Contributions to the capital repair fund have recently been added to the usual utility bills paid by apartment owners. Some confusion in concepts leads to the fact that some residents consider these expenses to be unnecessary and avoid transferring monthly payments to the Federal Fund of the Russian Federation. This material is detailed instructions on how not to pay for major repairs and not run into fines.
Contribution for major repairs - Law
Since the end of 2012, a new expense item has appeared in utility bills: “Payments for major repairs.” Although many residents expressed dissatisfaction, payments began to be accrued monthly and were mandatory for payment, like others. The need is due to the fact that responsibility for the condition of owned residential premises rests with the residents. It turns out that when purchasing an apartment in an apartment building, a citizen also becomes a co-owner of the building, that is, basements, attics, roofing and other elements.
The costs for this item are significant. Therefore, they are stored in the account of the apartment building or transferred to the regional fund, in accordance with current legal acts.
Have any changes been made?
These regulations are constantly subject to amendments and additions. Thus, Federal Law No. 44 on public procurement is subject to changes annually. As of today, the edition dated June 2, 2016, number 21, is in effect. Reaction 22 of June 2, with changes that have not yet entered into force, is being prepared for entry into force.
As for Federal Law No. 185, this act has been amended more than 30 times. Today, for Federal Law 185 - major overhaul, current edition 32 dated June 2, 2021 . 271 of the Federal Law on the major repairs of apartment buildings, as amended, has only two editions, since it is very new and so far suits the State Duma. Today the second edition dated June 29, 2015 .
We describe in a separate publication what changes regarding major repairs have been made to legislative acts recently.
In order to demand legal overhaul, the residents themselves first need to be familiar with the rules of law and know where their rights and interests begin and end. Only awareness guarantees that your interests are served.
Categories of beneficiaries 2021
Beneficiaries are divided into 2 categories of citizens. Some are completely exempt from the need to deposit money, while others are only half exempt.
Elderly people - owners who have reached eighty years of age, living alone or in a family that consists only of pensioners - have a 100% benefit. However, if people of working age also live in the premises, the benefit does not apply to the pensioner.
The following persons may be exempt from paying contributions by fifty percent:
- Owners who have reached the age of seventy, who are no longer working and live alone or in a family consisting of persons who are also non-working pensioners.
- Families raising disabled children.
- Owners of residential premises who are parents of many children.
- Disabled people of groups 1 and 2.
- Veterans and participants of the Second World War, persons who were rehabilitated.
- Citizens who have been exposed to radiation.
- Low-income citizens if payments for housing and communal services and major repairs are higher than the share of income established in a particular region of residence.
- Persons who received the medal “For the Defense of the Mountains. Moscow" (the subsidy applies only to residents of the capital).
These are the main categories of beneficiaries living in multi-storey buildings. But local authorities have the right to include in the list other persons to whom the subsidy will apply in the relevant region.
After privatization of the first premises in the house, common shared ownership arises
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation reminded the plaintiffs that a citizen, purchasing residential premises free of charge by agreement with the owner of the housing stock in accordance with Law No. 1541, understands and confirms his readiness to independently bear the costs of maintaining the purchased object, taking into account its technical condition.
At the same time, the former landlord of residential premises in an apartment building retains the obligation to carry out major repairs of such a house at the expense of the budget in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 190.1 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation is an exception to the general rule that the owner bears the burden of maintaining his property.
After the privatization of the first premises in a house, such a house loses its status as an exclusively municipal or state housing stock. In relation to the common property of such an apartment building, common shared ownership arises, the participants of which are the corresponding public legal entity and the citizen who privatized the residential premises (clause 4 of article 244, clause 1 of article 290 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, part 1 of article 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation , part 2 article 3, part 2 article 24 No. 1541).
After the privatization of the first residential premises in the house, the former landlord ceases to solely bear the burden of maintaining the apartment building: each of the owners is obliged to participate in such expenses in proportion to the size of the area of the residential premises belonging to him.
Who and how issues receipts for paying contributions for major repairs?
867248
Who else and in what cases may not pay for repairs?
Attention! As stated above, major repairs are carried out at the expense of the homeowners. Therefore, if the premises are not privatized, the municipality is considered the owner. The tenant (under the social tenancy agreement) does not have to make the corresponding payment. There is no obligation for other tenants of housing (under a commercial lease agreement). The owners should do this for them.
Article 169 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation provides for two more cases in which deductions for housing repairs are not made. These include situations:
- If there is a dilapidated house that should be demolished soon.
- If the land under the building is withdrawn for the needs of the state or municipality.
In these situations, the question of overhaul is no longer raised. Therefore, no deductions are made.
According to Article 170 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, if the minimum amount provided by law for the capital repair fund of apartment buildings is reached, the owners have the right to suspend the corresponding financing. Then payment will be collected only from those residents who are in arrears for this payment.
If the building is not included in the modernization program, the item is also not paid. Once a new home is enrolled in this program, payments must be made no later than five years. If the house is not a new building, then the corresponding obligation arises after eight months.
We look at the provisions of the law
Is the payment for major repairs mandatory or voluntary? Just a couple of years ago, these contributions were indeed voluntary.
In 2014 (from July 1), amendments were made to Federal Law No. 271-FZ. In particular, Article 13 was “decorated” with clause 8.2, and it precisely implies minimum contributions for major repairs.
Is the law perfect? At the moment, the ambiguities are really striking , for example, the lack of a boundary between current repairs and major ones.
That is, in practice, of course, everyone understands the difference in terminology - routine repairs are minor corrections, such as painting, plastering, structural repairs. Major works include larger-scale works - improvements to structures, restoration of worn parts, etc.
But the fact of the matter is that the column in payments from housing and communal services is called “current repairs” . But the residents are already paying for it, that’s why they are indignant: why are they obliging them to pay more?!
In fact, one should only be outraged by unclear wording of the law , which cannot always be correctly understood right away. In fact, the money will go to the intended purposes.
The trouble is that the border between current and major repairs is often very arbitrary. What is the difference between contributions for major and current repairs, we explained here.
Another reason for the dissatisfaction of the inhabitants of the houses is the putting of money into what they think is a “common pot”. That is, there are two “piggy banks”:
- special account for a separate building (established in agreement with the meeting of homeowners);
- regional operator account.
It is clear that the last “piggy bank” is more voluminous and contributions from many houses are received there. Is it necessary to pay into the capital repair fund, since many people absolutely rightly do not want to pay for other people’s repairs?
But according to the authorities, there is no need to fear this - strict records of all incoming tranches are kept and not a single house will be repaired at the expense of another.
Where and how you can find out where the money paid for major repairs went and who should provide such information, we tell you here.
The size of the trenches also varies in different regions of Russia . Its size is influenced by many nuances, for example, how old the building is, what material it is built from, whether it has an elevator or not, etc.
How to get a benefit - step-by-step instructions
As with receiving benefits for housing and communal services, in order to take advantage of the subsidy for repairs, which the owner of the premises has the right to legally count on, you must contact the municipal subsidy department. How registration is carried out is stated in Article 159 of the RF Housing Code, as well as in RF PP No. 761.
When calculating, the following points are taken into account:
- Relaxations are provided to citizens if they have no debt to pay taxes, utility bills, or repairs themselves. Therefore, if there is a debt, it must first be paid.
- You should find out whether the residential building is included in the region's program. This information is provided by the capital repair fund or the management organization.
- You need to obtain documents confirming your right to benefits from the social security office at your place of registration or from the MFC.
After this, the required package of documents is collected, in particular:
- Identity cards of apartment owners and family members.
- Documents that confirm membership of specific beneficiaries, for example, ID of a pensioner, veteran, etc.
- Receipts that confirm payment for repairs and services.
- Certificates of income of the applicant and family members.
- Extract from the house register.
- Statement. This document requires you to indicate the account. It will receive a subsidy.
Keep in mind! If you do not provide any of the above documents, you will not be able to obtain the benefit.
How legal are the contributions?
Only those contributions that are included in the receipt and accepted into the account of the management organization can be considered illegal. This is illegal because the location of the capital repair fund is determined at a meeting of owners. Until this time, the management company cannot conduct fundraising.
In addition, illegal contributions include payments that are accrued to preferential categories of citizens. Some apartment owners are completely exempt from fees or have certain subsidies. It is also worth considering that they must confirm their eligibility independently.
Compensation for major repairs – who is entitled to it and how to get it
Returning to the question of those citizens who may not pay for major repairs, it should be said that benefits for them can be both state and regional. If a benefit is allocated at the state level, then it applies to persons specified in the Federal Law (namely, in the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). If a benefit is allocated at the regional level, then it is provided for by the law of the corresponding subject of the federation, and is valid only there.
Information about this is clarified from the housing department or the social security authority. Examples of federal beneficiaries are disabled children, and regional ones are large and low-income families.
Regardless of whether the owner of the premises must pay for repairs or was exempted from this payment (in whole or in part), he is obliged to make payment. After this, the subsidy is credited monthly to the account of the beneficiary indicated in the application upon appropriate registration. This is done no later than the 26th of each month.
If a citizen is a beneficiary for several reasons at once, he can use only one of his choice. Usually the most advantageous benefit is chosen.
If a citizen owns several real estate properties for which major repairs need to be paid, then the subsidy is paid only for one premises, at the choice of the beneficiary.
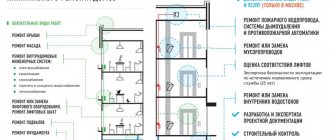
What work is performed during a major overhaul?
In order to understand where the funds from paying for major housing repairs go, let’s consider the work that must be performed as part of this project. These include:
- insulation of the facade, walls, basement;
- repair of engineering systems inside the house - ventilation, sewerage, heating, water supply systems;
- repair of the roof, parapet, barriers and drainage;
- repairing the basement, if the latter belongs to common property;
- repair of elevators and their equipment, elevator shafts;
- reconstruction of balconies and buildings, replacement of waterproofing;
- reconstruction of emergency stairs;
- changing the fillings of windows and balconies to noise-saving ones;
- repair of staircases.
A detailed list of work that must be carried out can be found in the law “On Major Repairs”. In addition to this, the housing code of the Russian Federation contains the regulatory framework for carrying out repairs in an apartment building. According to it, major repairs are aimed at:
- replacement of building elements and structures that are unsuitable for use;
- restoration of the fundamental part of the building;
- working with communication systems;
- equipping the house with metering devices for used utility resources (more information about who should pay for the installation of house metering devices can be found in our material).
Major repairs involve partial work - in individual areas of the house and complex work. The latter involve work in all areas of the apartment building.
What happens if you don't pay
If a citizen is not a beneficiary, he has to pay the appropriate fee in full. Despite the desire, you should not ignore this payment, as a debt will form, which, sooner or later, will still have to be repaid. Not only that, as mentioned above, beneficiaries also pay for repairs. But then they will get their money back by transferring it to their personal account. If they do not make the appropriate payments for at least two months, the subsidies are suspended and the debtor is notified of the period during which the money must be paid. If payment is made, the benefit continues to apply.
For other citizens, the following situation occurs. For the resulting debt, a penalty is charged, the amount of which is 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the overdue day (as stated in Article 255 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). If a significant amount of debt accumulates, the organization that is involved in the formation of this account has the right to apply to the court with a statement of claim to collect the debt. Then deductions will be carried out by bailiffs, on the basis of a writ of execution (and for this they are endowed with many tools).
Some citizens believe that after repair work has been carried out on the house, there is no longer a need to pay the corresponding fee. But in practice this is not the case. Often, credit funds are used to carry out these works, and repairs are done on credit. Therefore, the obligation to pay remains even if the house is renovated. But if the residents have completed the main repairs themselves, then it is possible to cancel this payment for a certain period or at least reduce it.
After privatization of the first premises in the house, major repairs are paid for by all owners
Deputies of the State Duma of the Russian Federation did not agree that the former landlord is obliged to pay for major repairs of the house only if such repairs were required before the date of privatization of the first premises, and is not obliged to pay for the work if the house was included in the major repairs program after the first premises were privatized .
According to the plaintiffs, Part 1 of Art. 190.1 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation leads to inequality between the owners of premises that were privatized before the house was included in the capital repair plan, and the owners who registered ownership rights after the apartment building was included in such a plan.
The deputies expressed disagreement with the reduction of the obligations of the former landlord in relation to citizens who privatized premises in a house that needed major repairs at the time they registered ownership of the apartment.
Conclusion
Major repairs must be paid every month. Even those who are exempt (fully or partially) from paying for major repairs must make this payment. But he gets his money back. If residents who are not beneficiaries ignore the corresponding expense column, a penalty will be charged. Therefore, they will have to pay even more later.
In some cases, the law allows for the possibility of not making this payment. Then we are not talking about specific citizens who are beneficiaries. This expense item may be absent, for example, due to a building that is in disrepair, or the land under the house being seized for the needs of the state or municipality.