failure to comply with mandatory requirements when designing, carrying out engineering surveys, construction or operation of buildings and engineering infrastructure facilities) in the amount of 4 to 20 basic units, and for a legal entity - from 25 to 100 basic units.
Overestimation by the contractor (subcontractor) of the volumes and (or) cost of construction, installation and other works, costs during construction (reconstruction, repairs), carried out and incurred at the expense of the budget, state target budget, state extra-budgetary, innovation funds or with the attraction of preferential loans, entails a fine in the amount of 10 to 40 basic units, and for an individual entrepreneur or legal entity (except for budgetary organizations) - in the amount of up to 150% of the overstated amount (Article 21.7 of the Administrative Code). If the customer commits the same acts, he will be fined in the amount of 10 to 40 basic units, and for a legal entity (except for budgetary organizations) - in the amount of up to 50% of the overstated amount.
Article 21.19 of the Code of Administrative Offenses provides for liability for violation of legislation in the field of construction, in particular, for the absence or improper execution of design and estimate documentation. Thus, reconstruction, repair, restoration, improvement of the facility (construction phase, launch complex), as well as the implementation of types, stages, complexes of construction and installation work without the availability of design and estimate documentation developed in the prescribed manner, unless otherwise provided by legislative acts, or according to design and estimate documentation that has not passed the mandatory state examination, or according to design and estimate documentation that is not approved in the prescribed manner, entail a fine of up to 50 basic units, and for a legal entity - from 20 to 300 basic units.
S. P. Manyuk, head of the department of CS and TC RUE "Departmental Control Service under the Ministry of Construction and Architecture"
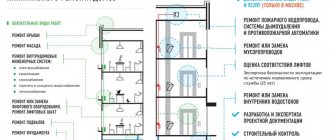
List of works related to current repairs of the premises
What is current residential renovation?
It should be noted that there is no specific list of current repairs inside apartments (other residential premises). By definition, such actions are associated with eliminating problems that have arisen and improving the condition of the premises.
Such work should not make major changes to the premises, affect supporting structures, or involve a complete replacement of engineering equipment.
In-line work includes painting floors, walls, wallpapering, whitewashing ceilings, replacing plumbing fixtures, replacing windows, radiators, replacing pipes, repairing wiring and sockets. As for the repair of common premises and other property in the apartment building, here is an approximate list of such work.
According to the Rules approved by the State Construction Committee on September 27, 2003, the following types of work are considered continuous:
- plastering and painting walls and ceilings;
- restoration of floor coverings;
- repair of stairs, fences, railings;
- replacement and repair of door and window fillings;
- filling potholes, cracks and crevices;
- insulation of individual parts of premises during freezing;
- repair and partial replacement of pipes, taps, mixers, pumps;
- restoration of gas equipment;
- repair of waste chute elements;
- strengthening existing partitions;
- replacement and repair of fans and other ventilation equipment;
- replacement of lamps in entrances and common areas;
- repair of faults in electrical networks.
And this is not all of the work provided for by these rules. Their full list can be seen in Appendix No. 7 of these Rules, Appendix No. 2 MDK 2-04.2004.
At the same time, apartment owners in apartment buildings, when concluding contracts with management companies, can determine specific types of work.
According to Appendix 7 of Gosstroy Resolution No. 170 of September 27, 2003:
Appendix No. 7 (recommended)
LIST OF WORK RELATED TO CURRENT REPAIRS
1. Foundations
Elimination of local deformations, strengthening, restoration of damaged areas of foundations, ventilation ducts, blind areas and entrances to basements.
2. Walls and facades
Sealing of joints, sealing and restoration of architectural elements; changing sections of wooden wall cladding, repairing and painting facades.
3. Floors
Partial change of individual elements; sealing seams and cracks; strengthening and coloring.
4. Roofs
- Strengthening the elements of a wooden rafter system, antiseptic and anti-perforation;
- troubleshooting steel, asbestos-cement and other roofs, replacing drainpipes;
- repair of waterproofing, insulation and ventilation.
5. Window and door fillings
Replacement and restoration of individual elements (devices) and fillings.
6. Apartment partitions
Strengthening, changing, sealing individual areas.
7. Stairs, balconies, porches (umbrellas-visors) above the entrances to the entrances, basements, above the balconies of the upper floors
Restoration or replacement of individual sections and elements.
8. Floors
Replacement and restoration of individual sections.
9. Stoves and hearths
Troubleshooting work.
10. Interior decoration
Restoration of the finishing of walls, ceilings, floors in separate sections in entrances, technical rooms, and other general building auxiliary rooms and service apartments.
11. Central heating
Installation, replacement and restoration of the functionality of individual elements and parts of elements of internal central heating systems, including house boiler rooms.
12. Water supply and sewerage, hot water supply
Installation, replacement and restoration of functionality of individual elements and parts of internal water supply and sewerage systems, hot water supply, including pumping units in residential buildings.
13. Power supply and electrical devices
Installation, replacement and restoration of operability of the building's electrical supply, with the exception of intra-apartment devices and appliances, except for electric stoves.
14. Ventilation
Replacing and restoring the functionality of the in-house ventilation system, including the fans themselves and their electric drives.
15. Garbage chutes
Restoring the functionality of ventilation and flushing devices, waste collection valve covers and gate devices.
16. Special common house technical devices
Replacement and restoration of elements and parts of elements of special technical devices, carried out by specialized enterprises under a contract agreement with the owner (the body authorized by him) or with an organization servicing the housing stock, according to regulations established by manufacturers or relevant industry ministries (departments) and agreed upon state supervisory authorities organs.
17. External landscaping
Repair and restoration of destroyed sections of sidewalks, driveways, paths, blind areas of fences and equipment for sports, utility and recreation areas, platforms and sheds for waste containers.
Who should carry out routine repairs?
As for routine work inside apartments (other premises), their owners (tenants) must independently carry out such work. For these purposes, they can also involve third-party organizations, but the repairs will still be carried out at their expense.
Repairs of apartment building property should be carried out by service organizations and (or) contractors attracted by them.
Depending on the chosen management method, HOA or management company:
- develop a plan for ongoing repair work;
- determine the procedure for their implementation;
- conclude contracts for their implementation;
- notify owners about the cost and scope of work.
Current repairs when renting premises
Agreeing on the conditions for carrying out routine repairs of the premises in the lease agreement is in the interest of both parties, as it allows to avoid conflicts when carrying out repairs.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 616 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the tenant is obliged to carry out current repairs at his own expense, unless otherwise provided by law or the lease agreement. Based on this, the parties can agree on the conditions for carrying out routine repairs of the rented premises and include them in the contract.
To avoid conflicts and risks in the future, the parties to the transaction are recommended to include the following conditions in the contract:
- The party that will carry out routine repairs of the rented premises;
- The party at whose expense the repairs will be carried out or the possibility of offset or reimbursement of funds;
- List of works and their cost;
- Duration of current repairs.
But if such conditions were not included in the lease agreement, then you can always draw up an additional agreement to such an agreement during the period of its validity, including all the necessary points. Read this article to learn how to change a lease agreement.
Answers to the most frequently asked questions
Answers on questions
The actions of service organizations for routine repairs of property common to apartment buildings always raise many questions. Next, we will look at the most frequently asked questions.
***
What ongoing work should be carried out by management companies? It should be repeated that approximate lists of works in MKD related to current ones are contained in Resolution of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2003 N 170, MKD 2-04.2004. In addition, a specific list of works is included in the contract with the management company. Therefore, first you should study the agreement concluded with the management company, and then other regulatory documents.
According to Appendix 7 of VSN 58-88:
APPENDIX 7 Recommended
List of main works for current repairs of buildings and facilities
Foundations and walls of basements
- Sealing and filling out joints, seams, cracks, restoring in some places the cladding of foundation walls from basements and plinths.
- Elimination of local deformations by re-lining and strengthening walls.
- Restoration of individual waterproofing sections of basement walls.
- Punching (sealing) holes, sockets, grooves.
- Strengthening (arrangement) of foundations for equipment (ventilation, pumping).
- Changing individual sections of strip, columnar foundations or chairs under wooden buildings, buildings with walls made of other materials.
- Installation (sealing) of ventilation ducts and pipes.
- Repair of pits, basement entrances.
- Replacement of individual sections of blind areas around the perimeter of buildings.
- Sealing of entrances to basements and technical undergrounds.
- Installation of beacons on walls to monitor deformations.
Walls
- Repairing cracks, filling joints, restoring cladding and relaying individual sections of brick walls up to 2 m2 in area.
- Sealing joints between elements of prefabricated buildings and sealing potholes and cracks on the surface of blocks and panels.
- Punching (sealing) holes, sockets, grooves.
- Changing individual crowns, frame elements, strengthening, insulation, caulking of grooves, changing sections of wooden wall cladding.
- Restoration of individual walls, lintels, cornices.
- Putting individual fallen stones into solution.
- Insulation of freezing areas of walls in individual rooms.
- Elimination of dampness and airflow.
- Cleaning and repair of ventilation ducts and exhaust devices.
Floors
- Temporary fastening of floors.
- Partial replacement or strengthening of individual elements of wooden floors (areas of inter-beam filling, plank lining, individual beams). Restoration of backfill and lubrication. Antiseptic and fire protection of wood.
- Sealing of seams in joints of prefabricated reinforced concrete floors.
- Sealing potholes and cracks in reinforced concrete structures.
- Insulating the top flanges of steel beams in the attic and painting them.
- Additional insulation of attic floors with the addition of backfill.
Roofs
- Strengthening the elements of a wooden rafter system, including changing individual rafter legs, racks, struts, sections of purlins, beams, mauerlats and sheathing.
- Antiseptic and fire protection of wooden structures.
- All types of work to eliminate malfunctions of steel, asbestos-cement and other roofs made of piece materials (except for complete replacement of the covering), including junctions with parapet covering structures, caps and umbrellas over pipes, and other places of passages through the roof, risers, racks, etc. .
- Strengthening and replacement of drainpipes and small coverings of architectural elements along the facade.
- Partial replacement of rolled carpet.
- Replacement (restoration) of individual sections of non-roll roofing.
- Strengthening and replacement of parapet gratings, fire escapes, stepladders, sleeves, roof railings, grounding devices, anchors, radio and television antennas, etc.
- Installation or restoration of the protective and finishing layer of rolled and non-rolled roofs.
- Replacement or repair of roof exits, dormer windows and special hatches.
- Cleaning the roof from snow and ice.
Window and door fillings, translucent structures
- Replacement, restoration of individual elements, partial replacement of window, door stained glass or showcase fillings (wooden, metal, etc.).
- Installation of closers, springs, stops, etc.
- Replacement of window and door fixtures.
- Replacement of broken glass and glass blocks.
- Inset of vents.
Partitions
- Strengthening, strengthening, changing individual sections of wooden partitions.
- Sealing cracks in slab partitions, re-lining individual sections.
- Improving the soundproofing properties of partitions (sealing connections with adjacent structures, etc.).
Stairs, balconies, porches, umbrellas, canopies over the entrances to the entrances, balconies of the upper floors
- Filling potholes, cracks in steps and platforms.
- Replacement of individual steps, treads, risers.
- Partial replacement and strengthening of metal railings, balcony grilles, balcony screens and loggias.
- Partial replacement of wooden staircase elements.
- Sealing potholes and cracks in concrete and reinforced concrete balcony slabs.
- Restoration of waterproofing of floors and galvanized overhangs of balcony slabs, sealing of porch coverings, umbrellas, replacement of boardwalks with steel roofing sheathing.
- Restoration or replacement of individual porch elements; restoration or installation of umbrellas over the entrances to the entrances, basements and balconies of the upper floors.
- Partial or complete replacement of handrails for staircases and balcony railings.
- Repair of the entrance group (entrance block, vestibule) annually.
Floors
- Replacement of individual sections of floor covering.
- Replacement (installation) of waterproofing of floors in individual sanitary units with a complete change of covering.
- Filling potholes and cracks in cement, concrete, asphalt floors and subfloors.
- Bonding plank floors.
Stoves and hearths
- All types of work to eliminate malfunctions of stoves and kitchen hearths, reinstalling them in individual apartments.
- Relaying of individual sections of chimneys, pipes, hogs.
Interior decoration
- Restoration of plaster walls and ceilings in separate places.
- Restoration of wall cladding with ceramic and other tiles in separate places.
- Restoration and strengthening of molded cuts and rosettes, cornices.
- All plastering and painting works in all premises, except residential ones, in which they are carried out by the employer.
Exterior decoration
- Sandblasting, washing, painting of facades.
- Restoration of areas of plaster and tile cladding.
- Strengthening or removing from the façade architectural details, facing tiles, individual bricks that threaten to fall, restoration of molded parts.
- Oil painting of windows, doors, balcony railings, parapet gratings, drainpipes, pergolas, plinths.
- Restoration of house signs and street names.
Central heating
- Replacement of individual sections of pipelines, sections of heating devices, shut-off and control valves.
- Installation (if necessary) of air valves.
- Insulation of pipes, devices, expansion tanks, plungers.
- Re-lining of boilers, blow ducts, chimney ducts (in the boiler room).
- Replacement of individual sections of cast iron boilers, fittings, instrumentation, grates.
- Replacement of individual electric motors or low-power pumps.
- Restoration of destroyed thermal insulation.
- Hydraulic testing and flushing of the system.
- Flushing of heating devices (along the riser) and heating systems in general.
- Adjustment and adjustment of heating systems.
Ventilation
- Changing individual sections and eliminating leaks in ventilation boxes, shafts, chambers, air ducts.
- Replacement of fans, air valves and other equipment.
- Repair and replacement of deflectors, pipe heads.
- Repair and adjustment of automatic fire extinguishing and smoke removal systems.
Water supply and sewerage, hot water supply (in-house systems)
- Sealing of connections, elimination of leaks, insulation, strengthening of pipelines, replacement of individual sections of pipelines, fittings, siphons, drains, revisions, restoration of destroyed thermal insulation of pipelines, hydraulic testing of the system, elimination of blockages, cleaning of yard sewerage and drainage.
- Replacement of individual water taps, mixers, showers and shut-off valves.
- Insulation and replacement of fittings for water tanks in attics.
- Replacement of individual sections and extension of external water supply outlets for watering yards and streets.
- Replacement of internal fire hydrants.
- Repair and replacement of individual pumps and low-power electric motors.
- Replacement of individual components or water heating devices for baths, strengthening and replacement of smoke exhaust pipes, cleaning of water heaters and coils from scale and deposits.
- Cleaning of yard sewerage and drainage.
- Anti-corrosion coating, marking.
- Repair or replacement of control valves.
- Flushing of water supply and sewerage systems.
- Replacement of control and measuring instruments.
Electrical and low-current devices
- Replacement of faulty sections of the building's electrical network, as well as installation of new ones.
- Replacement of damaged sections of the intra-apartment group power supply line for stationary electric stoves.
- Replacement of failed switches, plugs, sockets, etc. (except for residential apartments).
- Replacement of faulty lamps, as well as fencing lights and holiday illumination.
- Replacement of fuses, circuit breakers, batch switches of input distribution devices, panels, electric stoves.
- Replacement and installation of photo switches, time relays and other devices for automatic or remote control of building lighting.
- Replacement of electric motors and individual components of electrical installations of technical devices.
- Replacement of failed burners, switches, oven heaters and other replaceable elements of stationary electric stoves.
- Replacement of failed stationary electric stoves.
- Replacement of metering devices.
- Replacement or installation of automatic systems for monitoring the operation of central heating of in-house communication and alarm networks, instrumentation, etc.
- Connecting technical devices of buildings to ODS, RDS.
- Repair of electrical protection devices for metal pipes of internal central heating and water supply systems from corrosion.
- Repair or installation of radio networks, telephone installation and installation of television antennas for collective use of residential buildings.
- Restoration of grounding circuits.
- Replacement of failed sensors, wiring and fire and security alarm equipment.
External landscaping
- Restoration of destroyed sections of sidewalks, driveways, paths and platforms.
- Repair, strengthening, replacement of individual sections of fences and equipment for children's playgrounds, sports and utility areas, yard restrooms, garbage bins, platforms and canopies for waste containers, etc.
- Equipment for animal walking areas.
Other works
- Strengthening and installation of metal bars enclosing basement windows, canopies over basement entrances.
- Restoration and installation of new passages in the attic through central heating pipes, ventilation ducts, etc.
- Strengthening and installation of house signs and flag holders.
- Installation and repair of locking and intercom devices.
- Replacement or strengthening of garbage chute valves, installation of devices for cleaning trunks.
- Adjustment of all types of in-house equipment.
- Installation and repair of gas stoves.
- Construction and repair of benches in neighborhoods.
Defective statement for repair of premises in xls, doc, pdf format
Major and current repairs (concept and differences)
List of works for major repairs of an apartment building
conclusions
Carrying out routine repair work is necessary to maintain the satisfactory condition of the property and prevent its damage and wear.
Approximate lists of such work are established by the regulatory documents of the State Construction Committee. Owners resolve other issues independently by concluding agreements with management companies or contractors.
You can listen to the seminar on the topic “Maintenance and current repairs of common property of apartment buildings” in this video:
See also Telephone numbers for consultation Oct 27, 2021 kasjanenko 1064
Share this post
Discussion: 4 comments
- Lera says:
01/11/2018 at 00:35During renovations, our neighbors installed a door in a load-bearing wall, without anyone’s permission, now our wall is also collapsing because of their door, what can be done in such a case?
Answer
- 5master5 says:
01/17/2019 at 21:31
If the purchased apartment is in poor condition and the previous owner has not carried out routine repairs in it for thirty years, can a claim be made against him for this? Although the acceptance certificate was signed, it reflects the unsatisfactory condition.
Answer
- Olga says:
07/27/2019 at 01:42
If a residential building does not belong to anyone in the city, but residents live in it, then who should carry out the repairs? We only pay for garbage, gas, water and electricity, we don’t pay for anything else.
Answer
- Oleg says:
03/19/2020 at 13:57
I would like to understand what type of repair includes repairing damage caused by replacing communications during a major repair of communications. Who should repair cracks and holes in walls caused by pipe replacement? Is it the owner of the apartment or is it money from the capital repair fund?
Answer