Young people usually encounter the nuances of employment after they have signed the contract. So that the actual working conditions do not become an unpleasant surprise for you, let's look at the details. Let's talk about the methods of official employment: according to the labor and civil law codes.
In our country, everyone is required to pay tax to the state on any income. This can be organized in different ways, and the cost will vary. We will consider who should pay and how much, and also take into account working conditions.
In this article:
Employment contract
Civil contract (CLA)
An employee hired according to the labor code will cost the employer the most. Perhaps the company has even more responsibility than the employee.
Exceptions to the general rule
According to Art.
65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a work book (or electronic information about work activity) is one of the mandatory documents that an employee must provide to the personnel service when applying for a position. The same standard lists cases when it is not necessary to provide a book:
- Hiring an employee without work experience (initial registration of the book, in accordance with Article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is carried out within 5 days from the date of admission).
- Concluding a part-time agreement.
- Absence of a book due to its loss, damage or other reasons (the document is drawn up by the new employer based on an application from the employee stating the reason for the absence of the book).
Read about correctly filling out an employee’s document in the material “Instructions for filling out work books.”
Analyzing labor legislation in more detail, we can find other cases when hiring without a work book is possible:
- Conclusion of a civil contract with a hired person (Article 11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Work for an individual not related to entrepreneurial activity (Article 309 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Remote work (Article 312.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In all cases of work under an employment contract without a work book, confirmation of length of service in the Pension Fund will be the pension contributions transferred by the employer according to the employee’s SNILS, as well as a copy of the work agreement. Let us consider the features of such employment methods in more detail.
Complaint to the court or prosecutor's office
Many people are interested in the question of what to do if an employee is faced with the employer’s reluctance to officially employ the employee and where to complain. There are three authorities:
- court;
- prosecutor's office;
- State Labor Inspectorate.
An application to court to force an employer to conclude an employment contract must be accompanied by the provision of documents that, in the employee’s opinion, prove the existence of an official labor relationship with the employer.
The application is submitted at the location of the employing organization. The elements of the claim are as follows:
- Name, surname, patronymic of the plaintiff.
- Name of the defendant organization.
- Place of registration of the parties.
- Statement of the problem.
- Links to legal norms violated by the employer.
- The essence of the employee's requirements.
- Date and signature of the plaintiff.
- An appendix with a list of documents attached to the claim as evidence.
If the lawsuit is a class action, different cases with one employer may be combined into one proceeding.
If you file a complaint with the prosecutor's office, you must write a statement and bring it by hand or by land (e-mail). Often such cases are referred to the State Labor Inspectorate for consideration.
An employment contract without an entry in the work book when working with a part-time worker
In accordance with Art. 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part-time work is additional work performed either at the place of primary employment or with another employer in free time from the main job.
The main feature of this form of employment is that a part-time worker’s work shift cannot exceed 4 hours a day (Article 284 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This restriction does not apply to days on which the employee is released from performing duties at his main place (including weekends and holidays). But even taking into account this possibility, a part-time worker cannot work more than half the monthly standard hours established for employees in similar positions.
It is possible to exceed the 50 percent standard working time limit only if the employee has suspended work at his main place of work due to a delay in salary or is temporarily suspended from work due to a refusal to transfer to another position for medical reasons (or the absence of one at the enterprise).
The contract must indicate that the person is accepted part-time. Then the employee can maneuver between the decision to include information about the length of service in his documents and employment without a work book under a part-time contract.
What threatens an employer who does not register an employee?
In fact, as practice shows, the benefits and savings of the employer in this situation are not justified by high legal and other risks. The shadow economy is becoming a thing of the past. In recent years, state control over business has increased significantly. The gray turnover of remuneration is becoming more and more transparent, and the employer’s responsibility is only growing.
At the same time, for example, inspections by labor inspectorates since 2018 can be carried out without prior notification of an upcoming inspection by the State Labor Inspectorate.
For violation of labor laws, there are currently many penalties, and in some cases, employers may be held criminally liable.
So, let's look at what exactly threatens the employer if regulatory authorities reveal facts of unofficial employment.
Employment using a GPC agreement
Unlike an employment agreement, which is regulated by the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a civil contract is subject to the articles of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For this reason, there is no need to enter a record of the conclusion/termination of a civil law contract (CLA) in the work book.
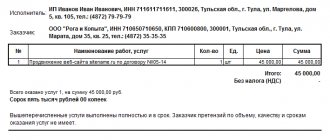
The subject of a civil law agreement (GPC) is remuneration for specific work or service, the result of which will be recorded in the closing accounting act. This form of arrangement without a work book requires weighing all the pros and cons, taking into account the interests of both parties:
- Remunerations under the GPC agreement are not included in the tax base for VNiM insurance. Payments are subject to “unfortunate” contributions only if the agreement between the parties obliges to mention this. For the employee, this will mean no sick pay in case of injury.
- Extension of the GPC contract is not permitted, and work under it is not carried out on a regular basis.
- Compliance with social guarantees in the form of vacation pay, compensation upon dismissal, etc. with mercenaries is not provided for in the GPC agreement.
If the audit reveals the slightest signs of labor relations under the GPA, including regular payments based on monthly acts, the contract will be qualified as an employment contract. Then the employer will pay to the budget all due amounts of insurance premiums and penalties on them.
Important! ConsultantPlus warns It is dangerous to replace an employment contract with a civil law one. An employee can complain to the labor inspectorate or to court. If the contract is recognized as an employment contract, the organization faces a fine of 50,000 - 100,000 rubles. In addition, the court may oblige you to pay the employee all the money that would be due to him under the employment contract (Part 4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, paragraph 24 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of May 29, 2018 N 15, paragraph 15 of the Review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court) . Read more about the differences between an employment contract and a civil law contract in K+. Trial access is free.
Criminal liability
In cases where the volume of evasion from paying “salary taxes” (personal income tax and insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds) over the past three years reaches a large or especially large amount, the employer may be brought to criminal liability simultaneously under several articles of the Criminal Code:
● 199 CC – evasion of taxes and insurance premiums;
● 199.1 of the Criminal Code – failure to fulfill the duties of a tax agent (we are talking about non-payment of personal income tax from an employee’s salary);
● 199.2 of the Criminal Code – concealment of funds or property of an organization from which taxes and insurance contributions should be collected;
● 199.4 of the Criminal Code – evasion of the employer from paying “accident contributions” (we are talking about insurance of accidents, industrial injuries and the prevention of occupational diseases).
● 159 of the Criminal Code - Fraud, which, as a rule, always goes in conjunction with the “tax articles” of the code itself.
Please note that large and especially large amounts, depending on the specific criminal offense, may be different amounts, directly indicated in the notes to the relevant articles of the Criminal Code.
Hired work for an individual
In Art. 303 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains provisions that allow regular work for individuals not related to business activities. At the same time, making entries in the work book by an individual is strictly prohibited (Article 309 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This does not mean that the relationship between employer and employee will not be recorded anywhere. When concluding such an agreement for an individual employer, Art. 303 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation imposes certain obligations to the state and the hired employee. Thus, an individual is obliged:
- put the agreement in writing;
- pay all salary taxes in accordance with the law;
- issue SNILS for workers without experience;
- notify the city administration at the place of residence about the conclusion/termination of the contract.
Other employer risks
One should not discount the fact that an employee without registration can also greatly “annoy” an unscrupulous employer. Since he is not officially employed, he may also not show up for work any day, sell the company’s trade secrets, leak the customer base, etc. and so on.
At the same time, it will no longer be possible to hold such an employee accountable. Thus, it is obvious that the legal consequences of refusing official employment can be very painful for both the employer and the employee. Every decision of the employer and employee related to employment must be balanced and take into account all the advantages and disadvantages.
Registration of an employment contract without a work book for remote workers
An obvious achievement of the legislation is the introduction into the Labor Code of the Russian Federation since 2013 of provisions regulating the specifics of the work of remote workers who are not representatives of outsourcing companies.
Draw up a remote work contract correctly using the article “Sample employment contract with a remote worker 2021.”
A selection of forms from ConsultantPlus experts will help you process the transfer of an employee to remote work. If you don't already have access to this legal system, get a trial access. It's free.
According to Art. 312.1 a remote employee is a person who works outside the territory under the control of the employer using telecommunication networks, including the Internet.
With such employees, all exchange of documents can occur electronically through the use of enhanced qualified digital signatures. At the same time, the employer is obliged to send the original contract and additional agreements to it to the distance worker by registered mail, as well as other working documents at the employee’s request.
Before the law, permanent and remote employees are equal in their rights and responsibilities. But the main “highlight” of remote work is the opportunity (by agreement with the employee) not to fill out or register a work book (Article 312.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Personal income tax
Tax officials have promised to collect the full amount of unpaid personal income tax from “salaries in envelopes” from 2021, not from the employee’s salary, but at the expense of the employer.
Thus, offended workers, who were previously afraid to complain about an unscrupulous employer for fear that they would have to pay the entire personal income tax, will now be active, turning to the court, prosecutors and labor inspectors.
They may do this not only out of a desire for revenge, but also in the hope that they will be able to restore their seniority, replenish their pension points, and at the same time recover vacation and sick pay from the employer.
Taxes and fees
The obligations imposed on the entrepreneur to make insurance contributions for hired employees continue to exist. The tax office collects such transfers.
The employer must pay for each employee:
- Personal income tax (rate 13 or 30%);
- contributions to the Pension Fund;
- contribution for medical and social insurance associated with the loss of the employee’s ability to work while performing work.
Conclusion
If you are an employer, no matter an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity, you are obliged to officially employ your employees, pay them their due salaries and pay taxes. Otherwise, you will be subject to criminal liability.
If you decide to save on your employees, then you will have to spend several times more money.
The employee, for his part, must demand official employment in order to provide himself with all social benefits and not receive wages “in an envelope.”
Does the form have legal force?
The concept of working relationships is defined in Art. 15 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. As such, we understand relationships in which the parties are the employee and the employer, for the purpose of performing certain functions by the employed person, with his subordination to the internal working order, as well as the creation by the employer of such working conditions as determined by the legislator or the provisions of the employment contract.
Almost all the conditions that are fixed are determined by law. The parties do not have the right to change them, except in cases where such changes improve the situation of the participants.
In situations where an agreement implying the existence of civil legal relations is recognized by the court as one that regulates labor relations, labor law norms are applied to it.
The main task assigned to the legislator is to provide citizens who are participants in labor relations with the full range of guarantees stipulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts regulating labor relations.
What points should you be wary of?
It is unlikely that there will be employers who will say in plain text that, in fact, they are not going to hire you. Most likely, one of the tricks will be used to obtain, albeit for a short period, free labor.
If you hear the following phrases, think a hundred times about whether to hire for a vacant position.
- The director cannot sign the contract because he is sick, on vacation, etc.
- Rewrite the application submitted 3 days ago without errors, but put the date today.
- Today it’s impossible to get it done, since the accounting department is very busy (filing reports, auditing, etc.).
- Work for a week on the test. Assess your capabilities, understand whether you like it with us, we will look at you, and then we will arrange for you as it should be.
Often, employees themselves give a free hand to dishonest employers. Some naively believe the promises, others ignore negative reviews, and others simply do not know about the rights. Before hiring, soberly weigh the pros and cons, and even if the work is very necessary, do not rush to become someone who is ready to work for free.