Home / Family law / Adoption and guardianship
Back
Published: 07/26/2018
Reading time: 5 min
0
304
Adoption is a procedure regulated at the legislative level. For this reason, certain legal consequences arise for adoptive parents and their children.
- Legislation
- Legal consequences of adoption Forms
- When do they arise?
- Implications for the adoptive parent
Adoption and family ties
Since adoption is intended to provide a family for a lonely child who has lost his parents, it entails the emergence of real family ties between the adoptive parents and the adopted children. This is the main legal consequence of adoption, the result of which is a change in the nature of the relationship between the adopted child, his adoptive parents, and their relatives.
As follows from the provisions of family law, at the request of the adoptive parents, children can change their first name, patronymic, assign a different last name, and also make an entry in the registry office indicating the adoptive parent in the “parent” column.
In fact, the relationship that arises during adoption replaces the blood relationship that previously existed between the biological parents and their child. Children who find themselves in a new family lose connections with former relatives. Meanwhile, the status of a stepchild adopted is no different from the status of natural children. He is entitled to the same rights as others. And the adoptive parents have similar parental rights and responsibilities towards him.
Does the adoptive parent have the right to change the child’s data?
- Adopted children retain their first, last and patronymic names. If the adoptive parent requests a change of surname and first name, then this request is fulfilled. If the baby is adopted by a man, then the middle name can be in his name, if a woman, then the middle name will be the one she indicates.
- If parents have more than one surname, then the child is assigned the surname of one of them by agreement.
- If the child has reached 10 years of age, then the change of full name is carried out only with his permission.
- Information on changing the name of the adopted child is contained in the court decision.
- To maintain the secrecy of adoption (according to Article 139 of the Family Code), the baby’s date and place of birth can be changed. In this case, the date changes by no more than 3 months.
- Changing the baby's date of birth is possible only up to one year. If the court decides that there are valid and serious reasons (or circumstances), then a decision may be made to extend this period.
Legal consequences of adopting a child and his relationship with the adoptive parent’s relatives
During adoption, the relationship changes not only directly between the adopted child and his adoptive parent, but also the latter’s relatives. By accepting another child into his family, the adoptive parent actually entails a change in the scope of rights in relation to his relatives. Moreover, the law requires only the spouse’s consent to this procedure; the opinions of others are not taken into account. In practice, courts, when considering adoption cases, sometimes request the consent of all persons living with the adoptive parent, who are not necessarily relatives, but this does not comply with the provisions of the law. Thus, the establishment of family ties is carried out against the will of close adoptive parents, but in a certain way affects the scope of their property and immaterial personal rights.
Is it possible for adoptive parents to include information about themselves in the certificate?
Such action is quite possible through the court. However, if the ward has reached 10 years of age, then his permission for this action is required.
You may also be interested in other materials from our experts. Read about whether it is possible to adopt an adopted child or an adult, whether there are restrictions for adoptive parents and whether people with hepatitis C can adopt a child, what documents are needed for the procedure, as well as how the adoption of Russian children by foreigners occurs, how to adopt child from Africa and other issues of international adoption.
To summarize, it can be noted that when adopting children, there is a serious responsibility for their life, upbringing, adaptation, future, etc.
It is worth remembering this and never forgetting. It is necessary to make a final decision on adoption only when you have seriously considered all the nuances and details, and also studied the Legislation of the Russian Federation.
Legal consequences of adopting a child. Rights and obligations of the adopted child and the adoptive parent
The legal consequences of adopting a child also include the acquisition by the adoptive parent of a set of personal non-property as well as property rights in relation to the child adopted by him. The time when the legal consequences of adopting a child arises coincides with the entry into force of a judicial act issued following the consideration of the issue of placing young citizens into a family. It is from this moment that the legal consequences of adopting a child arise: the adoptive parent can be considered the parent of the adopted child, exercise the associated rights and fulfill the corresponding responsibilities, and refer to this circumstance in relations with other persons. Moreover, this does not depend on whether an entry about him is made in the birth register.
Legislation
Children left without care have the opportunity to find a family as a result of adoption by their adoptive parents. This form of placement of children is described in detail in Art. 124 of the Family Code.
In Art. 137 of the Family Code provides for certain legal consequences that occur for parents and children from the moment the adoption is formalized.
Personal non-property and property rights
After the decision of the judicial authority on adoption has entered into force, mutual obligations arise between the adoptive parents and their adopted children, and the same range of personal and property rights as natural children and their parents have. This is provided not only by family law, but also by the norms of other branches of law. What are the legal consequences of adopting a child?
Adoptive parents, along with biological parents, have every right to primary upbringing of the child they have adopted. They have the right to demand the return of the child from any persons who unlawfully and without justification keep him for any period of time. Adoptive parents act as legal representatives of adopted children when carrying out any transactions on their behalf, when protecting their legitimate interests and rights in relations with other persons or in government bodies.
They also give their consent to children under the age of majority to enter into and execute transactions, and are responsible for the actions of children and the harm caused by them. Adoptive parents have the right to move an adopted child into their home without obtaining the consent of the persons living with him. In this case, compliance with the minimum living space standards for each person is also not required. And the adopted child has the full right to use the residential premises of the adoptive parents. The right of use may also legitimately arise for the adoptive parent in relation to the residential premises of the adopted child.
Adoptive parents are entitled to various types of benefits for adopted children. In particular, women who have adopted newborn babies are entitled to leave and all payments related to the birth and care of a child.
Procedure for granting leave
According to Government Decree No. 719 of October 11, 2001 “On the procedure for granting leave to employees who have adopted a child,” such employees are provided with:
- 70 calendar days (one child);
- 110 calendar days (two or more).
If children are adopted by a married couple, then either the father or the mother is entitled to leave. This issue remains at the discretion of the adoptive parents. To obtain it, you must submit an application for leave, indicate its duration and attach copies of the birth certificate and the relevant court decision (or a copy thereof). Art. is also devoted to this issue. 257 Labor Code. Such persons retain their jobs.
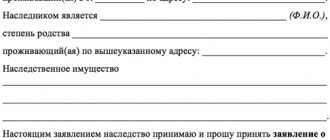
Inheritance
What are the legal consequences of the adoption of a child in the field of inheritance rights arising between adoptive parents and adopted children? From the provisions of Articles 137 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, 1147 of the Civil Code, it follows that adopted children are equated with the biological relatives of the adoptive parent in inheritance rights. And in the event of the death of the adoptive parents, such a child will have the right to claim the inheritance and be the heir of the first line along with the others. This rule also applies to the descendants of adopted children. Also, adoptive parents have the right to inherit after the death of their adopted children.
As for the blood parents of the adopted child, then, as a general rule, all relations, including hereditary ones, between them are terminated. However, there are situations when such rights are retained for adopted people.
Cases of preservation of property and personal rights with former parents and relatives
Let us repeat that with the entry into force of a judicial act on adoption, the rights and obligations between the adopted child and his parents from birth, as a rule, cease. These are the legal consequences of adopting a child. This applies to personal non-property and also property rights on both sides. The rules of family law establish exceptions to this rule. When it's possible?
Firstly, in the case of adoption of a child not by a married couple, but by one parent. Then, in relation to the biological parent of the opposite sex, if desired, certain rights can be reserved, not excluding property rights. This circumstance must be reflected in the judicial act.
Secondly, if the parent of the adopted child has died, his relatives may make a request to preserve the opportunity to see him and exercise other rights in relation to the adopted child.
In both cases, the adopted child retains the right of inheritance for persons with whom his relationship has not been terminated. However, this does not lead to the loss of such rights in relation to his adoptive parent. Likewise, these persons have the right to inherit from him and his descendants.
In addition, family law (Article 138 of the RF IC) establishes another exception that affects the child’s right to receive payments in connection with the death of his parents. A child who, at the time of adoption into a new family, has the right to cash benefits (pensions) due to him after the death of his parents, fully retains this right even when he is adopted.
What happens if the decision is canceled?
- all established relationships cease to exist (regarding the adoptive parent and the adopted child);
- changing the child’s full name if it was assigned by the adoptive parents;
- restoration of connections with parents (by blood) and the child (if this is for the benefit of the child);
- the former adoptive parent may be required to pay child support to the adopted child;
- if establishing contact with blood-related parents is not possible, the children are transferred to the authorized bodies;
- if the cancellation was made due to the fault of the adoptive parent, then the court may prohibit communication and seeing the previously adopted child.
Read more about cancellation of adoption and its legal consequences here.
Responsibilities
As you know, there are no rights without corresponding responsibilities. And adoptive parents, receiving a number of rights in connection with adoption, must also bear certain responsibilities. Like biological parents, adoptive parents are obliged to raise the child and take good care of his full development and proper health. Adoptive parents also provide the adopted child with a mandatory level of education. They assume the functions of maintaining the adopted child, in cases of dishonest performance of which alimony may be collected from them in court.
Adopted adults who are capable of working are also required to support their adoptive parents, who are in dire need of their help.